
-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
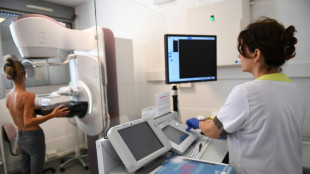 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'

-
 Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
-
Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?

-
 Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
-
Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
-
EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'

-
 Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
-
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy


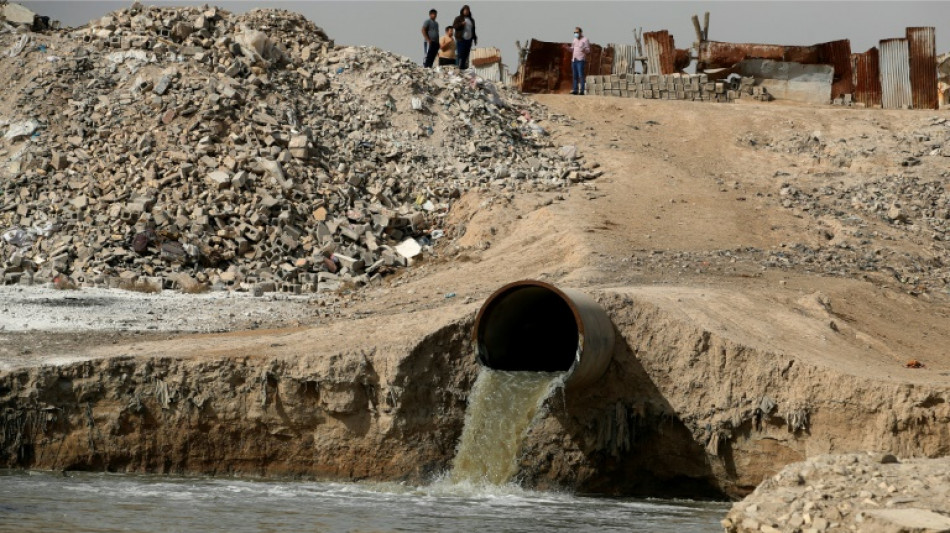
Rampant water pollution threatens Iraq's shrinking rivers
Stricken by drought and depleted by upstream dams, Iraq's once mighty rivers the Tigris and Euphrates are suffocating under pollutants from sewage to medical waste.
In a country where half the population lacks access to safe drinking water, according to UN figures, state institutions are to blame for a man-made disaster which is turning rivers into waste dumps.
"What is strange about water pollution in Iraq is that most government institutions are responsible for it," Khaled Shamal, the ministry of water resources spokesman, told AFP.
He warned that Iraq's sewage network dumps "large quantities" of wastewater into the two major waterways, after superficial treatment or none at all.
"Most hospitals near a river dump their medical waste and sewage straight into it," Shamal added. "It is dangerous and catastrophic."
Dirty and unsafe water is a prime health threat in Iraq, where decades of conflict, mismanagement and corruption have taken a toll on infrastructure, including the water system.
Petrochemical factories, power plants and agricultural drainage that carries fertilisers and other toxins further pollute Iraq's water.
- Overloaded with toxins -
In the country known as "the land of two rivers", water pollution has become so severe that it is now visible to the naked eye.
In Baghdad's eastern suburbs, AFP filmed a pipe discharging green-coloured water with a foul odour into the Diyala river.
Ali Ayoub, a water specialist from the UN children's agency UNICEF, warned that Baghdad's two main water treatment plants are overloaded with twice their intended capacity.
The treatment facilities were built for a population of three to four million, but at least nine million live in Baghdad today.
"Inadequate infrastructure, limited regulations and poor public awareness are the main factors contributing to the significant deterioration of water quality in Iraq", Ayoub said.
"Two-thirds of industrial and household wastewater are discharged untreated into the rivers," amounting to six million cubic metres a day.
But Iraq's government is taking steps to improve water quality, he said.
The government has said it no longer approves projects that could be a source of pollution unless they provide water treatment.
It has developed a three-year plan to "strengthen the water and sanitation system" to provide "safe drinking water, especially to the most vulnerable communities", Ayoub said.
In partnership with UNICEF, Baghdad's Medical City –- a complex of hospitals with 3,000 beds, on the banks of the Tigris –- has recently inaugurated a water treatment plant, Akil Salman, the complex's projects manager, told AFP.
The facility has started operating with three units, each capable of treating 200 cubic metres of waste a day. Four additional units with a capacity of 400 cubic metres each are expected to be completed "within two months".
Instead of directing its wastewater to Baghdad's overburdened treatment facilities, the Medical City can use the treated water for the hospitals' gardens and to fill the firefighters' tanks, Salman said.
- 'We have to buy water' -
Iraq, which endures blistering summer heat and regular sandstorms, is one of the five countries most impacted by some effects of climate change, says the United Nations.
The country of 43 million people has suffered four consecutive years of withering drought, and water scarcity has become extreme.
It is worsened, according to authorities, by upstream dams built by Iraq's neighbours Iran and Turkey, lowering water levels in the Tigris and Euphrates, which have irrigated Iraq for millennia.
The water flow to Iraq "has declined significantly, leading to an increase in the concentration of pollutants in the water", environment ministry spokesperson Amir Ali Hassoun said.
Previously, authorities routinely opened valves to increase the river flow and dilute pollutants, but this strategy has become impossible due to a shortage of water which has forced them to look for other options.
In addition to "raising awareness" among the population, Iraqi officials say they are closely monitoring wastewater management.
"Hospitals are required to install wastewater treatment facilities," Hassoun said.
"We hope that 2024 will be the year we eliminate all violations," referring to hospitals dumping untreated sewage and medical waste into the rivers.
In Iraq's south, water pollution is much worse.
"Wastewater from other areas is discharged into the river, polluting the water that reaches us," said 65-year-old Hassan Zouri from the southern province of Dhi Qar.
"The water carries diseases. We cannot drink it or use it at all," added the father of eight.
"We used to rely on the river for drinking, washing, and irrigation, but now we have to buy water."
A.Zbinden--VB



