
-
 Imperious Sinner barrels into Australian Open round three
Imperious Sinner barrels into Australian Open round three
-
Storms, heavy rain kill 9 children across Afghanistan

-
 Games giant Ubisoft suffers share price collapse
Games giant Ubisoft suffers share price collapse
-
Exhausted Wawrinka battles on in Melbourne farewell after five-set epic

-
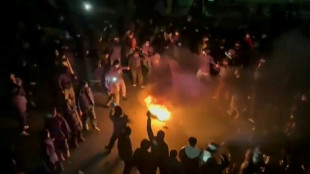 'Too dangerous to go to hospital': a glimpse into Iran's protest crackdown
'Too dangerous to go to hospital': a glimpse into Iran's protest crackdown
-
Bruised European allies wary after Trump's Greenland climbdown

-
 Austrian ex-agent goes on trial in Russia spying case
Austrian ex-agent goes on trial in Russia spying case
-
Japan suspends restart of world's biggest nuclear plant

-
 Djokovic, Swiatek roll into Melbourne third round, Keys defence alive
Djokovic, Swiatek roll into Melbourne third round, Keys defence alive
-
New Zealand landslips kill at least two, others missing

-
 Djokovic says heaving Australian Open crowds 'good problem'
Djokovic says heaving Australian Open crowds 'good problem'
-
Swiatek in cruise control to make Australian Open third round

-
 Austrian ex-agent to go on trial in Russia spying case
Austrian ex-agent to go on trial in Russia spying case
-
Bangladesh launches campaigns for first post-Hasina elections

-
 Afghan resistance museum gets revamp under Taliban rule
Afghan resistance museum gets revamp under Taliban rule
-
Multiple people missing in New Zealand landslips

-
 Sundance Film Festival hits Utah, one last time
Sundance Film Festival hits Utah, one last time
-
Philippines convicts journalist on terror charge called 'absurd'
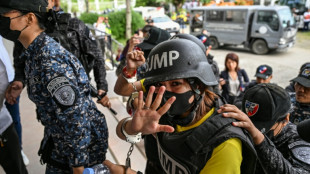
-
 Anisimova grinds down Siniakova in 'crazy' Australian Open clash
Anisimova grinds down Siniakova in 'crazy' Australian Open clash
-
Djokovic rolls into Melbourne third round, Keys defence alive

-
 Vine, Narvaez take control after dominant Tour Down Under stage win
Vine, Narvaez take control after dominant Tour Down Under stage win
-
Chile police arrest suspect over deadly wildfires

-
 Djokovic eases into Melbourne third round - with help from a tree
Djokovic eases into Melbourne third round - with help from a tree
-
Keys draws on champion mindset to make Australian Open third round

-
 Knicks halt losing streak with record 120-66 thrashing of Nets
Knicks halt losing streak with record 120-66 thrashing of Nets
-
Philippine President Marcos hit with impeachment complaint

-
 Trump to unveil 'Board of Peace' at Davos after Greenland backtrack
Trump to unveil 'Board of Peace' at Davos after Greenland backtrack
-
Bitter-sweet as Pegula crushes doubles partner at Australian Open

-
 Hong Kong starts security trial of Tiananmen vigil organisers
Hong Kong starts security trial of Tiananmen vigil organisers
-
Keys into Melbourne third round with Sinner, Djokovic primed

-
 Bangladesh launches campaigns for first post-Hasina polls
Bangladesh launches campaigns for first post-Hasina polls
-
Stocks track Wall St rally as Trump cools tariff threats in Davos

-
 South Korea's economy grew just 1% in 2025, lowest in five years
South Korea's economy grew just 1% in 2025, lowest in five years
-
Snowboard champ Hirano suffers fractures ahead of Olympics

-
 'They poisoned us': grappling with deadly impact of nuclear testing
'They poisoned us': grappling with deadly impact of nuclear testing
-
Keys blows hot and cold before making Australian Open third round

-
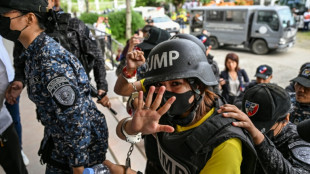 Philippine journalist found guilty of terror financing
Philippine journalist found guilty of terror financing
-
Greenlanders doubtful over Trump resolution

-
 Real Madrid top football rich list as Liverpool surge
Real Madrid top football rich list as Liverpool surge
-
'One Battle After Another,' 'Sinners' tipped to top Oscar noms

-
 Higher heating costs add to US affordability crunch
Higher heating costs add to US affordability crunch
-
Eight stadiums to host 2027 Rugby World Cup matches in Australia

