
-
 Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig

-
 Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
-
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says

-
 Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
-
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals

-
 Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
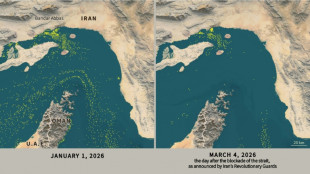 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs

-
 Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
-
Voices from Iran: protests, fear and scarcity

-
 Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
-
This is how Ukraine has countered Russia's Iran-designed drones

-
 Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
-
Sleepless Iranians count cost of war as damage mounts

-
 Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
-
Leading satellite firm to hold back Gulf state images

-
 Tuipulotu urges Scotland to stay in Six Nations title hunt against France
Tuipulotu urges Scotland to stay in Six Nations title hunt against France
-
Trump says only Iran's 'unconditional surrender' can end war

-
 US releases Epstein files with uncorroborated Trump allegations
US releases Epstein files with uncorroborated Trump allegations
-
Securing shipping lane from Mideast war 'challenging', say experts

-
 Italy have to start beating the best, says captain Lamaro
Italy have to start beating the best, says captain Lamaro
-
India's Bumrah only 'human' says Phillips ahead of T20 World Cup final

-
 Oil prices climb as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
Oil prices climb as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
-
US retail sales decline as consumer pullback deepens


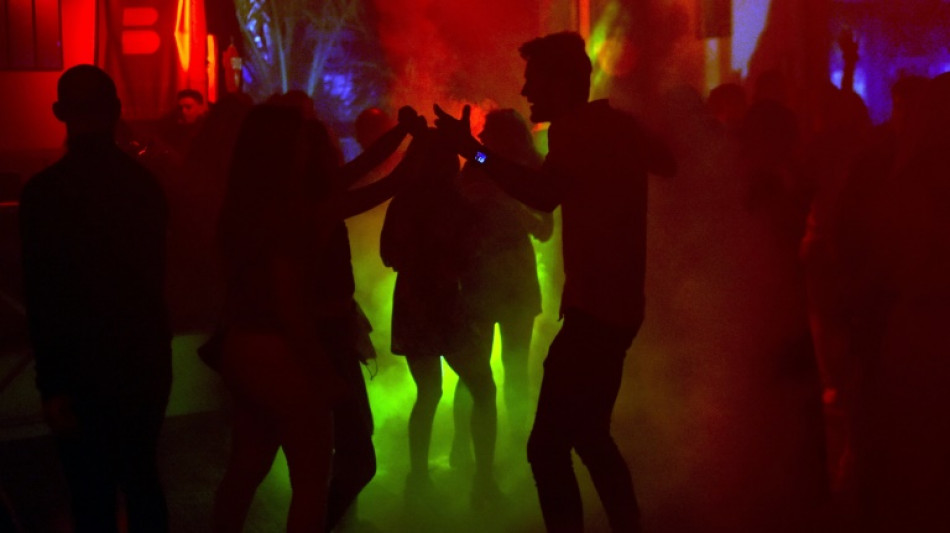
Science confirms: to light up the dance floor, turn up the bass
Electronic music lovers know the drill: as soon as the DJ turns up the bass, the crowd goes wild and dances with heightened enthusiasm. But to what extent is this a conscious reaction?
Researchers have taken a closer look at the relationship between bass frequencies and dancing, thanks to an experiment conducted during a real-life electronic music concert.
The results, published Monday in the journal Current Biology, showed that participants danced almost 12 percent more when researchers introduced a very low frequency bass -- one that dancers could not hear.
"They couldn't tell when those changes happened, but it was driving their movements," neuroscientist David Cameron of McMaster University, who led the study, told AFP.
The results confirm the special relationship between bass and dance, which has never been scientifically proven.
- The pulse of the music -
Cameron, a trained drummer, notes that people attending electronic music concerts "love when they can feel the bass so strong" and tend to turn it up very loud.
But they are not alone.
In many cultures and traditions across the world "it tends to be the low-frequency instruments like the bass guitar or the bass drum, that give the pulse of the music" that gets humans moving.
"What we didn't know is, can you actually make people dance more with bass?" said Cameron.
The experiment took place in Canada, in a building known as LIVElab, which served both as a concert hall and a research laboratory.
About 60 out of 130 people who went to see a concert by electronic music duo Orphyx were equipped with motion-sensing headbands to monitor their dance moves.
During the concert, researchers intermittently turned very-low bass-playing speakers on and off.
A questionnaire filled out by concert-goers confirmed that the sound was undetectable. This allowed researchers to isolate the impact of the bass and avoid other factors, such as dancers reacting to a popular part of a song.
- Below the level of consciousness -
"I was impressed with the effect," said Cameron.
His theory is that even when undetected, the bass stimulates sensory systems in the body, such as the skin and the vestibular system -- more commonly known as the inner ear.
These systems have a very close connection to the motor system -- responsible for movement -- but in an intuitive way that bypasses the frontal cortex.
He compares it to the way the body keeps the lungs breathing and the heart beating.
"It is below the level of consciousness."
Cameron said the research team believes the stimulation of these systems "give a little boost to your motor system. And that adds a little bit of energy and vigor to your real-world movements."
He hopes to verify this hypothesis in future experiments.
As for why humans dance at all, the mystery endures.
"I've always been interested in rhythm, and especially what it is about rhythm that makes us want to move," in the absence of a specific function of dance.
Most theories revolve around the idea of social cohesion.
"When you synchronize with people, you tend to feel bonded with them a little bit afterward. You feel good afterwards," said Cameron.
"By making music together, that allows us to feel better together as a group, and then we function better as a group, and we can be more efficient, and we can have more peace."
A.Gasser--BTB


