
-
 'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
-
Villa's Tielemans ruled out for up to 10 weeks

-
 Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
-
UK proposes to let websites refuse Google AI search

-
 'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
-
Trump issues fierce warning to Minneapolis mayor over immigration
-
 Anglican church's first female leader confirmed at London service
Anglican church's first female leader confirmed at London service
-
Germany cuts growth forecast as recovery slower than hoped

-
 Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
-
One dead, five injured in clashes between Colombia football fans

-
 Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
-
US YouTuber IShowSpeed gains Ghanaian nationality at end of Africa tour

-
 Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools
Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools
-
Turkey football club faces probe over braids clip backing Syrian Kurds

-
 Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
-
US embassy angers Danish veterans by removing flags

-
 Netherlands 'insufficiently' protects Caribbean island from climate change: court
Netherlands 'insufficiently' protects Caribbean island from climate change: court
-
Fury confirms April comeback fight against Makhmudov

-
 Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards
Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards
-
Trump says 'time running out' as Iran rejects talks amid 'threats'

-
 Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days
Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days
-
Greenland dispute 'strategic wake-up call for all of Europe,' says Macron

-
 'Intimidation and coercion': Iran pressuring families of killed protesters
'Intimidation and coercion': Iran pressuring families of killed protesters
-
Europe urged to 'step up' on defence as Trump upends ties

-
 Sinner hails 'inspiration' Djokovic ahead of Australian Open blockbuster
Sinner hails 'inspiration' Djokovic ahead of Australian Open blockbuster
-
Dollar rebounds while gold climbs again before Fed update

-
 Aki a doubt for Ireland's Six Nations opener over disciplinary issue
Aki a doubt for Ireland's Six Nations opener over disciplinary issue
-
West Ham sign Fulham winger Traore

-
 Relentless Sinner sets up Australian Open blockbuster with Djokovic
Relentless Sinner sets up Australian Open blockbuster with Djokovic
-
Israel prepares to bury last Gaza hostage

-
 Iran rejects talks with US amid military 'threats'
Iran rejects talks with US amid military 'threats'
-
Heart attack ends iconic French prop Atonio's career

-
 SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025
SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025
-
Greenland's elite dogsled unit patrols desolate, icy Arctic

-
 Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, cuts jobs
Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, cuts jobs
-
Musetti rues 'really painful' retirement after schooling Djokovic

-
 Russian volcano puts on display in latest eruption
Russian volcano puts on display in latest eruption
-
Thailand uses contraceptive vaccine to limit wild elephant births

-
 Djokovic gets lucky to join Pegula, Rybakina in Melbourne semi-finals
Djokovic gets lucky to join Pegula, Rybakina in Melbourne semi-finals
-
Trump says to 'de-escalate' Minneapolis, as aide questions agents' 'protocol'

-
 'Extremely lucky' Djokovic into Melbourne semi-finals as Musetti retires
'Extremely lucky' Djokovic into Melbourne semi-finals as Musetti retires
-
'Animals in a zoo': Players back Gauff call for more privacy

-
 Starmer heads to China to defend 'pragmatic' partnership
Starmer heads to China to defend 'pragmatic' partnership
-
Uganda's Quidditch players with global dreams

-
 'Hard to survive': Kyiv's elderly shiver after Russian attacks on power and heat
'Hard to survive': Kyiv's elderly shiver after Russian attacks on power and heat
-
South Korea's ex-first lady jailed for 20 months for taking bribes

-
 Polish migrants return home to a changed country
Polish migrants return home to a changed country
-
Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, eyes bright AI future

-
 South Korea's ex-first lady jailed for 20 months for corruption
South Korea's ex-first lady jailed for 20 months for corruption
-
Minnesota congresswoman unbowed after attacked with liquid


