-
 Who rules the seas? Torpedoed Iran ship brings focus underwater
Who rules the seas? Torpedoed Iran ship brings focus underwater
-
Mideast war escalates as fresh strikes batter Iran

-
 Pirovano takes downhill at Val di Fassa for first World Cup win
Pirovano takes downhill at Val di Fassa for first World Cup win
-
Iran drone strike on Azerbaijan raises fears of Mideast war spreading to Caucasus

-
 Decades of planning and US backing helps fuel Israel's air power
Decades of planning and US backing helps fuel Israel's air power
-
Hungary to expel seven Ukrainians as Zelensky, Orban quarrel over Russian oil

-
 Mideast war is heightening uncertainty, Lufthansa warns
Mideast war is heightening uncertainty, Lufthansa warns
-
Fresh Israeli strikes on Lebanon as PM warns of 'looming humanitarian disaster'

-
 Italian general challenges Meloni from the right
Italian general challenges Meloni from the right
-
China says 'clearly aware' of economic risks, vows to boost spending

-
 Hungary detains seven Ukrainians as Kyiv, Budapest quarrel over Russian oil
Hungary detains seven Ukrainians as Kyiv, Budapest quarrel over Russian oil
-
North Korea, China power into Women's Asian Cup quarter-finals

-
 Extensive destruction in Beirut's southern suburbs following Israeli strikes
Extensive destruction in Beirut's southern suburbs following Israeli strikes
-
Most Asian equities drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 'Super special' Allen can light up big occasion for New Zealand
'Super special' Allen can light up big occasion for New Zealand
-
'Genie' Bumrah: India's yorker king who carries a billion hopes

-
 'There will be nerves': India face New Zealand for T20 World Cup glory
'There will be nerves': India face New Zealand for T20 World Cup glory
-
Lufthansa warns of heightened 'uncertainty' from Mideast war

-
 Mideast war enters 'next phase' as strikes hit Iran, Lebanon
Mideast war enters 'next phase' as strikes hit Iran, Lebanon
-
Equities mixed as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Sri Lanka denounces war deaths, houses Iran sailors
Sri Lanka denounces war deaths, houses Iran sailors
-
Inoue primed for 'historic' Nakatani clash in Tokyo

-
 Italy challenges EU over key climate tool
Italy challenges EU over key climate tool
-
Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice

-
 Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday
Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday
-
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn

-
 Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems
-
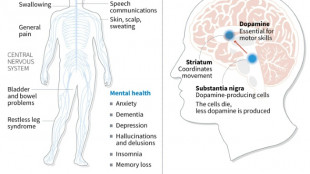
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
 Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'
-
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning

-
 Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer
-
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse

-
 Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
-
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice

-
 Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
-
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election

-
 Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
-
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game

-
 French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
-
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output

-
 Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
-
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut

-
 Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv

-
 US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
-
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates

-
 Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
-
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63

-
 Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
-
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis


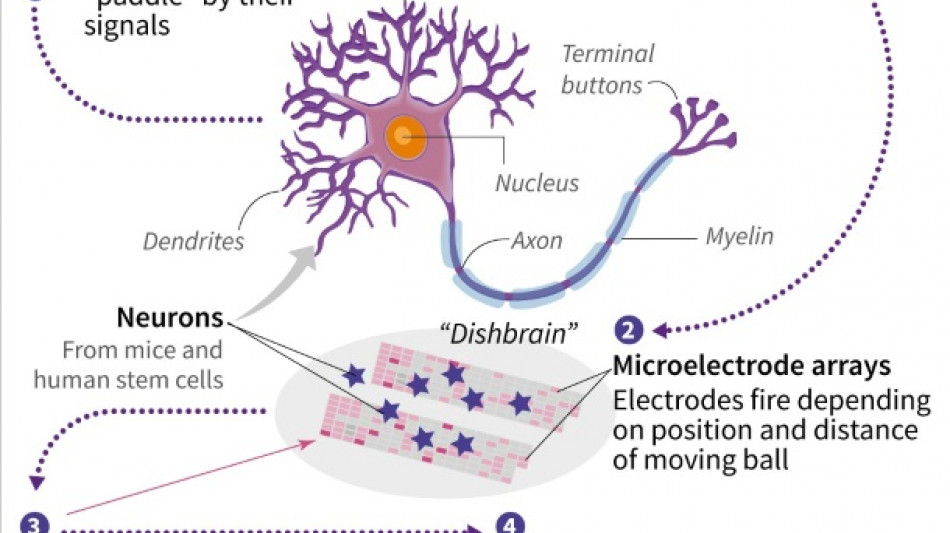
Brain cells in dish learn to play video game
Neuroscientists have shown that lab-grown brain cells can learn to play the classic video game Pong, and could be capable of "intelligent and sentient behavior."
Brett Kagan, who led a study published in the journal Neuron Wednesday, told AFP his findings open the door to a new type of research into biological information processors, complementing normal digital computers.
"What machines can't do is learn things very quickly -- if you need a machine learning algorithm to learn something, it requires thousands of data samples," he explained.
"But if you ask a human, or train a dog, a dog can learn a trick in two or three tries."
Kagan, chief scientific officer at Melbourne-based Cortical Labs, set out to answer whether there is a way to harness the inherent intelligence of neurons.
Kagan and colleagues took mice cells from embryonic brains, and derived human neurons from adult stem cells.
They then grew them on top of microelectrode arrays that could read their activity and stimulate them. The experiments involved a cluster of around 800,000 neurons, roughly the size of a bumblebee brain.
In the game, a signal was sent from the left or right of the array to indicate where the ball was located, and "DishBrain," as the researchers called it, fired back signals to move the paddle, in a simplified, opponent-free version of Pong.
- 'Sentient, but not conscious' -
One of the major hurdles was figuring out how to "teach" the neurons.
In the past, it has been proposed to give them a shot of the "feel good" hormone dopamine to reward a correct action -- but that was difficult to achieve in a time-sensitive way.
Instead, the team relied on a theory called the "free energy principle" that was coined by the paper's senior author Karl Friston, which says cells are hardwired to minimize unpredictability in their environments.
When the neurons succeeded in making the paddle hit the ball, they received "predictable" electrical signals. But when they missed, they were sent randomized, or "unpredictable" signals.
"The only thing that the neurons could do is actually get better at trying to hit the ball to keep their world controllable and predictable," said Kagan.
DishBrain's performance isn't up to AI (artificial intelligence) or human standards, but "the fact we see any significant learning is really just evidence of how robust neurons are at processing information and adapting to their environment," he added.
The team believes DishBrain is sentient -- which they defined as being able to sense and respond to sensory information in a dynamic way -- but drew the line at calling it "conscious," which implies awareness of being.
DishBrain also tried out another task -- the dinosaur game that appears in Google Chrome when no internet connection is found -- and the preliminary results were encouraging, said Kagan.
For their next steps, the team plans to test how DishBrain's intelligence is affected by medicines and alcohol -- though Kagan himself is most excited by the future possibilities of biological computers based on this discovery.
"We compare it to the first transistor," he said, the building block of modern electronics invented in 1947, which eventually led to today's powerful digital computers.
"This is robustly conducted, interesting neuroscience," said Tara Spires-Jones of the Centre for Discovery Brain Science at the University of Edinburgh, who was not involved in the study.
"Don't worry, while these dishes of neurons can change their responses based on stimulation, they are not SciFi style intelligence in a dish, these are simple (albeit interesting and scientifically important) circuit responses."
G.Schulte--BTB




