
-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
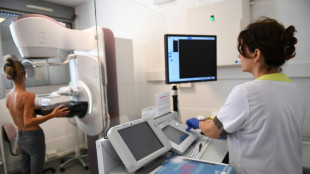
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack

-
 If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
-
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial

-
 Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
-
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown

-
 Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
-
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation

-
 Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week
-
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown

-
 Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years
-
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study

-
 Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year
-
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks


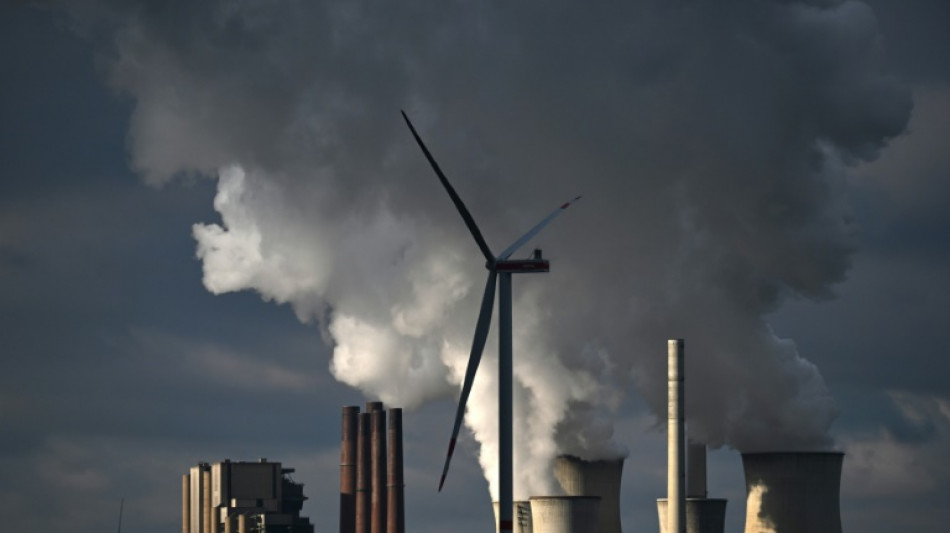
Coal use hits record in 2023, Earth's hottest year
Global consumption of coal reached an all-time high in 2023, the IEA energy watchdog said Friday, as Earth experienced its hottest recorded year.
The International Energy Agency reported that nations would burn even more coal this year than in 2022, the previous record for consumption of the key source of planet-warming gases.
Scientists say greenhouse gases will need to be cut almost in half this decade to meet the world's targets of limiting global heating and avoiding catastrophic impacts on the Earth's climate.
The EU's Copernicus Climate Change Service said earlier in December that 2023 will be the hottest on record after November became the sixth record-breaking month in a row.
The IEA said, nevertheless, that after peaking this year, worldwide coal consumption was expected to start declining in 2024, as renewable power generation from solar and wind continues to expand.
Its latest forecasts were published two days after the conclusion of the United Nations climate negotiations (COP28) in Dubai -– where nearly 200 countries reached a deal that the world should be "transitioning away from fossil fuels" to limit global warming.
It was the first time in the 28-year history of the annual climate negotiations that all fossil fuels were mentioned in an accord.
The disruption in the Earth's climate has contributed to an increase in the intensity and frequency of storms, droughts and lethal wildfires around the world.
- Asia powering coal use -
The IEA said consumption of coal, the dirtiest fossil fuel, rose by 1.4 percent in 2023 to a record 8.5 billion tonnes, as increases in China, India and Indonesia outweighed sharply falling demand in Europe and the United States, the IEA said.
"We expect to see a trend emerging of declining worldwide coal demand, starting in 2024," the Paris-based energy watchdog said, as renewable power generation from solar and wind continues to expand.
The appetite for coal is strongest in Asia, it said. Consumption in China alone grew by 220 million tonnes or 4.9 percent in 2023, while in India it grew eight percent and in Indonesia by 11 percent.
Elsewhere, coal use fell 23 percent or by 107 million tonnes in Europe, while in the United States it dropped 95 million tonnes or by 21 percent, largely due to weakening industrial activity and an ongoing shift away from coal-fired generation towards renewables.
The IEA said it was difficult to forecast demand in Russia, currently the fourth-largest coal consumer, because of the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, and forecasts for Ukraine were equally uncertain.
While the IEA predicted a decline in coal in power stations, it said its use in heavy industries like cement production was expected to continue at high levels.
Paradoxically, the high demand for coal in Indonesia's mining sector stems from its booming industry in extracting and refining nickel for use in electric car batteries.
China remains the world's largest user of coal, responsible for half (54 percent) of all coal burned worldwide.
- Europe champions renewables -
More than 60 percent of coal burned in China is used to generate electricity and the country continues to build coal-fired power stations.
This year alone, the country has approved new projects totalling 52 gigawatts of new electricity-generating capacity.
The IEA nevertheless expects coal consumption in China to start declining, unless heatwaves and very cold spells lead to higher demand on its power plants.
Burning coal to generate electricity would decline in China to 2.8 billion tonnes, a drop of 175 million, over the period 2024-26.
In its place, the main demand for coal would come from India, at least as far as 2026, the IEA said.
In the European Union, an expansion of renewable energies, which generate very little greenhouse gas emissions, is curbing demand for coal.
In Germany, the use of ignite- and coal-powered power stations is expected to tail off significantly by 2025, the watchdog forecast, as solar and wind farms come on stream.
R.Fischer--VB