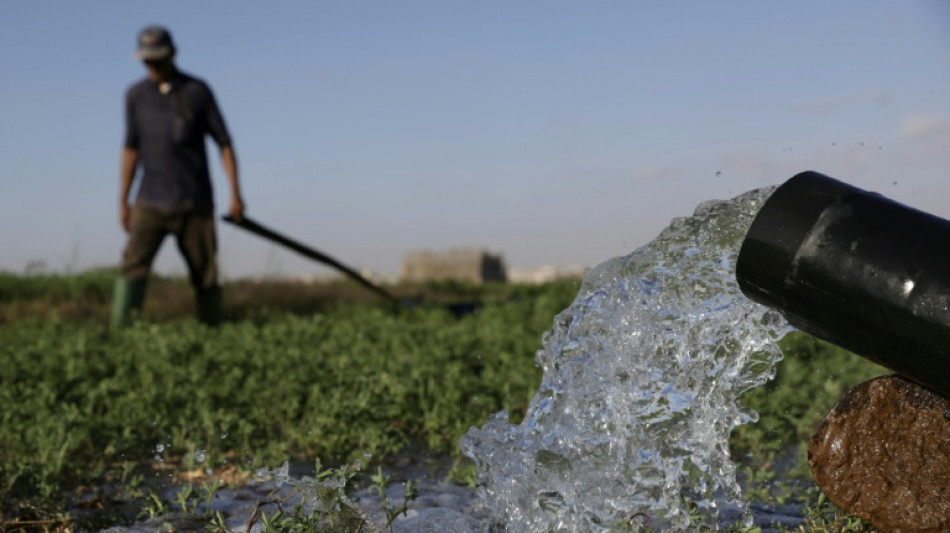
Drought-hit Morocco turns to desalination to save vegetable bounty
On the drought-stricken plains of Morocco's Chtouka region, cherry tomato farms stretch as far as the eye can see, clinging to life through a single, environmentally contentious lifeline: desalination.
"We wouldn't be here without it," said Abir Lemseffer, who manages production for the tomato giant Azura.
Severe drought driven by climate change has gripped the North African country since 2018, leaving Azura's 800 hectares (2,000 acres) of farms entirely dependent on desalinated water.
But the technology comes at a high cost -- both financially and environmentally.
It is energy-intensive, and in a country where more than half of the electricity still comes from coal, it carries a heavy carbon footprint.
Since 2022, Morocco's largest desalination plant, located nearby, has been producing 125,000 cubic metres (4.4 million cubic feet) of water a day.
The supply irrigates 12,000 hectares of farmland and provides drinking water for 1.6 million people in Agadir and surrounding areas, said Ayoub Ramdi of the regional agricultural development office.
By the end of 2026, officials hope to boost production to 400,000 cubic metres of water, half of which would be designated for agriculture.
Without that water, "a catastrophic scenario would loom over Morocco", said Rqia Bourziza, an agronomist.
Agriculture, which contributes about 12 percent to Morocco's overall economy, has been badly hit by six consecutive years of drought -- prompting the country to go all-in on desalination.
Across Morocco, there are 16 plants capable of producing 270 million cubic metres of water per year, with a target of reaching 1.7 billion cubic metres by 2030.
- Pricey water -
While around 1,500 farmers in the Agadir region make use of the water provided by the plant, others don't because it's simply too expensive.
Among them is Hassan, who grows courgettes and peppers on half a hectare of land and uses water from a well shared with 60 other farmers.
"I can't afford to use that water," he said, declining to give his full name.
Desalinated water is sold at $0.56 per cubic metre, excluding taxes, compared with $0.11 per cubic metre for conventional water.
That hefty price tag comes despite a 40 percent subsidy from public coffers.
Ali Hatimy, another agronomist, said "the cost of desalinated water significantly reduces the range of potential crops because only very high-value-added crops can offset it".
Bourziza insisted that desalination was "a very good alternative" but only for high-value crops such as tomatoes and orchard fruits.
Beyond the financial cost, desalination also exerts an environmental cost, said Hatimy.
"The production of desalinated water requires tremendous amounts of electrical energy and brine discharges impact marine ecosystems," he said.
Highly concentrated brine is a byproduct of the desalination process.
Ramdi, from the agricultural development office, said that "no impact" had been observed in the waters around Agadir, adding that the brine was diluted before its release.
While Morocco has a growing share of renewable energy, 62 percent of its electricity came from coal in 2023 and 14 percent from oil and gas, according to the International Energy Agency.
- Insufficient groundwater -
The stakes in the wider region of Souss-Massa, which accounts for 85 percent of Morocco's fruit and vegetable exports, are high.
Nearly two million tonnes are produced each year, with a turnover of $1.1 billion.
Ramdi said the desalination plant had thus helped to protect $1 billion of revenue a year and more than a million jobs.
"Desalination has saved agriculture in Chtouka," said Mohamed Boumarg, walking through one of his tomato greenhouses.
"Before, I only cultivated five hectares because I was constrained by the amount of water I had. Groundwater was not sufficient," said the 38-year-old farmer who now grows 20 hectares of tomatoes, with 60 percent of his crop marked for export.
"Our survival depends on it," said Lemseffer of Azura. "Either we accept sacrificing some of our margin by using desalinated water, or we close up shop."
O.Schlaepfer--VB


