
-
 France's ex-president Sarkozy to be jailed over Libya funding conviction
France's ex-president Sarkozy to be jailed over Libya funding conviction
-
Blue Jays sink Mariners to reach World Series

-
 France intensifies hunt for Louvre raiders
France intensifies hunt for Louvre raiders
-
EU takes aim at plastic pellets to prevent their nightmare cleanup

-
 Equities rally on China-US hopes, new Japanese PM lifts Tokyo
Equities rally on China-US hopes, new Japanese PM lifts Tokyo
-
'Dream come true' for US pianist Eric Lu after Chopin competition win

-
 Nepal's 'hidden' mountains draw new wave of climbers
Nepal's 'hidden' mountains draw new wave of climbers
-
Climate change, population growth threats as malaria fight stalls

-
 EU timber imports linked to deforestation on Indonesia's Borneo: NGOs
EU timber imports linked to deforestation on Indonesia's Borneo: NGOs
-
Canada crime bill and rap group fracas spark free-speech debate

-
 Peru's Gen Z lead movement against crime, political paralysis
Peru's Gen Z lead movement against crime, political paralysis
-
Migrants brace for hostile climate after Chile's election

-
 Trump demolishes part of White House for new ballroom
Trump demolishes part of White House for new ballroom
-
Nuno admits Hammers 'have a problem' after Brentford defeat

-
 Maccabi Tel Aviv to decline tickets for European tie at Aston Villa
Maccabi Tel Aviv to decline tickets for European tie at Aston Villa
-
US, Australia sign rare earths deal as Trump promises submarines

-
 Former Bucs running back Martin died in custody: police
Former Bucs running back Martin died in custody: police
-
US confirms Mexico, Costa Rica, Jamaica as co-hosts for 2031 Women's World Cup bid

-
 Mourinho expects more Newcastle silverware after League Cup triumph
Mourinho expects more Newcastle silverware after League Cup triumph
-
Crisis-hit Argentina inks $20 bn rescue with US
-
 US appeals court says Trump can deploy soldiers in Portland
US appeals court says Trump can deploy soldiers in Portland
-
Colombia awaits ruling on ex-president Uribe's house arrest

-
 Disgraced Andrew may face more legal woes: UK biographer
Disgraced Andrew may face more legal woes: UK biographer
-
Dembele, Marquinhos return for PSG's trip to Leverkusen

-
 Bolivia's president-elect says will resume ties with US after nearly two decades
Bolivia's president-elect says will resume ties with US after nearly two decades
-
Shaheen Afridi appointed Pakistan ODI captain for South Africa series

-
 Howe looking forward to facing 'incredible' Mourinho in Champions League
Howe looking forward to facing 'incredible' Mourinho in Champions League
-
Athapaththu conjures miracle as Sri Lanka snatch victory over Bangladesh

-
 Trump to Australian ambassador: 'I don't like you either'
Trump to Australian ambassador: 'I don't like you either'
-
Servers, software and data: how the cloud powers the web

-
 Trump says Australia will get submarines as PM visits
Trump says Australia will get submarines as PM visits
-
Athletes swap skis for skates in a glimpse of winter sport's future

-
 Brazil greenlights oil drilling in sensitive Amazon region
Brazil greenlights oil drilling in sensitive Amazon region
-
Struggling Rangers appoint Rohl as new manager

-
 Louvre heist: five things to know about missing jewellery
Louvre heist: five things to know about missing jewellery
-
Stock markets climb as China-US trade fears ease

-
 Colombia recalls ambassador to US as Trump-Petro feud intensifies
Colombia recalls ambassador to US as Trump-Petro feud intensifies
-
UK lawmakers urge govt to strip Prince Andrew of his titles

-
 US begins sending nuke workers home as shutdown drags
US begins sending nuke workers home as shutdown drags
-
Dembele returns for PSG after six weeks out

-
 Pope Leo holds first meeting with abuse survivors' group
Pope Leo holds first meeting with abuse survivors' group
-
'I probably have to change my behaviour', Flick says after red card

-
 Three things we learned from the United States Grand Prix
Three things we learned from the United States Grand Prix
-
To beat football violence, Brazilian clubs scan every fan

-
 South Africa call up uncapped prop Porthen for November tour
South Africa call up uncapped prop Porthen for November tour
-
Ireland wing Hansen out of All Blacks Test

-
 Shares in French bank BNP Paribas plummet after US verdict
Shares in French bank BNP Paribas plummet after US verdict
-
Internet services cut for hours by Amazon cloud outage

-
 Pakistan punish sloppy South Africa to reach 259-5 in second Test
Pakistan punish sloppy South Africa to reach 259-5 in second Test
-
Tourists upset as Louvre stays shut after jewel heist


