-
 France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz
France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz
-
Anthropic takes Trump administration to court over Pentagon row

-
 Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists
Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists
-
Beating Barca would make us Newcastle legends: Howe

-
 Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
-
Zelensky says 11 countries asking Ukraine for drone help against Iran

-
 France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron
France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron
-
Ships brandish China-links to weave through Strait of Hormuz

-
 Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers
Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers
-
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace

-
 War in the Middle East: economic impact around the world
War in the Middle East: economic impact around the world
-
Huge numbers at imminent risk from S.Sudan army offensive: MSF

-
 G7 'not there yet' on release of oil reserves: French minister
G7 'not there yet' on release of oil reserves: French minister
-
Live Nation settles antitrust case with US Justice Dept, states object

-
 EU lawmakers set to greenlight 'return hubs' for migrants
EU lawmakers set to greenlight 'return hubs' for migrants
-
Water emerges as a dangerous new war target

-
 Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash
Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash
-
Stocks slide as oil soars past $100 on Mideast war

-
 NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara
-
South Korea squeeze into World Baseball Classic quarter-finals

-
 Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash
Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash
-
North Korea cancels Pyongyang international marathon: tour agency

-
 Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv
Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv
-
Macron discusses security in Cyprus, plans aircraft carrier visit

-
 Russia wins 'dream' first Paralympic gold since 2014
Russia wins 'dream' first Paralympic gold since 2014
-
UK PM Starmer says 'monitoring' economic impact of Iran war

-
 Stranded Iran sailors put Sri Lanka, India in diplomatic dilemma
Stranded Iran sailors put Sri Lanka, India in diplomatic dilemma
-
Bangladesh scraps light displays as Mideast war worsens fuel crunch

-
 Incensed North Korea briefly refuse to play in bitter Asian Cup loss
Incensed North Korea briefly refuse to play in bitter Asian Cup loss
-
Landmark trial opens for Turkish opposition champion Imamoglu

-
 Indonesia landfill collapse kills five
Indonesia landfill collapse kills five
-
African players in Europe: Marmoush torments Newcastle again

-
 Kenya flash floods death toll rises to 45
Kenya flash floods death toll rises to 45
-
Asian economies move to limit Mideast war's impact at home

-
 Jail for up to 16 years for Australian hitmen who killed compatriot in Bali
Jail for up to 16 years for Australian hitmen who killed compatriot in Bali
-
Landmark trial opens for Turkey opposition champion Imamoglu

-
 Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014
Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014
-
'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory

-
 Indonesia landfill collapse kills four
Indonesia landfill collapse kills four
-
Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history

-
 Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring
Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring
-
Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis

-
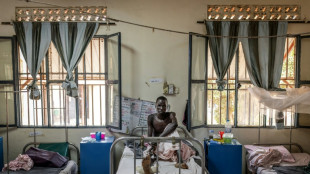 Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
-
Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival

-
 Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports
Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports
-
Sinner sets up Fonseca clash, Zverev advances at Indian Wells

-
 Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions
Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions
-
Gauff retires with 'scary' injury to send Eala through at Indian Wells

-
 Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader
Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader
-
Wemby shines as Spurs thrash Rockets, Lakers down Knicks


