
-
 US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
-
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
-
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
-
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics

-
 Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
-
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter

-
 US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files
-
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud

-
 French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing
-
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash

-
 Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery
-
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls

-
 'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown
-
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz

-
 Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest
-
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset

-
 Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains
-
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence

-
 Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday
-
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign

-
 Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon
-
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck

-
 Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation
-
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans

-
 Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race
-
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb

-
 Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup
-
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim

-
 IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns
-
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes

-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
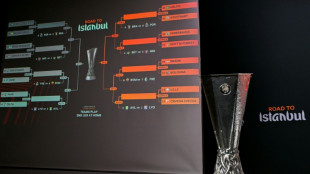 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support

-
 Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
-
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties

-
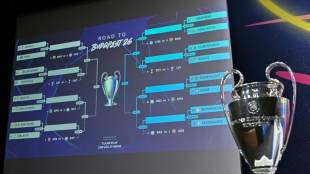 Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
-
Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble

-
 Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
-
Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump

-
 Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
-
Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat

-
 Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention
Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention
-
'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.65% | 83.78 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.69% | 16 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.98% | 79.39 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.27% | 12.99 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.11% | 23.67 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.21% | 60.335 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.33% | 51.34 | $ | |
| NGG | -0.44% | 84.68 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.59% | 35.6 | $ | |
| RIO | -5.36% | 90.29 | $ | |
| BCE | 0.25% | 25.55 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.58% | 14.625 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.59% | 93.14 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.06% | 24.075 | $ | |
| BP | -1.52% | 37.47 | $ |

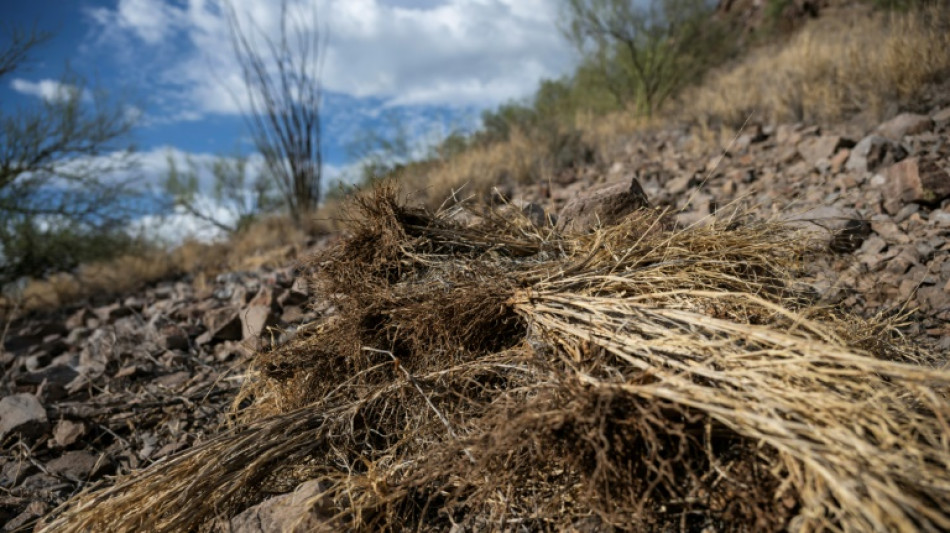
Invasive firestarter: How non-native grasses turned Hawaii into a tinderbox
After a catastrophic wildfire that killed more than 100 people in Hawaii, eyes have turned toward an unexpected culprit: invasive grass species that have spread massively over the archipelago for decades, serving as the perfect fuel.
Drought-resistant, capable of invading difficult terrain, and gradually muscling out local species, they are also a growing threat in the western United States, where devastating fires are increasing.
"Invasive grasses are very ignitable. They change the landscape," Carla D'Antonio, a professor of ecology at the University of California, Santa Barbara told AFP.
"They make conditions that are more conducive to more fire, and all of a sudden, we just have a lot more fire."
Rather than decomposing when they die, they stay "standing there for a long time, dry as a bone," said D'Antonio, who has been studying these species for more than 30 years. They're also hardy, surviving fires better than native species and gradually replacing them.
Most of these grasses -- buffelgrass, Guinea grass, molasses grass -- came from Africa, and were introduced as pasture for cattle, without knowing the danger they would come to represent decades later.
In Hawaii, the demise of sugar cane plantations in the 1990s as a result of globalization had disastrous consequences: huge tracts of land were abandoned, allowing the invasive species an opening.
"Yes, many parts of Hawaii are trending towards dryer conditions, but the fire problem is mostly attributable to the vast extents of non-native grasslands left unmanaged by large landowners as we've entered a 'post-plantation era,'" said Clay Trauernicht, a fire ecologist at the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
Trauernicht said the annual area burned in Hawaii has increased by 300 percent in recent decades.
A 2021 fire prevention report by Maui County described fires as a growing threat due to increasing temperatures and prolonged periods of drought as a result of climate change, and the growing menace of intrusive grasses.
Hawaii, despite its tropical reputation, is getting drier: a 2016 study found 90 percent of the state received less rain compared to a century earlier.
The Maui County report recommended "an aggressive plan to replace these hazardous fuel sources with native plants to reduce combustible fuel while increasing water retention."
- 'Nothing natural about it' -
The problem isn't confined to Hawaii. Over in the mainland United States, "the deserts of the West and the conifer forests, and then the shrub lands in the coastal zone, invasive grasses are here to stay, they're now part of the ecosystem," said D'Antonio.
She herself spends some Saturday evenings weeding roadsides with neighbors in a mountainous area near Santa Barbara, California. Their goal: to prevent a fire from starting from a cigarette butt or an overheating vehicle.
Most of the major fires of the Mojave and Great Basin have been fueled by invasive grasses, she says, while also citing the Camp Fire of 2018, which destroyed the small California town of Paradise, killing more than 80 people. It was started by a power line igniting dry grass.
"(I'm) not making the mistake of calling it a natural disaster because there's almost nothing natural about it," emphasizes the scientist.
One of the invaders, buffelgrass, also threatens the emblematic cactus of the Saguaro National Park in Arizona, by smothering young saguaros and fueling fires in the region. Organizations regularly organize clearing operations. The same species is spreading in Mexico and in Australia.
According to a 2019 study, six invasive grass species caused fire frequency to increase by up to 150 percent in US ecosystems.
For D'Antonio of UC Santa Barbara, tragedies like that of Hawaii are linked to many factors: the alteration of the landscape by humans, the invasion of alien species, droughts made worse by climate change, but also a lack of preparation.
In the American West, widespread logging of conifer forests in the 19th century and a long history of excessive fire suppression in the 20th century contributed to accumulation of tinder on the forest floor.
"The potential for disaster is huge," said D'Antonio, leaving society with daunting questions to address. "How do we plan for the extreme? Not for the average fire, but the extreme fire?"
K.Brown--BTB




