
-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
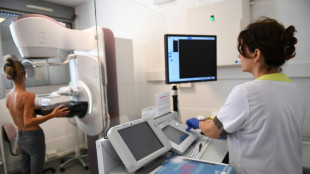
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack


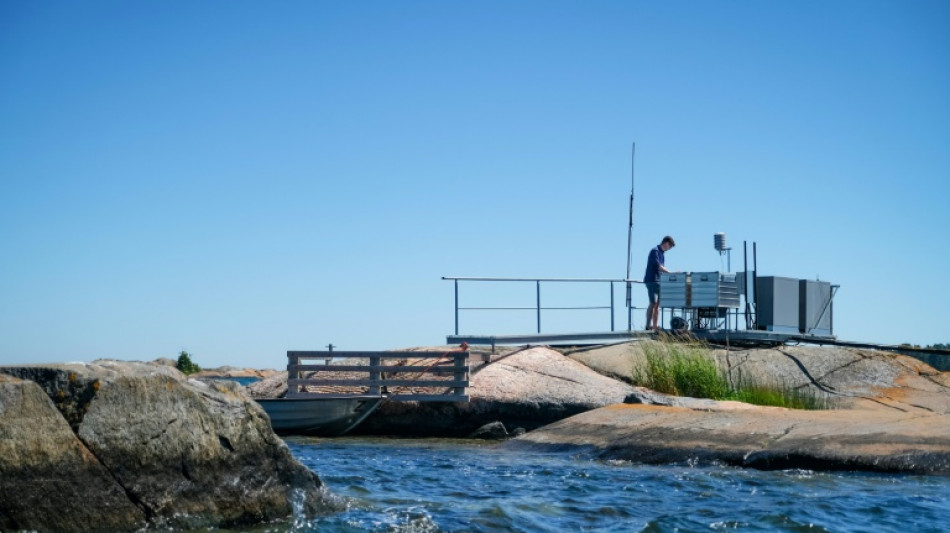
Warming Baltic Sea: a red flag for global oceans
Climate change combined with pollution from farming and forestry could flip northern Europe's Baltic Sea from being a sponge for CO2 to a source of the planet-warming gas, scientists studying told AFP.
This should be a red flag, they warned, noting that other coastal marine zones around the world are trending in the same direction.
"We are at the forefront of these changes," said University of Helsinki professor Alf Norkko.
The Baltic Sea –- connected to the Atlantic by the straights of Denmark, and surrounded by Germany, Poland, Finland, Sweden and the Baltic states –- has warmed at twice the pace of global oceans generally.
Its relatively shallow waters are extremely sensitive to changes in the environment and climate.
AFP recently accompanied Norkko, who leads the largest marine research station in the Baltic Sea, and some of his colleagues on a research excursion to the Finnish waterfront town of Hanko.
Slender terns dart above the lush marsh-like landscape surrounding the over 120-year-old field station, a common sight along Finland's 1,100-kilometre (680-mile) coastline, which is dotted by more than 81,000 islands.
Measurements conducted since 1926 show that average sea temperature have spiked by two degrees Celsius over the last 30 years.
"The Baltic Sea is basically a small bathtub compared to the global oceans," said doctoral researcher Norman Gobeler, an expert on marine heatwaves.
"We are seeing the first effects of the temperature increase."
- Linking marine ecosystems to climate change -
During one foray into the field, coastal ecologist and doctoral researcher Margaret Williamson –- sporting waist-high waders and sunglasses –- moved through a swaying, green reedbed collecting stems, roots and soil to measure CO2 levels.
"The Baltic Sea is really important for understanding what climate change is doing worldwide," said Williamson, who is part of a joint research project with Helsinki and Stockholm universities.
Many coastal areas across the globe -- coral reefs, estuaries, and mangrove forests –- are among the planet's richest biodiversity hotspots, providing vital nurseries and habitats for hundreds of marine species.
They are also the most vulnerable to the kind of changes observed in the Baltic.
Up to now, oceans have been our most important natural ally in coping with global warming.
Over decades, they have consistently absorbed 90 percent of the heat generated by human-induced climate change, and about a quarter of the carbon dioxide humanity injects into the atmosphere.
But scientists say there is a lot we do not know about the capacity of oceans to continue serving as "sinks", or sponges, for our carbon pollution, Norkko noted.
"There has been a lot of emphasis on terrestrial forests' role as carbon sinks," he said. "Our coasts and oceans have been ignored. The question is, how much further the oceans can take of all these stressors?"
- From carbon sink to carbon source? -
Recent findings from the Finnish research station suggest coastal ecosystems in the Baltic Sea could start emitting greenhouse gases –- CO2 and methane –- instead of absorbing them, driven by both rising temperatures and environmental pollution.
The ecological condition of many coastal areas has deteriorated due to the runoff from forestry and nitrogen and phosphorus-rich fertiliser used in agriculture, as well as untreated waste water.
The overabundance of chemical nutrients leads to harmful algae blooms, and vast "dead zones" depleted of oxygen, a process known as eutrophication.
"A degraded ecosystem will be a net carbon source," Norkko said. "Our biggest concern is that what should be an efficient carbon sink could become a carbon source."
Norkko said the changes already witnessed in the Baltic Sea should sound the alarm for coastal regions across the world.
"Many of the world's densely populated coastal areas are affected by eutrophication and this has a huge effect on the ability of coastal ecosystems to mitigate climate change," he said.
While measures to protect and restore healthy marine ecosystems had been taken in the Baltic Sea and elsewhere, ramped up efforts are required to ensure their role as carbon absorbers.
Pointing to the dark green, bubbly bladderwrack -- a threatened seaweed that anchors coastal marine ecosystems –- Norkko compared the algae with an "old growth forest", noting it lives up to 30 years in a robust coastal ecosystem.
"Once the bladderwrack sucks up carbon it stores it for a long time," he said. "That's why a healthy system is a buffer against change and is important to maintain."
M.Vogt--VB



