
-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
-
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate

-
 Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
-
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
-
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16


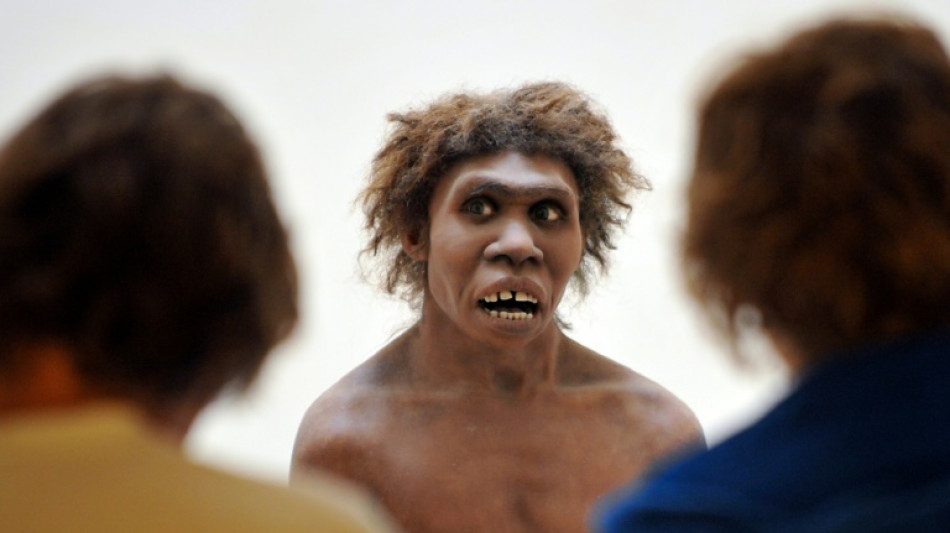
Homo erectus, not sapiens, first humans to survive desert: study
Our ancestor Homo erectus was able to survive punishingly hot and dry desert more than a million years ago, according to a new study that casts doubt on the idea that Homo sapiens were the first humans capable of living in such hostile terrain.
The moment when the first members of the extended human family called hominins adapted to life in desert or tropical forests marks "a turning point in the history of human survival and expansion in extreme environments," lead study author Julio Mercader Florin of the University of Calgary told AFP.
Scientists have long thought that only Homo sapiens, who first appeared around 300,000 years ago, were capable of living sustainably in such inhospitable regions.
The first hominins to have split off from the other great apes were believed to be limited to less hostile ecosystems, such as forest, grasslands and wetlands.
One of the world's most important prehistoric sites, Olduvai Gorge in modern-day Tanzania, was thought to home to those easier types of landscapes.
But this steep ravine in East Africa's Great Rift Valley, which has played a key role in the understanding of human evolution, was actually a desert steppe, according to the study published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment on Thursday.
After collecting archaeological, geological and palaeoclimatic data, the international team of researchers were able to reconstruct the gorge's ecosystem over the years.
Fossilised pollen of the Ephedra shrub -- which commonly lives in arid areas -- as well as traces of past wildfires and signs in the soil show there was an extreme drought in the area between one and 1.2 million years ago.
- Homo erectus: underestimated? -
Evidence collected from the Engaji Nanyori site in the gorge suggests that Homo erectus adapted to this hostile environment "by focusing on ecological focal points such as river confluences where water and food resources were more predictable", Mercader Florin said.
"Their ability to repeatedly exploit these focal points... and adapt their behaviours to extreme environments demonstrates a higher level of resilience and strategic planning than previously assumed."
Specialised tools found at the site, such as hand axes, scrapers and cleavers, showed that Homo erectus had also worked out how to process animal carcasses.
The bones of animals such as cows, hippopotamuses, crocodiles and antelopes also had cut marks, indicating they had been skinned and had their bone marrow extracted.
"This suggests they optimised their resource use to adapt to the challenges of arid environments, where resources were scarce and needed to be exploited fully," Mercader Florin said.
"Our findings show that Homo erectus was capable of surviving long term in extreme environments characterised by low density of food resources, navigational challenges, very low/very high plant life, temperature/humidity extremes, and the need for high mobility," he added.
"This adaptability expands Homo erectus's potential range into the Saharo-Sindian region across Africa and into similar environments in Asia."
T.Zimmermann--VB




