
-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
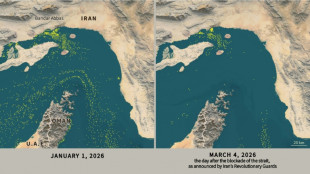 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs

-
 Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
-
Voices from Iran: protests, fear and scarcity

-
 Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
-
This is how Ukraine has countered Russia's Iran-designed drones

-
 Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
-
Sleepless Iranians count cost of war as damage mounts

-
 Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
-
Leading satellite firm to hold back Gulf state images

-
 Tuipulotu urges Scotland to stay in Six Nations title hunt against France
Tuipulotu urges Scotland to stay in Six Nations title hunt against France
-
Trump says only Iran's 'unconditional surrender' can end war

-
 US releases Epstein files with uncorroborated Trump allegations
US releases Epstein files with uncorroborated Trump allegations
-
Securing shipping lane from Mideast war 'challenging', say experts

-
 Italy have to start beating the best, says captain Lamaro
Italy have to start beating the best, says captain Lamaro
-
India's Bumrah only 'human' says Phillips ahead of T20 World Cup final

-
 Oil prices climb as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
Oil prices climb as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
-
US retail sales decline as consumer pullback deepens

-
 War in Middle East raises stagflation fears in Europe and beyond
War in Middle East raises stagflation fears in Europe and beyond
-
UN demands swift probe into Israeli strikes on Lebanon

-
 Chelsea happy to rotate goalkeepers, says Rosenior
Chelsea happy to rotate goalkeepers, says Rosenior
-
Soaring gas prices spark renewed debate about European electricity

-
 Elite pilots and US support drive Israel's air power
Elite pilots and US support drive Israel's air power
-
Germany's Axel Springer swoops for British newspaper The Telegraph

-
 US sheds jobs in February in warning sign for Trump's economy
US sheds jobs in February in warning sign for Trump's economy
-
Sole Iranian competitor out of Paralympics due to Middle East war

-
 Spanish PM says 'cooperation' with US should prevail over 'confrontation'
Spanish PM says 'cooperation' with US should prevail over 'confrontation'
-
Lebanese relive 'nightmare' of displacement from war

-
 US must probe Iran school strike 'very quickly', UN says
US must probe Iran school strike 'very quickly', UN says
-
AC Milan hoping to revive dimming title hopes in derby against Inter

-
 Iceland proposes August 29 referendum on resuming EU membership talks
Iceland proposes August 29 referendum on resuming EU membership talks
-
Hungary to expel 7 Ukrainians as Zelensky, Orban quarrel over Russian oil

-
 Ohtani homers as Japan thrash Taiwan at World Baseball Classic
Ohtani homers as Japan thrash Taiwan at World Baseball Classic
-
Who rules the seas? Torpedoed Iran ship brings focus underwater

-
 Mideast war escalates as fresh strikes batter Iran
Mideast war escalates as fresh strikes batter Iran
-
Pirovano takes downhill at Val di Fassa for first World Cup win

-
 Iran drone strike on Azerbaijan raises fears of Mideast war spreading to Caucasus
Iran drone strike on Azerbaijan raises fears of Mideast war spreading to Caucasus
-
Decades of planning and US backing helps fuel Israel's air power


