
-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
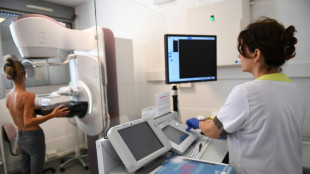 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'

-
 Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
-
Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?

-
 Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
-
Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
-
EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'

-
 Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
-
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy


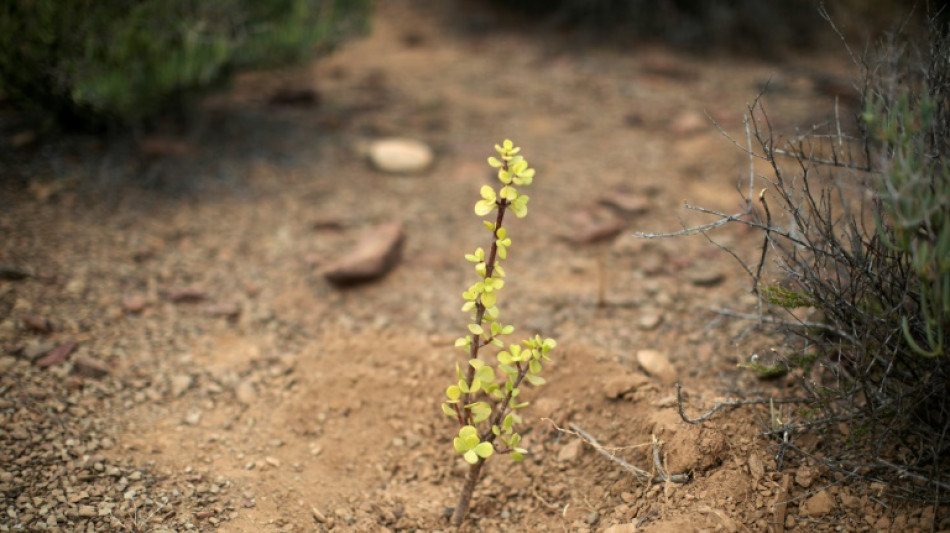
Spekboom bushes protect earth but can they cool Earth?
Andre Britz pulled over his pick-up truck on a rocky mountain track to show off the nature-preserving powers of southern Africa's spekboom shrub.
The 62-year-old Afrikaner is an evangelist for Portulacaria afra, a red-stemmed bush or small tree with thick, dense green leaves that acts as a sponge for carbon dioxide.
"Here you can see the difference between degraded land and what we call pristine spekboom veld," he said, pointing out a division running like a contour between lush green hilltop and arid valley side.
The plant once dominated the dry terrain of the Little Karoo in South Africa's Western Cape.
But decades of what Britz calls over-grazing and mismanagement have destroyed the shrub and the vital shade it offers the sun-scorched earth, not to mention its strength at absorbing carbon.
"The spekboom does carbon sequestration day and night. It is one of the few plants that do it," Britz told AFP on a tour to explain his ten-year-old mission.
"And the other thing is that it occurs here naturally," he said. "So that was why it was important to plant spekboom here and to have that secondary effect on the change of climate."
Ten years ago Britz founded Jobs 4 Carbon, an organisation dedicated to replanting and encouraging the spekboom in an area where farming was devastated by the long 2015-2020 drought.
Now he has a team of planters, labouring with shovels and picks in the rocky terrain to nurture new plants that could once more blanket the dry ground with lush green leaves.
- 'Miracle plant' -
Nearby, a two-year-old replanted Spekboom has begun to spread its branches above fresh shoots. Jobs 4 Carbon has already replanted almost 700 hectares (1,730 acres).
"It brings nature back to life," team leader Jan Cloete, 49, said with a smile.
To botanist Alastair Potts, 41, in its natural semi-arid ecosystem or "subtropical thicket", it is a "miracle plant".
It "creates forest-like micro-environments", a "carpet" of leaves that "trap water and dust and nutrients", as well as carbon, he said.
The latter is stored in large quantities because of the succulent's rare ability to swing between two types of photosynthesis.
In dry, hot weather, spekboom sucks carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere at night and stores it in the form of malic acid.
During the day, the plant closes its pores, called stomata, to minimise water loss and uses its night stash for photosynthesis.
This greatly boosts its sequestration capacity.
Fact-checkers have debunked overenthusiastic claims that the plant rivals the Amazon rainforest in terms of carbon absorption, but proponents say it still pulls above its weight when allowed to grow in its natural environment.
A 2006 paper estimated that one hectare of spekboom sequestered on average four tonnes of CO2 per year. Others put the figure at more than 15 tonnes.
- Carbon credits -
Jobs 4 Carbon is hoping to plant more of it and fund the venture selling carbon credits, a financial instrument bought by companies to offset their greenhouse gas emissions.
To make that viable, however, scientists first have to agree on just how much CO2 the little succulent exactly sequesters.
Still, Potts is optimistic. Spekboom doesn't have the drawbacks of other tree-planting projects criticised for setting up monocultures in unsuitable ecosystems, he said.
And by restoring the environment, it helps prevent emissions from land degradation.
"I feel that carbon farming and spekboom is the perfect mix," he said.
"We're changing the ecosystem functioning back to what it was, through carbon, which is fantastic."
With funding from international foundations and private companies, Jobs 4 Carbon is looking to green 13,000 hectares across the region, said Andre Britz.
But much more could be done across the country, according to Potts.
The group currently plants the shrub for free if landowners agree to leave their plot fallow for at least 15 years in return.
In the courtyard of his village church, 15,000 small plants are ready to put down roots in the arid ground, which reminds him of an old saying he heard from his grandfather: "Take care of your veld, and your veld will take care of you".
L.Stucki--VB



