
-
 Silent Italy to remain 'humble' after historic England win
Silent Italy to remain 'humble' after historic England win
-
South Korea's Lee wins on LPGA Tour for first time since 2017

-
 Wolfsburg fire coach Bauer with relegation looming
Wolfsburg fire coach Bauer with relegation looming
-
Bangladesh rations fuel as Mideast war deepens energy crunch

-
 Iran players salute and sing national anthem at Women's Asian Cup
Iran players salute and sing national anthem at Women's Asian Cup
-
New hunt for flight MH370 ends with no clues to 12-year mystery

-
 Kuwait airport, Bahrain desalination unit struck as Iran presses Gulf attacks
Kuwait airport, Bahrain desalination unit struck as Iran presses Gulf attacks
-
F1 world champion Norris fears 'long, tough season'

-
 Russell takes pop at rival Norris over 'worst F1 cars' claim
Russell takes pop at rival Norris over 'worst F1 cars' claim
-
'Whole country will stop' as India dreams of home World Cup glory

-
 Leclerc 'positively surprised' by Ferrari but says more work needed
Leclerc 'positively surprised' by Ferrari but says more work needed
-
Djokovic says Alcaraz equipped to extend winning streak

-
 Russell warns that Mercedes must raise game despite Australia 1-2
Russell warns that Mercedes must raise game despite Australia 1-2
-
China FM urges US to manage differences in face of trade woes

-
 Piastri takes blame for crashing out before home Australian Grand Prix
Piastri takes blame for crashing out before home Australian Grand Prix
-
Turkey's jailed mayor says demand for change cannot be stopped

-
 Venezuela frees more political prisoners under amnesty law
Venezuela frees more political prisoners under amnesty law
-
Dominant Russell wins Australian Grand Prix in Mercedes 1-2

-
 Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round, Djokovic fights through
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round, Djokovic fights through
-
Iran says can fight for months as Israel strikes Beirut hotel

-
 Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
-
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic

-
 Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise
-
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users

-
 Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record
-
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide

-
 White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje
-
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs

-
 Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up
-
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent

-
 Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries
-
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent

-
 German state election a test for Chancellor Merz
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz
-
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon

-
 'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
-
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?

-
 Kuwait airport, Saudi Arabia targeted as Iran presses Gulf attacks
Kuwait airport, Saudi Arabia targeted as Iran presses Gulf attacks
-
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener

-
 Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup
-
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer

-
 Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops
-
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United

-
 Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran
-
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad

-
 Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1
-
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more

-
 Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao
-
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare

-
 Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways


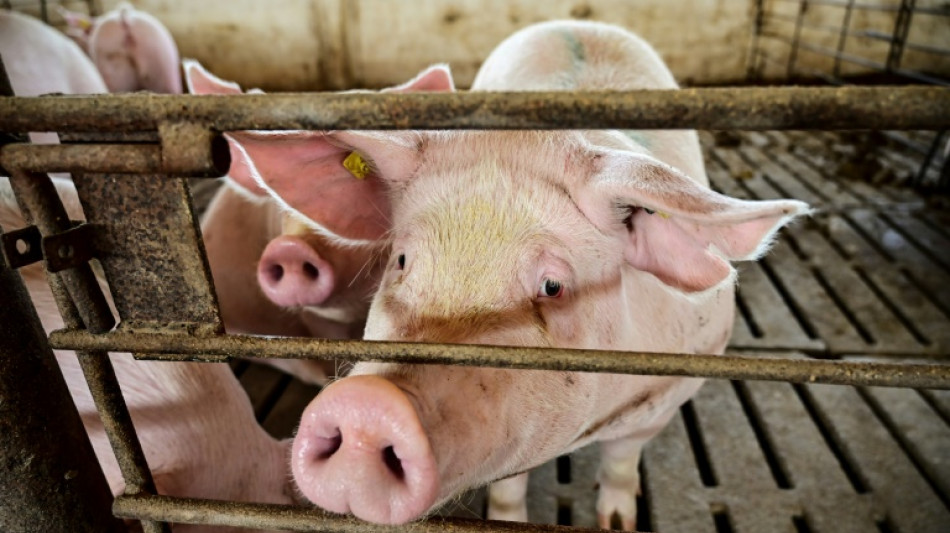
Scientists grow human-like kidneys in pigs
Chinese scientists have succeeded in growing kidneys containing human cells in pig embryos, a world first that could one day help address organ donation shortages.
But the finding, published in a study in the journal Cell Stem Cell on Thursday, raises ethical issues -- especially since some human cells were also found in the pigs' brains, experts said.
The researchers from the Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health focused on kidneys because they are on the first organs to develop, and the most commonly transplanted in human medicine.
"Rat organs have been produced in mice, and mouse organs have been produced in rats, but previous attempts to grow human organs in pigs have not succeeded," senior author Liangxue Lai said in a statement.
"Our approach improves the integration of human cells into recipient tissues and allows us to grow human organs in pigs."
This is a different approach to the recent high-profile breakthroughs in the United States, where genetically modified pig kidneys and even a heart have been placed inside humans.
The new paper "describes pioneering steps in a new approach to organ bioengineering using pigs as incubators for growing and cultivating human organs," said Dusko Ilic, a professor of stem cell sciences at King's College London who was not involved in the research.
Ilic cautioned there would be many challenges to turning the experiment into a viable solution, but "nevertheless, this captivating strategy warrants further exploration."
- Gene editing -
A major challenge in creating such hybrids has been that pig cells outcompete human cells.
To overcome the obstacles, the team used CRISPR gene editing to delete two genes essential for kidneys to form inside a pig embryo, creating what's called a "niche."
They then added specially prepared human pluripotent stem cells -- cells that have the potential to develop into any cell type -- which filled the niche.
Before implanting the embryos in sows, they grew them in test tubes containing substances that nourished both the human and pig cells.
In total, they transferred 1,820 embryos into 13 surrogate mothers. The pregnancies were terminated at 25 and 28 days to assess how the experiment had worked.
Five embryos selected for analysis were found to have functionally normal kidneys for their stage of development. They contained between 50 and 60 percent human cells.
"We found that if you create a niche in the pig embryo, then the human cells naturally go into these spaces," said co-author Zhen Dai.
"We saw only very few human neural cells in the brain and spinal cord and no human cells in the genital ridge."
But the presence of any human cells in the pig brains raises concerns, said Darius Widera, a professor of stem cell biology at the University of Reading.
"Although this approach is a clear milestone and the first successful attempt to grow whole organs containing human cells in pigs, the proportion of human cells in the generated kidneys is still not high enough," he added.
In the long run, the team wants to optimize their technology for use in human transplantation, but admits it's not ready yet.
An important limitation was the kidneys had pig-derived vascular cells, which could cause rejection if transplanted into a human.
Nevertheless, the team is already working on growing other human organs in pigs such as the heart and pancreas.
A.Kunz--VB



