
-
 Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
-
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win

-
 Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs

-
 Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
-
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three

-
 Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
-
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily

-
 Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
-
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
-
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump

-
 Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
-
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level

-
 Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
-
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win

-
 Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
-
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola

-
 Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
-
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
-
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales

-
 Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
-
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January

-
 Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
-
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
-
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march

-
 Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
-
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony

-
 Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round

-
 NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
-
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row

-
 'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
-
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold

-
 Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening
-
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war

-
 Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports
-
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control

-
 Middle East war a new shock for financial markets
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets
-
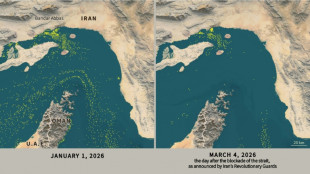
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
 Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup
-
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say

-
 Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up
-
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe

-
 Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
-
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland


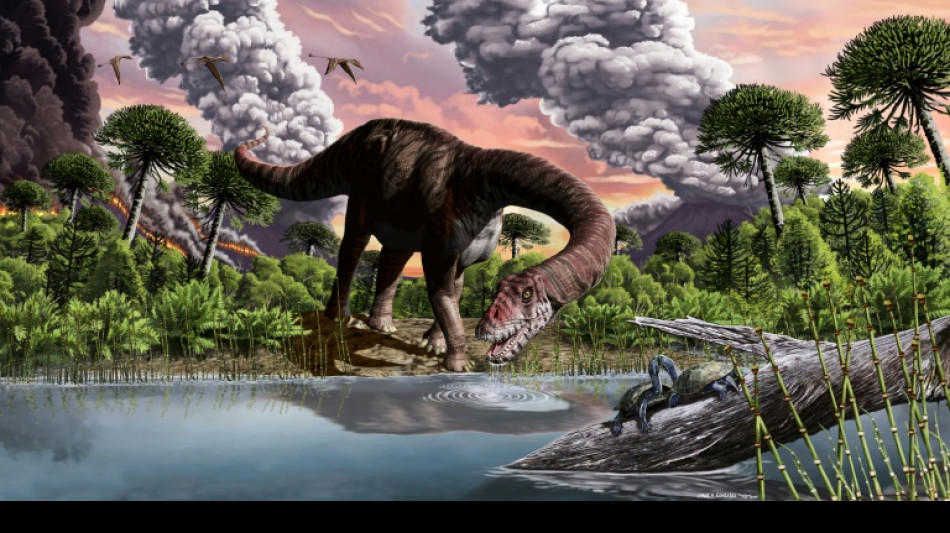
Faeces, vomit offer clues to how dinosaurs rose to rule Earth
Faeces, vomit and fossilised food from inside stomachs have provided new clues into how dinosaurs rose to dominate Earth, a new study revealed on Wednesday.
Scientists have discovered plenty about dinosaurs -- particularly about how they vanished off the face of the planet 66 millions years ago.
But "we know very little about their rise," Martin Qvarnstrom, a researcher at Sweden's Uppsala University and the study's lead author, told AFP.
Dinosaurs first appeared at least 230 million years ago, fossils have shown.
But they would not become the world's dominant animal until the start of the Jurassic Period some 30 million years later.
What caused this ascension -- and why it took so long -- have long been a subject of fevered debate between scientists.
For the new study in Nature, a European team exhaustively probed more than 500 "bromalites" -- the fossilised remains of dinosaur faeces, vomit and undigested food inside intestines -- from sites in Poland.
"By linking the bromalites to the producers and identifying what's in them, we can start connecting who ate whom or who ate what," Qvarnstrom explained.
The researchers used new technology such as synchrotron microtomography to build a 3D image of the samples.
This revealed that the excrement contained the remains of insects, plants, fish and bigger animals.
The researchers compared this with data about fossils, plants and the climate to construct a model for the step-by-step rise of the dinosaurs.
- 'Opportunistic animal' -
This ascension was illustrated by the bromalites themselves, which tripled in average length and width over the 30 million-year period.
This demonstrated how the animals that digested, vomited or excreted these remains tripled in size over that time.
Some of the fossilised remains belonged to an early ancestor of dinosaurs, the Silesaurus.
Far from the mighty T-Rex, the "pretty small" Silesaurus weighed around 15 kilograms at most, Qvarnstrom said.
The dominant animal at the time were barrel-chested herbivorous reptiles called Dicynodonts, which weighed a few tons.
But Silesaurus had a big advantage over its stocky rival -- it was omnivorous.
"What we see from its droppings is that it was eating a lot of insects, fish and plants," Qvarnstrom said.
This meant the "opportunistic animal" was better at adapting to sudden changes in the environment.
For example, a massively rainy period called the Carnian Pluvial Episode lead to the evolution of many new plants.
The big herbivorous reptiles struggled to adapt to this new diet.
But the Silesaurus -- and later long-necked dinosaurs that were ancestors of the Diplodocus -- "were able to just feast on all these new plants", Qvarnstrom said.
As the smaller dinosaurs grew bigger from this new grub, so did larger carnivores that fed on them.
By the time the Jurassic period rolled around, the landscape was dominated by giant plant-eating dinosaurs and ferocious carnivores.
- Two competing theories -
The study will not settle the debate about what led to the rule of dinosaurs once and for all.
There are two main theories for their rise. One is that early dinosaurs used key physiological advantages -- such as standing upright -- to outcompete their rivals.
The other is that environmental upheaval, such as volcanic eruptions or a changing climate, killed off many of the previously dominant animals, creating an opening at the top.
The researchers behind the bromalites study suggested it was a combination of the two theories, in which the dinosaurs used their evolutionary advantages to capitalise on environmental changes that had knocked back their rivals.
Lawrence Tanner, a researcher at Le Moyne College in New York, said the study "should be seen as a starting point for further work".
Although its methodology is "particularly creative", the study is "limited in its context and scope", Tanner commented in an attached Nature paper.
The research only covers the Polish Basin region, which at the time was part of the north of the Pangea supercontinent, he observed.
Qvarnstrom agreed, saying that he thought it would be "really cool" to use the model the team developed on other regions -- such as the south of Pangea, where the first dinosaurs appeared.
H.Weber--VB


