
-
 New hunt for flight MH370 ends with no clues to 12-year mystery
New hunt for flight MH370 ends with no clues to 12-year mystery
-
Kuwait airport, Bahrain desalination unit struck as Iran presses Gulf attacks

-
 F1 world champion Norris fears 'long, tough season'
F1 world champion Norris fears 'long, tough season'
-
Russell takes pop at rival Norris over 'worst F1 cars' claim

-
 'Whole country will stop' as India dreams of home World Cup glory
'Whole country will stop' as India dreams of home World Cup glory
-
Leclerc 'positively surprised' by Ferrari but says more work needed

-
 Djokovic says Alcaraz equipped to extend winning streak
Djokovic says Alcaraz equipped to extend winning streak
-
Russell warns that Mercedes must raise game despite Australia 1-2

-
 China FM urges US to manage differences in face of trade woes
China FM urges US to manage differences in face of trade woes
-
Piastri takes blame for crashing out before home Australian Grand Prix

-
 Turkey's jailed mayor says demand for change cannot be stopped
Turkey's jailed mayor says demand for change cannot be stopped
-
Venezuela frees more political prisoners under amnesty law

-
 Dominant Russell wins Australian Grand Prix in Mercedes 1-2
Dominant Russell wins Australian Grand Prix in Mercedes 1-2
-
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round, Djokovic fights through

-
 Iran says can fight for months as Israel strikes Beirut hotel
Iran says can fight for months as Israel strikes Beirut hotel
-
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors

-
 USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
-
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise

-
 Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
-
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record

-
 Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
-
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje

-
 Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
-
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up

-
 US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
-
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries

-
 India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
-
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz

-
 Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
-
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase

-
 Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?
-
Kuwait airport, Saudi Arabia targeted as Iran presses Gulf attacks

-
 Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
-
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup

-
 Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
-
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops

-
 Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
-
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran

-
 Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
-
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1

-
 New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
-
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao

-
 Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
-
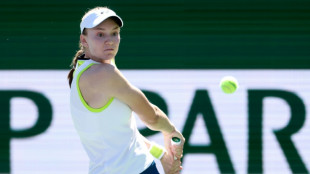
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
 Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
-
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'

-
 Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
-
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations

-
 Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
-
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'


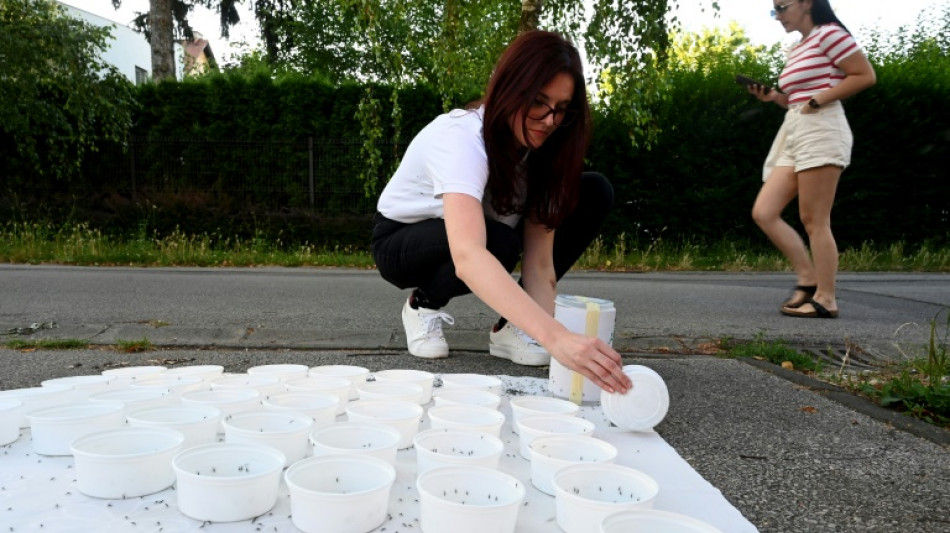
Croatia targets latest climate-change threat: mosquitoes
Hordes of buzzing but sterile mosquitoes are being let loose in Zagreb as Croatia gets ahead of worries that climate change could bring tropical diseases to the Mediterranean nation.
The release is part of a pilot project focused on eradicating invasive Asian Tiger mosquitoes known for carrying sicknesses like Dengue Fever, Chikungunya and Zika.
The species has appeared to thrive in the country and across the region in recent years due in part to climate change -- with the warmer weather providing fertile ground for the mosquito.
"It's too early to say whether this one will yield results," Zagreb resident Kruno Lokotar told AFP. "But I'm glad that we are not just sticking with spraying."
Croatia's effort centres on a method that uses sterilised male mosquitoes -- which once released into the wild will mate with females and neutralise the potential for future offspring.
The Zagreb project kickstarted in June, when 100,000 mosquitoes were released in a high-risk area with thick foliage where mosquitoes often congregate.
"If we release a sufficient number of sterile males during a certain period in an area, the mosquito population in that area will decrease," Ana Klobucar, a medical entomologist of the Zagreb-based teaching institute of public health who is overseeing the project, told AFP.
The plan is rooted in the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) -- a method that has been used for decades across the world to combat various harmful insects, but is still being tested for its effectiveness against mosquitoes in urban areas.
Croatia started using it for mosquitoes last year in northern Istria peninsula.
This year a total of 1.2 million specially treated insects will be released there over a three-month period, entomologist Nediljko Landeka of the regional public health institute told AFP.
- Climate change impact -
The insects -- which have been rendered sterile after exposure to gamma rays -- are sourced from a laboratory in Italy, and shipped 500 kilometres (310 miles) to Croatia in special boxes.
Once received, Klobucar and her assistants carefully remove plastic bowls with the insects from cardboard tubes before they are later dispersed in local gardens in the target area.
Croatia's programme coincides with increasingly dire warning from experts that global warming could make swaths of Europe more vulnerable to infectious diseases spread by mosquito bites.
The presence of the Asian Tiger mosquito in Croatia was first recorded in 2004 after arriving in Europe in the late 1970s, with experts suggesting they made the journey in used tyres that arrived in Albania from China.
The breed has now spread to more than a dozen European countries, with the Mediterranean region having been hit the hardest, according to official figures.
As the mercury rises across the globe, the Asian Tiger mosquito is moving further north including in areas that were considered too cold for the species to thrive, including in Switzerland and Germany.
"We are afraid that together with the species, viruses could also easily adapt in the future to new environments," warned Greek entomologist Antonios Michaelakis.
Michaelakis -- who is also a researcher at the Benaki Phytopathological Institute in Athens -- has been instrumental in sharing his experiences from a programme in Greece with his Croatian counterparts.
In Greece in 2019, the project succeeded in slashing the population of Asian Tiger mosquitoes by 90 percent, he told AFP.
During a trial of the technique last year in Croatia's Istria, up to 14 percent of mosquito eggs in the area were found to be sterile and jumped to nearly 60 percent this year, Landeka added.
C.Kovalenko--BTB



