
-
 Fear in Sicilian town as vast landslide risks widening
Fear in Sicilian town as vast landslide risks widening
-
'Forced disappearance' probe opened against Colombian cycling star Herrera

-
 Seifert, Santner give New Zealand consolation T20 win over India
Seifert, Santner give New Zealand consolation T20 win over India
-
King Charles III warns world 'going backwards' in climate fight

-
 Minneapolis activists track Trump's immigration enforcers
Minneapolis activists track Trump's immigration enforcers
-
Court orders Dutch to protect Caribbean island from climate change

-
 Sterling agrees Chelsea exit after troubled spell
Sterling agrees Chelsea exit after troubled spell
-
Rules-based trade with US is 'over': Canada central bank head

-
 Lucas Paqueta signs for Flamengo in record South American deal
Lucas Paqueta signs for Flamengo in record South American deal
-
Holocaust survivor urges German MPs to tackle resurgent antisemitism

-
 'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
-
Villa's Tielemans ruled out for up to 10 weeks

-
 Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
-
UK proposes to let websites refuse Google AI search

-
 'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
-
Trump issues fierce warning to Minneapolis mayor over immigration
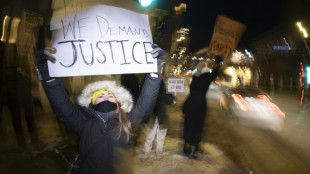
-
 Anglican church's first female leader confirmed at London service
Anglican church's first female leader confirmed at London service
-
Germany cuts growth forecast as recovery slower than hoped

-
 Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
-
One dead, five injured in clashes between Colombia football fans

-
 Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
-
US YouTuber IShowSpeed gains Ghanaian nationality at end of Africa tour

-
 Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools
Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools
-
Turkey football club faces probe over braids clip backing Syrian Kurds

-
 Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
-
US embassy angers Danish veterans by removing flags

-
 Netherlands 'insufficiently' protects Caribbean island from climate change: court
Netherlands 'insufficiently' protects Caribbean island from climate change: court
-
Fury confirms April comeback fight against Makhmudov

-
 Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards
Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards
-
Trump says 'time running out' as Iran rejects talks amid 'threats'

-
 Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days
Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days
-
Greenland dispute 'strategic wake-up call for all of Europe,' says Macron

-
 'Intimidation and coercion': Iran pressuring families of killed protesters
'Intimidation and coercion': Iran pressuring families of killed protesters
-
Europe urged to 'step up' on defence as Trump upends ties

-
 Sinner hails 'inspiration' Djokovic ahead of Australian Open blockbuster
Sinner hails 'inspiration' Djokovic ahead of Australian Open blockbuster
-
Dollar rebounds while gold climbs again before Fed update

-
 Aki a doubt for Ireland's Six Nations opener over disciplinary issue
Aki a doubt for Ireland's Six Nations opener over disciplinary issue
-
West Ham sign Fulham winger Traore

-
 Relentless Sinner sets up Australian Open blockbuster with Djokovic
Relentless Sinner sets up Australian Open blockbuster with Djokovic
-
Israel prepares to bury last Gaza hostage

-
 Iran rejects talks with US amid military 'threats'
Iran rejects talks with US amid military 'threats'
-
Heart attack ends iconic French prop Atonio's career

-
 SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025
SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025
-
Greenland's elite dogsled unit patrols desolate, icy Arctic

-
 Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, cuts jobs
Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, cuts jobs
-
Musetti rues 'really painful' retirement after schooling Djokovic

-
 Russian volcano puts on display in latest eruption
Russian volcano puts on display in latest eruption
-
Thailand uses contraceptive vaccine to limit wild elephant births

-
 Djokovic gets lucky to join Pegula, Rybakina in Melbourne semi-finals
Djokovic gets lucky to join Pegula, Rybakina in Melbourne semi-finals
-
Trump says to 'de-escalate' Minneapolis, as aide questions agents' 'protocol'

| CMSC | -0.72% | 23.631 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 0% | 82.4 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.69% | 16.7 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.32% | 84.58 | $ | |
| AZN | -2.12% | 93.615 | $ | |
| RIO | 0.32% | 93.21 | $ | |
| BTI | -1.06% | 59.705 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| BP | 0.07% | 37.645 | $ | |
| VOD | 0.31% | 14.545 | $ | |
| GSK | -1.9% | 49.855 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.91% | 80.205 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.07% | 24.08 | $ | |
| JRI | -5.35% | 12.985 | $ | |
| RELX | -2.72% | 37.345 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.89% | 25.295 | $ |

