
-
 Colombia's left boosted by legislative vote
Colombia's left boosted by legislative vote
-
Patrick Halgren: America's greatest showman at the Paralympics

-
 Four years after banning Russia, FIFA and IOC passive in the face of war
Four years after banning Russia, FIFA and IOC passive in the face of war
-
Iraq coach calls for World Cup playoff to be re-scheduled

-
 Germany's Max Kanter sprints to Paris-Nice second stage win
Germany's Max Kanter sprints to Paris-Nice second stage win
-
France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz

-
 Anthropic takes Trump administration to court over Pentagon row
Anthropic takes Trump administration to court over Pentagon row
-
Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists

-
 Beating Barca would make us Newcastle legends: Howe
Beating Barca would make us Newcastle legends: Howe
-
Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge

-
 Zelensky says 11 countries asking Ukraine for drone help against Iran
Zelensky says 11 countries asking Ukraine for drone help against Iran
-
France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron

-
 Ships brandish China-links to weave through Strait of Hormuz
Ships brandish China-links to weave through Strait of Hormuz
-
Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers

-
 NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace
-
War in the Middle East: economic impact around the world

-
 Huge numbers at imminent risk from S.Sudan army offensive: MSF
Huge numbers at imminent risk from S.Sudan army offensive: MSF
-
G7 'not there yet' on release of oil reserves: French minister

-
 Live Nation settles antitrust case with US Justice Dept, states object
Live Nation settles antitrust case with US Justice Dept, states object
-
EU lawmakers set to greenlight 'return hubs' for migrants

-
 Water emerges as a dangerous new war target
Water emerges as a dangerous new war target
-
Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash

-
 Stocks slide as oil soars past $100 on Mideast war
Stocks slide as oil soars past $100 on Mideast war
-
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara

-
 South Korea squeeze into World Baseball Classic quarter-finals
South Korea squeeze into World Baseball Classic quarter-finals
-
Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash

-
 North Korea cancels Pyongyang international marathon: tour agency
North Korea cancels Pyongyang international marathon: tour agency
-
Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv

-
 Macron discusses security in Cyprus, plans aircraft carrier visit
Macron discusses security in Cyprus, plans aircraft carrier visit
-
Russia wins 'dream' first Paralympic gold since 2014

-
 UK PM Starmer says 'monitoring' economic impact of Iran war
UK PM Starmer says 'monitoring' economic impact of Iran war
-
Stranded Iran sailors put Sri Lanka, India in diplomatic dilemma

-
 Bangladesh scraps light displays as Mideast war worsens fuel crunch
Bangladesh scraps light displays as Mideast war worsens fuel crunch
-
Incensed North Korea briefly refuse to play in bitter Asian Cup loss

-
 Landmark trial opens for Turkish opposition champion Imamoglu
Landmark trial opens for Turkish opposition champion Imamoglu
-
Indonesia landfill collapse kills five

-
 African players in Europe: Marmoush torments Newcastle again
African players in Europe: Marmoush torments Newcastle again
-
Kenya flash floods death toll rises to 45

-
 Asian economies move to limit Mideast war's impact at home
Asian economies move to limit Mideast war's impact at home
-
Jail for up to 16 years for Australian hitmen who killed compatriot in Bali

-
 Landmark trial opens for Turkey opposition champion Imamoglu
Landmark trial opens for Turkey opposition champion Imamoglu
-
Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014

-
 'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory
'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory
-
Indonesia landfill collapse kills four

-
 Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history
Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history
-
Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring

-
 Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis
Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis
-
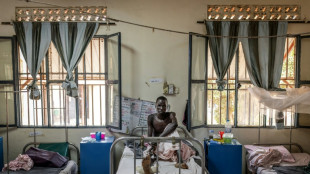
Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
-
 Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival
Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival
-
Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports


A whiff of tears reduces male aggression, says study
Watching someone cry often evokes an emotional response -- but according to a new study published Thursday, human tears themselves contain a chemical signal that reduces brain activity linked to aggression.
The research was carried out by the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, and appeared in PLOS Biology, a US science journal. Though it involved female tears, because women made themselves available as donors, it probably isn't a sex-dependent effect, the authors say.
Numerous studies have shown rodent tears contain chemicals serving as social signals they emit on demand -- female mice tears for example reduce fighting among males; and subordinate male mole rats smear themselves in their own tears so that dominant males attack them less.
To find out whether similar effects occurred in humans, a team led by PhD student Shani Agron first exposed 25 male volunteers to either "emotional" tears, or to saline. The volunteers couldn't tell what they were sniffing as both substances are clear and odorless.
The tears were obtained from six female volunteers who watched sad films in isolation and used a mirror to capture the liquid in a vial as it trickled down their cheeks.
"When we looked for volunteers who could donate tears, we found mostly women, because for them it's much more socially acceptable to cry," said Agron in a statement.
She added that since prior research had shown tears reduce testosterone levels in men, and that lowering testosterone has a greater effect on aggression in men than in women, "we began by studying the impact of tears on men because this gave us higher chances of seeing an effect."
They had the volunteers play a computer game that had been well established in prior aggression studies, and involves accumulating money while a fictitious opponent could steal their earnings.
Given the opportunity, the men could get revenge on the other player by causing them to lose money, even though in their own case they would not gain from the opponent's loss.
Such revenge-seeking, aggressive behavior in the game dropped 43.7 percent after men sniffed the tears.
This appeared to mirror what had been observed in rodents, but unlike rodents, humans don't have a structure in their noses called a vomeronasal organ, which was lost during our species' evolution and detects odorless chemical signals.
To find out what was going on, the researchers applied the tears to 62 olfactory receptors in a lab dish and found that four receptors were activated by tears, but not saline.
Finally, the scientists repeated the experiments with the men's brains connected to MRI scanners.
The imaging revealed the prefrontal cortex and anterior insula, which are related to aggression, became more active when men were provoked during the game, but the effect was not as strong if they had sniffed tears.
"We note that crying often occurs in very close-range interactions, to the extent that 'kissing teary cheeks' is a recurring theme across cultures," wrote the authors, adding that emitting chemical signals to prevent aggression was probably even more important among infants, where verbal communication isn't possible.
F.Mueller--VB



