
-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack


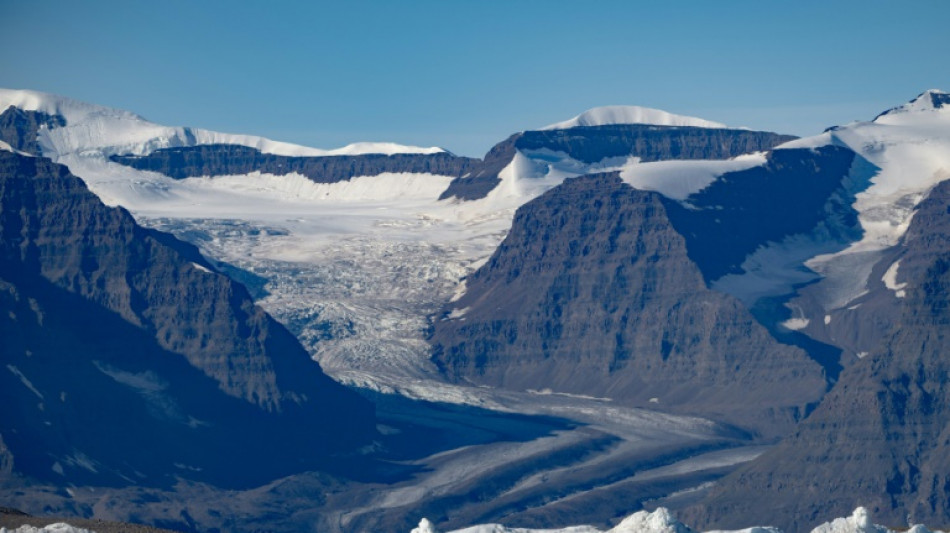
Oh my (long) days: Melting ice caps slow Earth's spin
It's well known that as far as the climate crisis goes, time is of the essence.
Now a study out Monday shows that the melting of the polar ice caps is causing our planet to spin more slowly, increasing the length of days at an "unprecedented" rate.
The paper, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows that water flowing from Greenland and Antarctica is resulting in more mass around the equator, co-author Surendra Adhikari of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory told AFP.
"It's like when a figure skater does a pirouette, first holding her arms close to her body and then stretching them out," added co-author Benedikt Soja of ETH Zurich.
"The initially fast rotation becomes slower because the masses move away from the axis of rotation, increasing physical inertia."
Earth is commonly thought of as a sphere, but it's more accurate to call it an "oblate spheroid" that bulges somewhat around the equator, a bit like a satsuma.
What's more, its shape is constantly changing, from the impacts of the daily tides that affect the oceans and crusts, to longer term effects from drift of tectonic plates, and abrupt, violent shifts caused by earthquakes and volcanoes.
The paper relied on observational techniques like Very Long Baseline Interferometry, where scientists can measure the difference in how long it takes for radio signals from space to reach different points on Earth, and use that to infer variations in the planet's orientation and length of day.
It also used the Global Positioning System, which measures Earth's rotation very precisely, to about one-hundredth of a millisecond, and even looked at ancient eclipse records going back millenia.
- Implications for space travel -
If the Earth turns more slowly, then the length of day increases by a few milliseconds from the standard measure of 86,400 seconds.
A currently more significant cause of slowdown is the gravitational pull of the Moon, which pulls on the oceans in a process called "tidal friction" that has caused a gradual deceleration of 2.40 milliseconds per century over millions of years.
But the new study comes to a surprising conclusion that, if humans continue to emit greenhouse gases at a high rate, the effect of a warming climate will be greater than that of the Moon's pull by the end of the 21st century, said Adhikari.
Between the year 1900 and today, climate has caused days to become around 0.8 milliseconds longer -- and under the worst-case scenario of high emissions, climate alone would be responsible for making days 2.2 milliseconds longer by the year 2100, compared to the same baseline.
That might not sound like a great deal, and certainly not something that humans are able to perceive.
But "there are definitely a lot of implications for space and Earth navigation," said Adhikari.
Knowing the exact orientation of Earth at any given moment is crucial when attempting to communicate with a spaceship, such as the Voyager probes that are now well beyond our solar system, where even a slight deviation of a centimeter can end up being kilometers off by the time it reaches its destination.
F.Wagner--VB