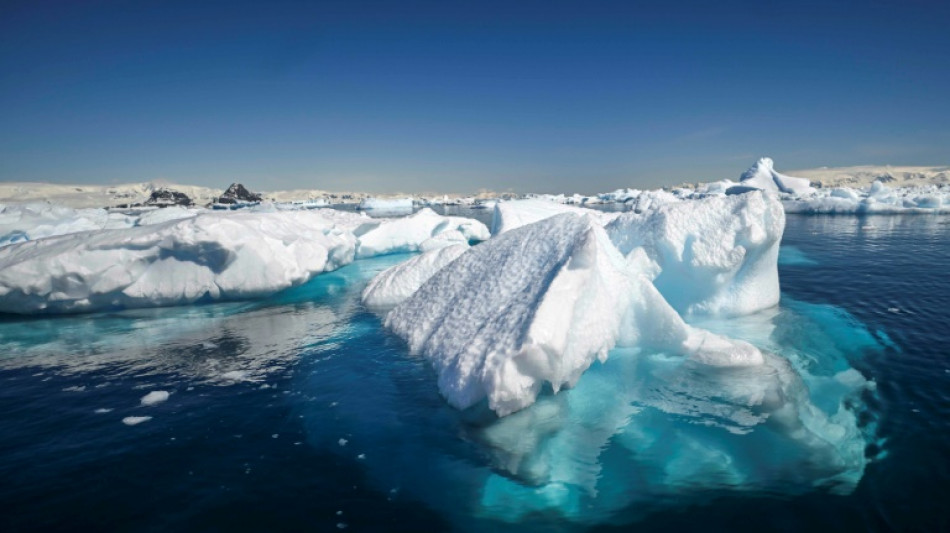
Melting ice could slow vital Antarctic ocean current: study
The world's strongest ocean current could slow as melting Antarctic ice sheets flood it with fresh water, according to research published on Monday that warned of "severe" climate consequences.
Scientists used one of Australia's most powerful supercomputers to model how melting ice sheets might change the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, which plays a major role in global climate patterns.
If fossil fuel emissions increased over the next 25 years -- a so-called high emissions scenario -- the current could slow by around 20 percent, the peer-reviewed research found.
"The ocean is extremely complex and finely balanced," said University of Melbourne scientist Bishakhdatta Gayen.
"If this current 'engine' breaks down, there could be severe consequences, including more climate variability -- with greater extremes in certain regions, and accelerated global warming due to a reduction in the ocean's capacity to act as a carbon sink."
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current acted as a kind of "ocean conveyor belt" shifting immense columns of water through the Indian, Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, Gayen said.
Melting ice sheets would "dump vast quantities of fresh water" into the current, the modelling found.
This would change the ocean's salt content, making it harder for cold water to circulate between the surface and the depths.
Oceans play vital roles as climate regulators and carbon sinks.
Cooler waters can absorb greater amounts of heat from the atmosphere.
The strength of the current -- which flows clockwise around Antarctica -- also acts as a barrier that stops invasive species washing up on the continent's shores.
Algae and molluscs could more easily colonise Antarctica if the current slowed down, the researchers wrote.
Even if global warming was limited to a threshold of 1.5 degrees Celsius, the Antarctic current could still slow down.
"The 2015 Paris Agreement aimed to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels," said climate scientist and co-author Taimoor Sohail.
"Many scientists agree that we have already reached this 1.5 degree target, and it is likely to get hotter, with flow-on impacts on Antarctic ice melting."
The research team, which included scientists from Australia, India and Norway, noted that their findings contrasted with previous studies that observed the current speeding up.
They said further observation and modelling was needed to understand how the "poorly observed region" was responding to climate change.
The research was published in the Environmental Research Letters journal.
A.Ruegg--VB

