
-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
-
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate

-
 Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
-
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
-
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16


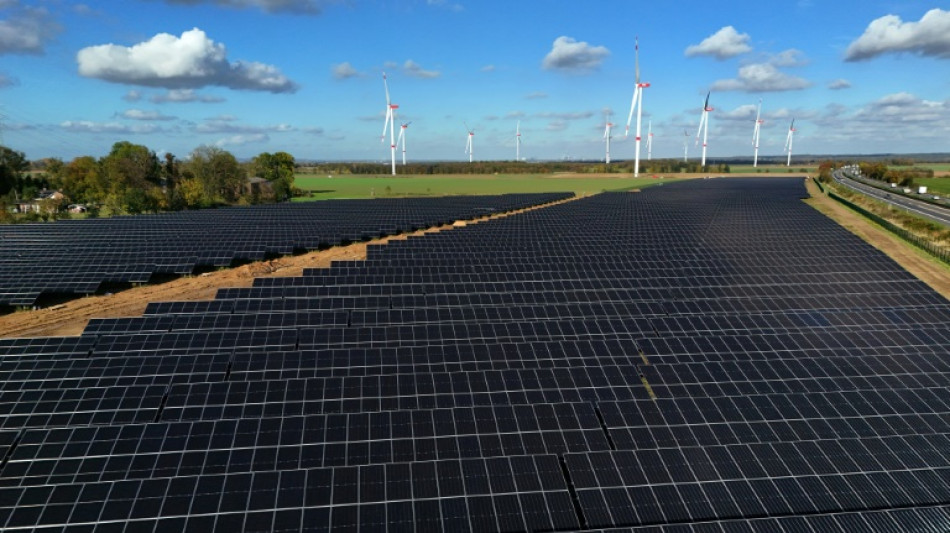
Solar power surpasses coal in EU for first time
Solar overtook coal in the European Union's electricity production in 2024, with the share of renewables rising to almost half the bloc's power sector, according to a report released Thursday.
Gas generation, meanwhile, declined for the fifth year in a row and fossil-fuelled power dipped to a "historic low", climate think tank Ember said in its European Electricity Review 2025.
"The European Green Deal has delivered a deep and rapid transformation of the EU power sector," the think tank said.
"Solar remained the EU's fastest-growing power source in 2024, rising above coal for the first time. Wind power remained the EU's second-largest power source, above gas and below nuclear."
Overall, strong growth in solar and wind have boosted the share of renewables to 47 percent, up from 34 percent in 2019.
Fossil fuels have fallen from 39 to 29 percent.
"A surge in wind and solar generation is the main reason for declining fossil generation. Without wind and solar capacity added since 2019, the EU would have imported 92 billion cubic metres more of fossil gas and 55 million tonnes more of hard coal, costing €59 billion," the report said.
According to Ember, these trends are widespread across Europe, with solar power progressing in all EU countries.
More than half have now either eliminated coal, the most polluting fossil fuel, or reduced its share to less than five percent of their energy mix.
"Fossil fuels are losing their grip on EU energy," said Chris Rosslowe, lead author of the report.
"At the start of the European Green Deal in 2019, few thought the EU's energy transition would be where it is today: wind and solar are relegating coal to the margins and pushing gas into decline."
- Battery storage -
But Rosslowe cautioned much work remains.
"We need to accelerate our efforts, particularly in the wind power sector," he said.
Europe's electricity system will also need to increase its storage capacity to make the most of renewable energies, which are by definition intermittent, he added.
In 2024, plentiful solar energy helped drive down prices in the middle of the day, sometimes even resulting in "negative or zero price hours" due to an overabundance of supply compared to demand.
"A readily available solution is a battery co-located with a solar plant. This gives solar power producers more control over the prices they receive and helps them avoid selling for low prices in the middle of the day," the report said.
The think tank suggested consumers could reduce their bills by shifting usage to periods of abundance (smart electrification), while battery operators could earn revenue from buying power when prices are low and selling it back when demand peaks.
Batteries have advanced significantly in recent years, with installed capacity across the EU doubling to 16 GW in 2023, compared with 8 GW in 2022, according to Ember.
But this capacity is concentrated in just a small number of countries: 70 percent of existing batteries were located in Germany and Italy at the end of 2023.
"More storage and demand flexibility is needed to sustain growth and for consumers to reap the full benefits of abundant solar," Ember said.
"After a challenging few years for the wind power sector, additions are set to grow, but not by enough to hit EU targets. Closing this gap will require continued policy implementation and political support, such that the rate of additions between now and 2030 is more than double that of recent years."
G.Haefliger--VB




