
-
 Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
-
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China

-
 US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
-
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites

-
 Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
-
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study

-
 Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
-
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits

-
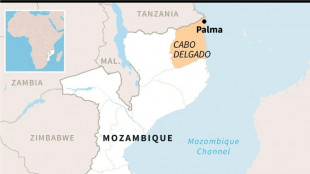 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain


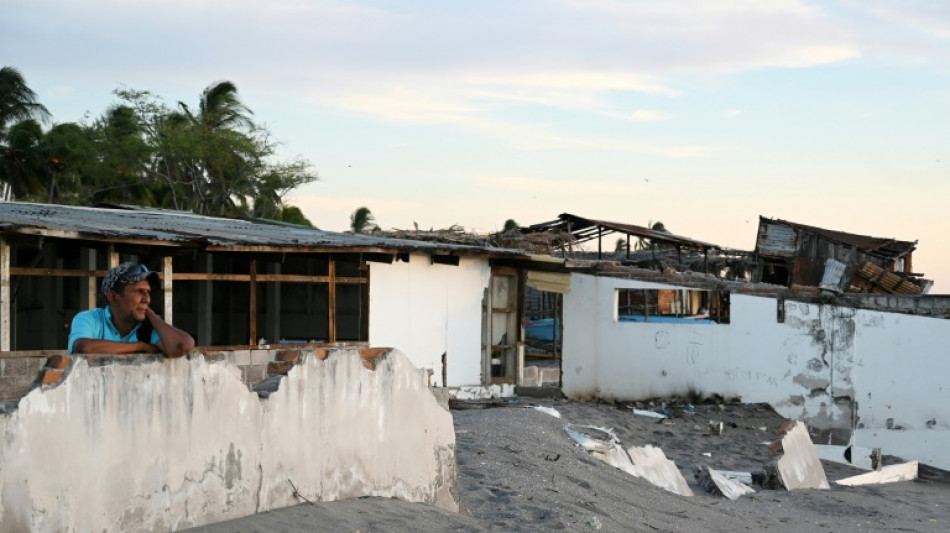
Rising seas eating away at Honduran fishing village
The coastline of Cedeno, a fishing village in southern Honduras, looks like it was hit by an earthquake. Houses, businesses and clubs stand in ruins. Forsaken.
But it was not a quake. Nor a tsunami. A much slower, but equally destructive force is at work in Cedeno and other villages on the Pacific Gulf of Fonseca: sea level rise.
The creeping ocean has claimed ever more of the protective mangrove forest off Cedeno's coast, and claws away at the land with increasingly violent sea surges.
Inhabitants of Cedeno and other fishing villages on the Gulf of Fonseca -- shared by Honduras, El Salvador and Nicaragua -- are at the forefront of one of the more visible symptoms of climate change: sea level rise caused by melting glaciers and ice sheets.
"The sea is advancing," said Telma Yadira Flores, a 40-year-old homemaker from Cedeno who lost her house in a storm surge last year and now lives in a rickety shack with her son and daughter-in-law. The sandy beach is their kitchen floor.
"If the sea comes again, we will have to move. We will have to see where," Flores told AFP.
According to the NGO Coddeffagolf (Committee for the Defense and Development of the Flora and Fauna of the Gulf of Fonseca), the sea has advanced 105 meters (344 feet) into Cedeno, a settlement of some 7,000 people, in 17 years.
Apart from numerous homes and small businesses, a marine laboratory, police headquarters and a park were also abandoned to the waves.
The Michel Hasbun primary school, which once served about 400 children, now stands empty.
"There was a soccer field, it was lost," Sergio Espinal, a 75-year-old fisherman, told AFP, pointing to where it once stood.
"There were good restaurants, good hotels..." But no more.
- 'Entire countries could disappear' -
The community has also had to contend with dwindling fish numbers.
The mangroves whose roots act as nurseries and hunting grounds for crustaceans, shellfish and many other species that in turn serve as food for bigger animals, are under attack from sea levels rising too fast for them to adapt.
"Before there were schools of dolphins, there were sharks, swordfish... and now everything has been lost," boat operator Luis Fernando Ortiz, 39, said as he pointed out the broken and abandoned mansion of a former president overlooking the idyllic turquoise waters.
The community's hopes now rest on a Coddeffagolf project, still in the planning phase, to improve coastal surge protections and reforest the battered mangrove.
Earlier this month, UN chief Antonio Guterres warned that global warming-induced sea level rise could force a mass exodus "on a biblical scale" as people flee low-lying communities.
"The danger is especially acute for nearly 900 million people who live in coastal zones at low elevations -- that's one out of 10 people on Earth," Guterres told the UN Security Council.
"Low-lying communities and entire countries could disappear forever," he said.
Honduras is already a mayor source of US-bound undocumented migrants.
The UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) says sea levels rose by 15-25 centimeters (6-10 inches) between 1900 and 2018.
And if the world warms by just two degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) compared to the pre-industrial era, those levels will rise again by 43 centimeters by the year 2100.
According to the IPCC, all mangrove forests could be lost in the next 100 years.
Mangroves not only sustain sea life but also help trap planet-warming carbon dioxide and protect coastlines from storms and surges.
Central America's Atlantic and Pacific coasts "are some of the most endangered on the planet with regard to mangroves, as approximately 40 percent of present species are threatened with extinction," according to the IPCC.
On Thursday and Friday this week, leaders of government, the private sector, civil society and academics will gather in Panama for the "Our Ocean" conference to discuss how to save under-pressure marine resources.
J.Bergmann--BTB



