
-
 Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice
Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice
-
Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday

-
 Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
-
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems

-
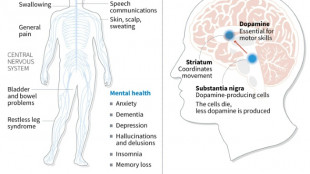 Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'

-
 North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
-
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer

-
 Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
-
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold

-
 Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
-
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
-
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett

-
 Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
-
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche

-
 Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
-
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets

-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup


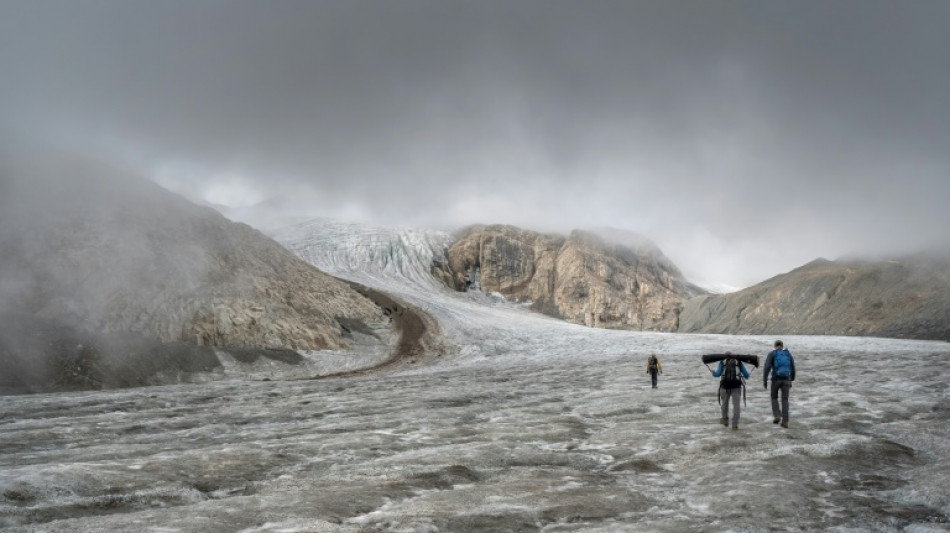
Swiss glaciers melting away at record rate
Switzerland's glaciers lost six percent of their total volume this year due to a dry winter and repeated summer heatwaves, shattering previous ice melt records, a report revealed Wednesday.
The study by the Cryospheric Commission (CC) of the Swiss Academy of Sciences laid bare the drastic scale of glacial retreat -- which is only set to get worse.
"2022 was a disastrous year for Swiss glaciers: all ice melt records were smashed," the CC said, adding that a two percent loss in 12 months had previously been considered "extreme".
Three cubic kilometres of ice -- three trillion litres of water -- have melted away, the report said.
"It's not possible to slow down the melting in the short term," said glaciology professor Matthias Huss, head of Glacier Monitoring in Switzerland, which documents long-term glacier changes in the Alps and is coordinated by the CC.
If carbon dioxide emissions are reduced and the climate protected, "this might save about one third of the total volumes in Switzerland in the best case", he told AFP.
Otherwise, the country "will be losing almost everything by the end of the century".
- Saharan dust speeds melt -
At the start of the year, the snow cover in the Alps was exceptionally light, then a large volume of sand dust blew in from the Sahara Desert between March and May, settling on the surface.
The contaminated snow absorbed more heat and melted faster, depriving the glaciers of their protective snow coating by early in the European summer.
The continuous heat between May and early September therefore ravaged the glacial ice.
By mid-September, the once-thick layer of ice that covered the pass between the Scex Rouge and Tsanfleuron glaciers had completely melted away, exposing bare rock that had been frozen over since at least the Roman era.
And in early July, the collapse of a section of the Marmolada glacier, the biggest in the Italian Alps, killed 11 people and highlighted how serious the situation had become.
According to an Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report published in February, the melting of ice and snow is one of the 10 key threats from climate change.
- Smallest glaciers hardest hit -
"The loss was particularly dramatic for small glaciers," the CC said.
The Pizol, Vadret dal Corvatsch and Schwarzbachfirn glaciers "have practically disappeared -- measurements were discontinued", the commission said.
In the Engadine and southern Valais regions, both in the south, "a four to six-metre-thick layer of ice at 3,000 metres above sea level vanished," said the report.
Significant losses were recorded even at the very highest measuring points, including the Jungfraujoch mountain, which peaks at nearly 3,500 metres.
"Observations show that many glacier tongues are disintegrating and patches of rock are rising out of the thin ice in the middle of glaciers. These processes are further accelerating the decline," said the report.
"The trend also reveals how important glaciers are to the water and energy supply in hot, dry years," the report stressed -- something to consider given that hydroelectricity provides more than 60 percent of Switzerland's total energy production.
The glacial meltwater in July and August alone would have provided enough water this year to completely fill all the reservoirs in the Swiss Alps.
But Huss said that if the country experienced this year's meteorological conditions in 50 years' time, "the impact would be much stronger, because in 50 years, we expect that almost all glaciers are gone and therefore cannot provide water in a hot and dry summer".
- Melt reveals macabre finds -
The melting of the glaciers has also had some unexpected consequences.
Hikers are regularly making macabre discoveries as bodies are being freed from the ice they have been encased in for decades or even centuries.
The melting can also be a boon for archaeologists who suddenly have access to objects that are thousands of years old.
Meanwhile the melting of a glacier between Italy and Switzerland has moved the border that ran along the watershed, forcing lengthy diplomatic negotiations.
A.Gasser--BTB