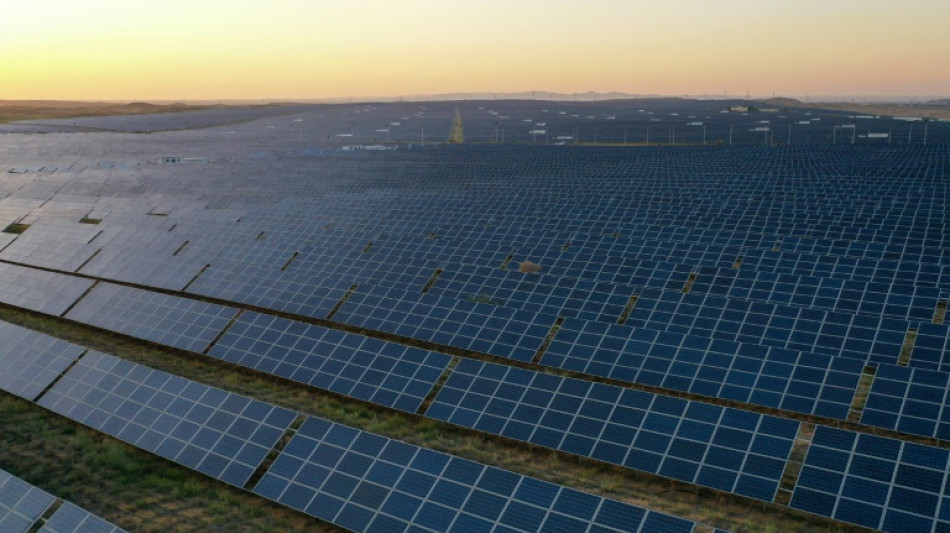
China's power paradox: record renewables, continued coal
Call it the China power paradox: while Beijing leads the world in renewable energy expansion, its coal projects are booming too.
As the top emitter of greenhouse gases, China will largely determine whether the world avoids the worst effects of climate change.
On the one hand, the picture looks positive. Gleaming solar farms now sprawl across Chinese deserts; China installed more renewables last year than all existing US capacity; and President Xi Jinping has made the country's first emissions reduction pledges.
Yet in the first half of this year, coal power capacity also grew, with new or revived proposals hitting a decade high.
China accounted for 93 percent of new global coal construction in 2024, the Centre for Research on Energy and Clear Air (CREA) found.
One reason is China's "build before breaking" approach, said Muyi Yang, senior energy analyst at think tank Ember.
Officials are wary of abandoning the old system before renewables are considered fully operational, Yang said.
"Think of it like a child learning to walk," he told AFP.
"There will be stumbles -- like supply interruptions, price spikes -- and if you don't manage those, you risk undermining public support."
Policymakers remain scarred by 2021–22 power shortages tied to pricing, demand, grid issues and extreme weather.
While grid reform and storage would prevent a repeat, officials are hedging with new coal capacity, even if it sits idle, experts said.
"There's the basic bureaucratic impulse to make sure that you don't get blamed," said Lauri Myllyvirta, CREA co-founder and lead analyst.
"They want to make absolutely sure that they don't block one possible solution."
- Grid and transmission -
There's also an economic rationale, said David Fishman, a China power expert at Lantau Group, a consultancy.
China's electricity demand has increased faster than even record-breaking renewable installations.
That may have shifted in 2025, when renewables finally met demand growth in the first half of the year. But slower demand played a role, and many firms see coal remaining profitable.
Grid and transmission issues also make coal attractive.
Large-scale renewables are often in energy-rich, sparsely populated regions far from consumers.
Sending that power over long distances raises the cost and "incentivises build-out of local energy capacity," Fishman told AFP.
China is improving its infrastructure for long-distance power trading, "but it's definitely not where it needs to be", he added.
Coal also benefits from being a "dispatchable resource" -- easily ramped up or down -- unlike solar and wind, which depend on weather.
To increase renewables, "you have to make the coal plants operate more flexibly... and make space for variable renewables," Myllyvirta said.
China's grid remains "very rigid", and coal-fired power plants are "the beneficiaries", he added.
- 'Instrumental' economic driver -
Other challenges loom. The end of feed-in tariffs means new renewable projects must compete on the open market.
Fishman argues that "green power demand is insufficient to keep capacity expansion high", though the government has policy levers to tip the balance, including requiring companies to use more renewables.
China wants 3,600 gigawatts of wind and solar by 2035, but that may not meet future demand, risking further coal increases.
Still, coal additions do not always equal coal emissions -- China's fleet currently runs at only 50 percent capacity.
And the "clean energy" sector -- including solar, wind, nuclear, hydropower, storage and EVs -- is a major economic driver.
CREA estimates it contributed a record 10 percent to China's gross domestic product last year, and drove a quarter of growth.
"It has become completely instrumental to meeting economic targets," said Myllyvirta.
"That's the main reason I'm cautiously optimistic in spite of these challenges."
P.Staeheli--VB