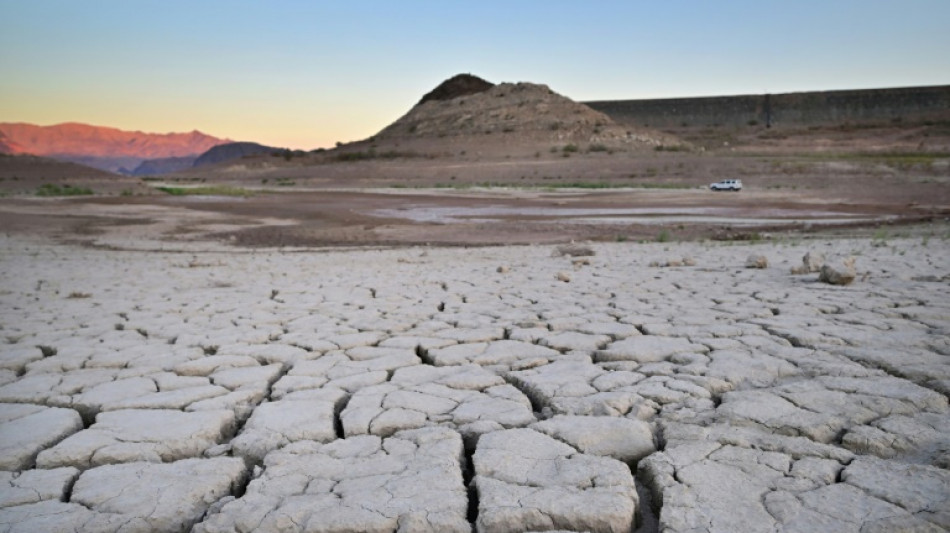
Climate change is speeding up, warns major UN report
Each of the last eight years, if projections for 2022 hold, will be hotter than any year prior to 2015, the UN said Sunday, detailing a dramatic increase in the rate of global warming.
Sea level rise, glacier melt, torrential rains, heat waves -- and the deadly disasters they cause -- have all accelerated, the World Meteorological Organization said in a report as the COP27 UN Climate Summit opened in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt.
"As COP27 gets underway, our planet is sending a distress signal," said UN chief Antonio Guterres, describing the report as "a chronicle of climate chaos".
Earth has warmed more than 1.1 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century, with roughly half of that increase occurring in the past 30 years, the report shows.
Nearly 200 nations gathered in Egypt have set their sights on holding the rise in temperatures to 1.5C (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit), a goal some scientists believe is now beyond reach.
This year is on track to be the fifth or sixth warmest ever recorded despite the impact since 2020 of La Nina -- a periodic and naturally occurring phenomenon in the Pacific that cools the atmosphere.
"The greater the warming, the worse the impacts," said WMO head Petteri Taalas.
Surface water in the ocean -- which soaks up more than 90 percent of accumulated heat from human carbon emissions -- hit record high temperatures in 2021, warming especially fast during the past 20 years.
Marine heat waves were also on the rise, with devastating consequences for coral reefs and the half-billion people who depend on them for food and livelihoods.
Overall, 55 percent of the ocean surface experienced at least one marine heatwave in 2022, the report said.
Driven by melting ice sheets and glaciers, the pace of sea level rise has doubled in the past 30 years, threatening tens of millions in low-lying coastal areas.
"The messages in this report could barely be bleaker," said Mike Meredith, science leader at the British Antarctic Survey.
- Records shattered -
"All over our planet, records are being shattered as different parts of the climate system begin to break down."
Greenhouse gases accounting for more than 95 percent of warming are all at record levels, with methane showing the largest one-year jump ever recorded, the WMO's annual State of the Global Climate found.
The increase in methane emissions has been traced to leaks in natural gas production and a rise in beef consumption.
In 2022, a cascade of extreme weather exacerbated by climate change devastated communities across the globe.
A two-month heatwave in South Asia in March and April bearing the unmistakable fingerprint of man-made warming was followed by floods in Pakistan that left a third of the country under water. At least 1,700 people died, and eight million were displaced.
In East Africa, rainfall has been below average in four consecutive wet seasons, the longest in 40 years, with 2022 set to deepen the drought.
China saw the longest and most intense heatwave on record and the second-driest summer.
Falling water levels disrupted or threatened commercial river traffic along China's Yangtze, the Mississippi in the US and several major inland waterways in Europe, which also suffered repeated bouts of sweltering heat.
Poorer nations least responsible for climate change but most vulnerable to its dire impacts suffered the most.
"But even well-prepared societies this year have been ravaged by extremes -– as seen by the protracted heatwaves and drought in large parts of Europe and southern China," Taalas said.
In the European Alps, glacier melt records have been shattered in 2022, with average thickness losses of between three and over four metres (between 9.8 and over 13 feet), the most ever recorded.
Switzerland has lost more than a third of its glacier volume since 2001.
"If there was ever a year to swamp, shred and burn off the blinkers of global climate inaction then 2022 should be it," said Dave Reay, head of the University of Edinburgh's Climate Change Institute.
"The world now has a monumental job of damage limitation."
N.Fournier--BTB