-
 Plastics everywhere, and the myth that made it possible
Plastics everywhere, and the myth that made it possible
-
Interim Venezuela leader to visit US

-
 Australia holds day of mourning for Bondi Beach shooting victims
Australia holds day of mourning for Bondi Beach shooting victims
-
Liverpool cruise as Bayern reach Champions League last 16

-
 Fermin Lopez brace leads Barca to win at Slavia Prague
Fermin Lopez brace leads Barca to win at Slavia Prague
-
Newcastle pounce on PSV errors to boost Champions League last-16 bid

-
 Fermin Lopez brace hands Barca win at Slavia Prague
Fermin Lopez brace hands Barca win at Slavia Prague
-
Kane double fires Bayern into Champions League last 16


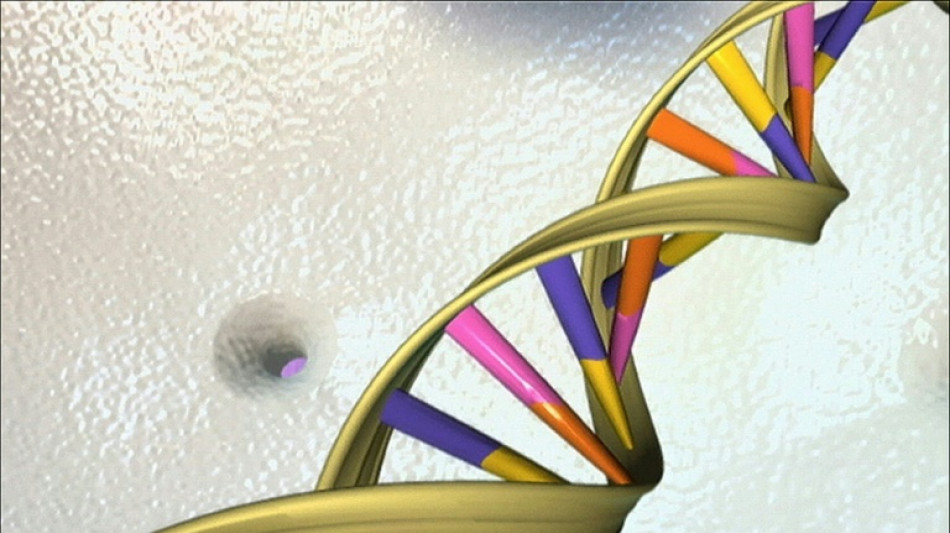
Google AI tool predicts danger of genetic mutations
Researchers at Google DeepMind, the tech giant's artificial intelligence arm, on Tuesday introduced a tool that predicts whether genetic mutations are likely to cause harm, a breakthrough that could help research into rare diseases.
The findings are "another step in recognising the impact that AI is having in the natural sciences," said Pushmeet Kohli, vice president for research at Google DeepMind.
The tool focuses on so-called "missense" mutations, where a single letter of the genetic code is affected.
A typical human has 9,000 such mutations throughout their genome; they can be harmless or cause diseases such as cystic fibrosis or cancer, or damage brain development.
To date, four million of these mutations have been observed in humans, but only two percent of them have been classified, either as disease-causing or benign.
In all, there are 71 million such possible mutations. The Google DeepMind tool, called AlphaMissense, reviewed these mutations and was able to predict 89 percent of them, with 90 percent accuracy.
A score was assigned to each mutation, indicating the risk of it causing disease (otherwise referred to as pathogenic).
The result: 57 percent were classified as probably benign, and 32 percent as probably pathogenic -- the remainder being uncertain.
The database was made public and available to scientists, and an accompanying study was published on Tuesday in the journal Science.
AlphaMissense demonstrates "superior performance" than previously available tools, wrote experts Joseph Marsh and Sarah Teichmann in an article also published in Science.
"We should emphasize that the predictions were never really trained or never really intended to be used for clinical diagnosis alone," said Jun Cheng of Google DeepMind.
"However, we do think that our predictions can potentially be helpful to increase the diagnosed rate of rare disease, and also potentially to help us find new disease-causing genes," Cheng added.
Indirectly, this could lead to the development of new treatments, the researchers said.
The tool was trained on the DNA of humans and closely-related primates, enabling it to recognize which genetic mutations are widespread.
Cheng said the training allowed the tool to input "millions of protein sequences and learns what a regular protein sequence looks like."
It then could identify a mutation and its potential for harm.
Cheng compared the process to learning a language.
"If we substitute a word from an English sentence, a person that is familiar with English can immediately see whether this word substitution will change the meaning of the sentence or not."
A.Ammann--VB



