
-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
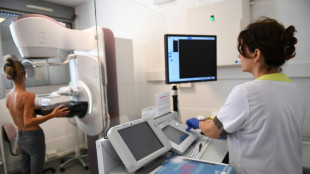
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack

-
 If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
-
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial

-
 Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
-
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown

-
 Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
-
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation


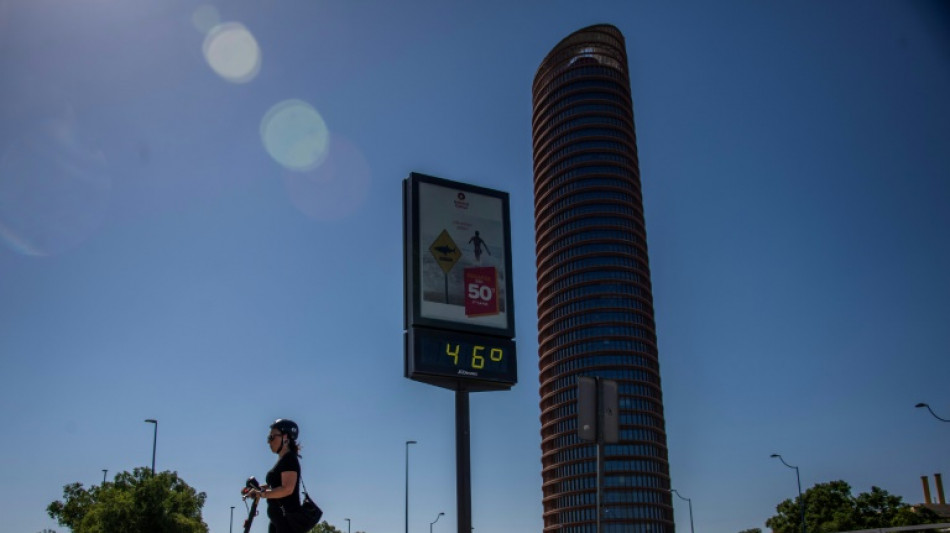
July 22 second day in row to break global heat record: EU monitor
Earth withered through a second-straight day of record-breaking temperatures on July 22, the EU's climate monitor said Wednesday, as parts of the world suffer devastating heatwaves and wildfires.
Preliminary data from the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) showed the daily global average temperature was 17.15 degrees Celsius (62.9 degrees Fahrenheit) on Monday, the warmest day in recorded history.
This was 0.06C hotter than the day before on July 21, which itself broke by a small margin the all-time high temperature set only a year before.
"This is exactly what climate science told us would happen if the world continued burning coal, oil and gas," said Joyce Kimutai, a climate scientist from Imperial College London, on Wednesday.
"And it will continue getting hotter until we stop burning fossil fuels and reach net zero emissions."
Copernicus, which uses satellite data to update global air and sea temperatures close to real time, said its figures were provisional and final values may differ very slightly.
It anticipated daily records could keep toppling as summer peaks in the northern hemisphere, and the planet endures an extraordinary stretch of unprecedented heat on the back of the hottest-ever year.
The monitor on Tuesday said global temperatures were expected to drop soon though there could be further fluctuations.
Global warming is causing longer, stronger and more frequent extreme weather events, and this year has been marked by major disasters across the globe.
The historic heat has been felt on many continents including Asia, North America and Europe, where heatwaves and wildfires have torn a path of destruction in recent weeks.
Fires have also ripped through the Arctic, which is warming much faster than elsewhere on the planet, while winter temperatures were well above normal in Antarctica.
- 'Horrific temperatures' -
Copernicus said it was less the fact daily temperature records were being rewritten than a broader pattern of never-before-seen warming that greatly worries climate scientists.
Every month since June 2023 has eclipsed its own temperature record compared to the same month in previous years, something never before seen.
The heat witnessed on Sunday and Monday only slightly exceeded the July 2023 record, but was far above the previous high of 16.8C set in August 2016.
Copernicus said that 16.8C record has been smashed 57 times since July 2023, around the time global temperatures began a steady rise into what scientists have called unchartered territory.
"The much used term 'unprecedented' no longer describes the horrific temperatures we are experiencing," Christiana Figueres, a former head of the UN's climate change body, said on Wednesday.
Copernicus records go back to 1940 but other sources of climate data such as ice cores, tree rings and coral skeletons allow scientists to expand their conclusions using evidence from much deeper in the past.
Climate scientists say the period being lived through right now is likely the warmest the earth has been for the last 100,000 years, back at the start of the last Ice Age.
The burning of fossil fuels is the primary driver of climate change and emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases keep rising despite global efforts to slow rising temperatures.
Copernicus on Tuesday said 2024 could pass 2023 as the hottest year on record but it was "too early to predict with confidence".
D.Schaer--VB


