
-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
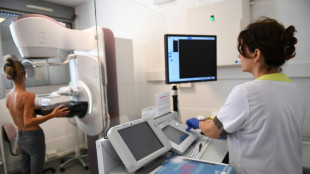
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack

-
 If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
-
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial

-
 Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
-
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown

-
 Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
-
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation

-
 Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week
-
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown

-
 Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years
-
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study


Building blocks? Cutting pollution from steel, concrete and aluminium
They hold modern life together in everything from airplane parts to apartment blocks, but steel, concrete and aluminium come with a hefty climate cost that the world could be paying for decades.
Heavily reliant on fossil fuels, they account for a significant chunk of greenhouse gas emissions -- pollution that is particularly hard to cut fast enough to meet global warming goals.
The three sectors say they aim to slash -- or even eliminate -- their CO2 emissions by 2050, despite growing demand in a rapidly urbanising world.
To do that will require a buildings "revolution", according to the United Nations, while the International Energy Agency wants greater recycling, cleaner energy and technological innovation.
- Cement and concrete -
"Concrete is the second most used substance on Earth after water, and vital for much of our modern infrastructure," said some of the industry’s biggest players including Cemex, Heidelberg and Holcim, Tuesday.
With demand expected to rise 50 percent by 2050, tackling the industry's emissions is becoming increasingly "urgent", they said.
Limestone and clay must be heated to 1,450 degrees Celsius to produce the rock-like residue known as "clinker" in cement. The fuel necessary to create such heat and the ensuing chemical reaction both produce CO2.
Switching to clinker substitutes, energy efficiency improvements, changing building design to cut down on the need for concrete, and using clean energy sources could substantially reduce emissions from the industry.
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology is also predicted to have a key role.
But observers fear that a planned reliance on solutions that are unproven at the scales required could distract from rapidly moving away from fossil fuels.
The Global Cement and Concrete Association said it expects the technology to account for 36 percent of the industry's global CO2 reductions by 2050.
- Steel -
Highly polluting coal makes up some 75 percent of the raw material and energy used by the steel and iron industry, according to the IEA.
The industry says it plans to replace coal-dependent blast furnaces with natural gas -- until that energy source can be swapped for "green hydrogen", produced by splitting water molecules using renewable electricity.
Green hydrogen paves the way for a gradual shutdown of polluting blast furnaces that could be replaced by the "direct reduction" of iron ore.
Steel firms are also betting on recycling scrap metals.
Europe is at the forefront of the green advances. The German industrial giant Thyssenkrupp -- singlehandedly responsible for 2.5 percent of the country's CO2 emissions -- plans to transform its historic plant in Duisburg to green steel.
But the scale of investment and rising energy prices have hampered the project.
The world's second-largest steelmaker, ArcelorMittal, acquired 80 percent of a Texas factory capable of producing steel without coal in 2022, and it is currently testing a pilot CCS system in Dunkirk, France.
Because of these difficulties, the IEA recognises that iron and steel manufacturing will remain "one of the last sectors in the Net Zero pathway that will still be using coal in 2050".
But it calls for carbon capture and hydrogen production to be "perfected and developed at scale" in the meantime.
- Aluminium -
Aluminium is a key for allowing for lighter cars and planes and in energy transition due to its ability to conduct electricity.
But it is also responsible for some of the highest emissions. One tonne of aluminium generates between five and 25 tonnes of CO2, depending on its source of electricity, according to Mineralinfo, a resource portal run by the French government.
Emissions depend above all on the type of fuel used -- often coal or heavy fuel oil -- to produce the vast quantities of energy necessary to make the metal.
The industry is hoping that recycling, CO2 capture, and emerging technology will bring down its emissions.
R.Fischer--VB