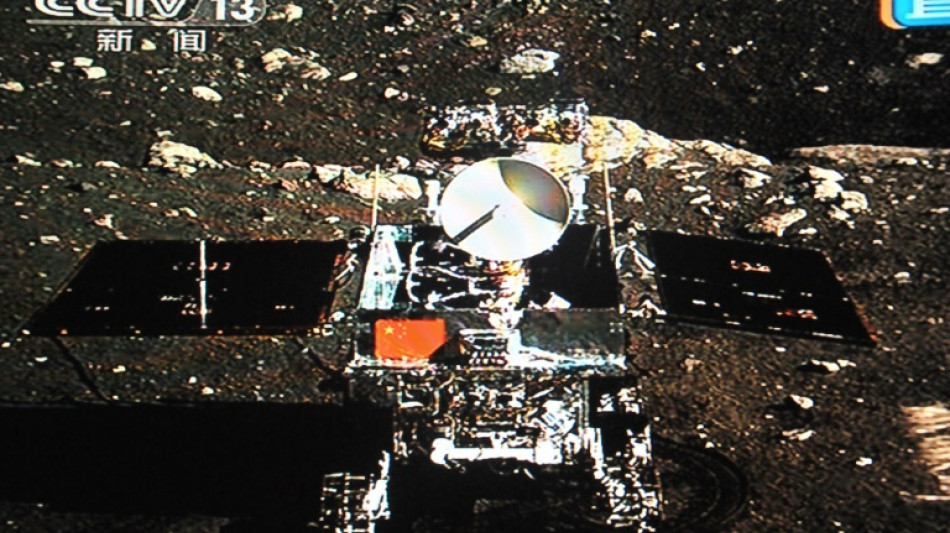
China's space programme: Five things to know
When Chang'e-3 became the first Chinese craft to land on the Moon 10 years ago, it kicked off nationwide celebrations -- and a decade of major successes for a rapidly accelerating space programme.
Since the December 14, 2013 landing, China has built a crewed space station, sent a robotic rover to Mars and become the first nation to make a controlled landing on the far side of the Moon.
Here are five things to know about China's space programme:
- A slow start -
Chinese leader Mao Zedong declared his nation's space ambitions soon after the Soviet Union launched the world's first satellite, Sputnik 1, in 1957.
It took 13 years for China to launch its first satellite Dong Fang Hong, or "The East is Red" -- named after the famous Communist revolutionary song it broadcast from orbit.
It was not until the late 1980s that the programme began to pick up pace, alongside China's ascent into the world's richest and most powerful nations.
Overseen by the military, its secretive space programme's goals became more ambitious. In 1992, it formally began a project to send humans into space.
- 'Taikonauts' -
More than three decades after its first satellite launch, on October 15, 2003, Yang Liwei became the first Chinese to travel into space, and an instant national hero.
With the success of his Shenzhou 5 mission, China became only the third nation after the United States and Russia to demonstrate the ability to launch humans into space.
In total, 20 Chinese astronauts have made the journey into space, including two women. State media have used the term "taikonaut" to describe China's spacefarers.
Many of them have journeyed to Tiangong, China's first long-term space station whose construction was completed last year.
Though much smaller than the International Space Station, it contains living quarters for a rotating crew, robotic arms and airlocks for conducting spacewalks.
- To the Moon -
China has also sent exploration missions to the Moon.
Named after the Moon goddess in Chinese folklore, Chang'e-3 touched down on the surface in 2013, making China only the third nation to successfully land there.
Two other milestones followed. In 2019, China became the first nation to make a controlled landing on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e-4.
A year later, Chang'e-5 brought the first lunar samples to Earth in more than 40 years.
Chinese space authorities have said they plan to land humans on the Moon by 2030, as well as build a lunar base.
- Mars and deep space -
One of the most spectacular successes of the Chinese space programme came in 2021 when its Tianwen-1 mission landed a rover named Zhurong on the surface of Mars.
China is only the second nation after the United States to put a robotic rover on the Red Planet.
Officials have said they aim to send a crewed mission there by 2033.
Aside from landers and orbiters, China is soon expected to launch a space telescope named Xuntian.
Orbiting close to the Tiangong space station, with which it can dock, Xuntian is expected to have a field of view far greater than NASA's Hubble telescope.
- Defence and prestige -
While China says it opposes the weaponisation of space, its policy makers have also identified space as critical to national defence and security.
Its military is a core player in the national space programme, and China is developing spy satellites, anti-satellite missiles and electronic warfare capabilities, according to the US military.
China "sees counterspace operations as a means to deter and counter a US intervention during a regional military conflict", the Pentagon said in a report to Congress this year.
And beyond the direct applications of these technologies, China considers success in space as a major driver of its image as a global power at home and abroad.
"National prestige is perhaps one of the most important, if not the most important, motives driving Chinese space ambitions," said Robert Hines, an assistant professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology in the United States.
"These symbols of increasing international status provide a powerful form of domestic propaganda."
F.Stadler--VB



