
-
 Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig

-
 Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
-
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says

-
 Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
-
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals

-
 Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
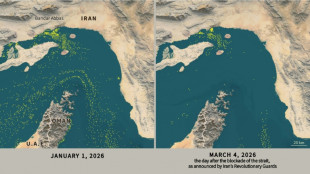 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs

-
 Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
-
Voices from Iran: protests, fear and scarcity

-
 Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
-
This is how Ukraine has countered Russia's Iran-designed drones

-
 Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
-
Sleepless Iranians count cost of war as damage mounts

-
 Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
-
Leading satellite firm to hold back Gulf state images

-
 Tuipulotu urges Scotland to stay in Six Nations title hunt against France
Tuipulotu urges Scotland to stay in Six Nations title hunt against France
-
Trump says only Iran's 'unconditional surrender' can end war

-
 US releases Epstein files with uncorroborated Trump allegations
US releases Epstein files with uncorroborated Trump allegations
-
Securing shipping lane from Mideast war 'challenging', say experts

-
 Italy have to start beating the best, says captain Lamaro
Italy have to start beating the best, says captain Lamaro
-
India's Bumrah only 'human' says Phillips ahead of T20 World Cup final

-
 Oil prices climb as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
Oil prices climb as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
-
US retail sales decline as consumer pullback deepens


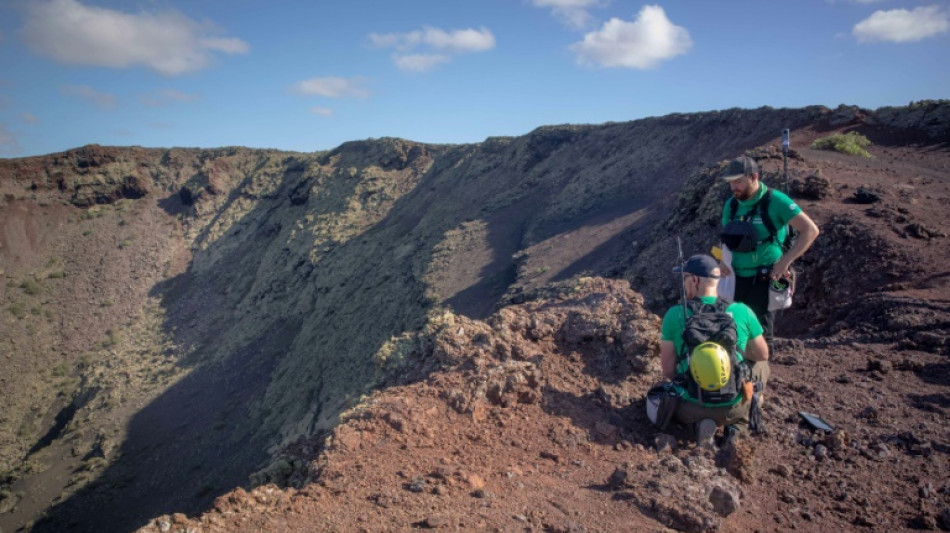
'Like the Moon': Astronauts flock to Spanish isle to train
Kneeling on the edge of a deep crater, astronaut Alexander Gerst uses a chisel to collect a sample of volcanic rock which he carefully puts inside a white plastic bag.
Gerst is not on the Moon, even if it looks like it. He is in the middle of Los Volcanes Natural Park on the island of Lanzarote in Spain's Canary Islands, off the northwest coast of Africa.
With its blackened lava fields, craters and volcanic tubes, Lanzarote's geology can be uncannily similar to that of the Moon and Mars -- so much so that the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA have for years been sending astronauts to the island to train.
"This place has lavas that are very, very similar to the ones that we find on the Moon," Gerst, a 46-year-old German astronaut with the ESA, told AFP.
He said the island was "a unique training ground".
Gerst, who has completed two missions on the International Space Station, is one of about a dozen astronauts who have taken part in the ESA's Pangaea training course in Lanzarote over the past decade.
Named after the ancient supercontinent, Pangaea seeks to give astronauts as well as space engineers and geologists the skills needed for expeditions to other planets.
Trainees learn how to identify rock samples and collect them, do on-the-spot DNA analysis of microorganisms, and communicate their findings back to mission control.
"Here, they are put into the field to experience the exploration of a terrain, which is something they will have to do on the Moon," said Francesco Sauro, the technical director of the course.
- Six-year eruption -
Gerst said the Pangaea training course, which he has just completed, helps prepare astronauts to work in a remote setting on their own.
"If we run into a problem, we have to solve it ourselves," he said.
He completed the Pangaea training along with Stephanie Wilson, one of NASA's most senior astronauts. Both are possible candidates for NASA's next crewed Moon missions.
Named for the goddess who was Apollo's twin sister in ancient Greek mythology, NASA's Artemis programme aims to return astronauts to the Moon's surface as early as 2025, though many experts believe that time frame might slip.
Twelve astronauts walked on the Moon during six Apollo missions from 1969 to 1972, the only spaceflights yet to place humans on the lunar surface.
NASA and the ESA also regularly use Lanzarote's landscape of twisted mounds of solidified lava to test Mars Rovers -- remote controlled vehicles designed to travel on the surface of the Red Planet.
Lanzarote's unique geography stems from a volcanic eruption that began in 1730 and lasted six years, spewing ash and lava over large swathes of land.
Considered one of the greatest volcanic cataclysms in recorded history, the eruption devastated over 200 square kilometres (77 square miles) of terrain -- about a quarter of the island which is currently home to around 156,000 people.
- 'See far away' -
While there are other volcanic areas such as Hawaii that could also be used for astronaut training, Lanzarote has the advantage that it has little vegetation due to its desert-like climate.
"You have a lot of different types of volcanic rocks in Lanzarote. And they are exposed. You don't have trees," said Pangaea project leader Loredana Bessone.
"You can see far away, as if you were on the Moon," she told AFP.
The Canary Islands is making a big contribution to space exploration in another way too. The island of La Palma is home to one of the world's largest optical telescopes.
Located on a peak, the Great Canary Telescope is able to spot some of the faintest, most distant objects in the Universe.
La Palma was selected as the site for the telescope because of its cloud-free skies and relatively low light pollution.
O.Krause--BTB


