
-
 France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz
France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz
-
Anthropic takes Trump administration to court over Pentagon row

-
 Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists
Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists
-
Beating Barca would make us Newcastle legends: Howe

-
 Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
-
Zelensky says 11 countries asking Ukraine for drone help against Iran

-
 France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron
France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron
-
Ships brandish China-links to weave through Strait of Hormuz

-
 Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers
Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers
-
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace

-
 War in the Middle East: economic impact around the world
War in the Middle East: economic impact around the world
-
Huge numbers at imminent risk from S.Sudan army offensive: MSF

-
 G7 'not there yet' on release of oil reserves: French minister
G7 'not there yet' on release of oil reserves: French minister
-
Live Nation settles antitrust case with US Justice Dept, states object

-
 EU lawmakers set to greenlight 'return hubs' for migrants
EU lawmakers set to greenlight 'return hubs' for migrants
-
Water emerges as a dangerous new war target

-
 Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash
Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash
-
Stocks slide as oil soars past $100 on Mideast war

-
 NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara
-
South Korea squeeze into World Baseball Classic quarter-finals

-
 Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash
Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash
-
North Korea cancels Pyongyang international marathon: tour agency

-
 Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv
Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv
-
Macron discusses security in Cyprus, plans aircraft carrier visit

-
 Russia wins 'dream' first Paralympic gold since 2014
Russia wins 'dream' first Paralympic gold since 2014
-
UK PM Starmer says 'monitoring' economic impact of Iran war

-
 Stranded Iran sailors put Sri Lanka, India in diplomatic dilemma
Stranded Iran sailors put Sri Lanka, India in diplomatic dilemma
-
Bangladesh scraps light displays as Mideast war worsens fuel crunch

-
 Incensed North Korea briefly refuse to play in bitter Asian Cup loss
Incensed North Korea briefly refuse to play in bitter Asian Cup loss
-
Landmark trial opens for Turkish opposition champion Imamoglu

-
 Indonesia landfill collapse kills five
Indonesia landfill collapse kills five
-
African players in Europe: Marmoush torments Newcastle again

-
 Kenya flash floods death toll rises to 45
Kenya flash floods death toll rises to 45
-
Asian economies move to limit Mideast war's impact at home

-
 Jail for up to 16 years for Australian hitmen who killed compatriot in Bali
Jail for up to 16 years for Australian hitmen who killed compatriot in Bali
-
Landmark trial opens for Turkey opposition champion Imamoglu

-
 Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014
Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014
-
'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory

-
 Indonesia landfill collapse kills four
Indonesia landfill collapse kills four
-
Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history

-
 Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring
Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring
-
Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis

-
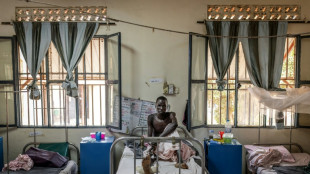 Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
-
Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival

-
 Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports
Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports
-
Sinner sets up Fonseca clash, Zverev advances at Indian Wells

-
 Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions
Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions
-
Gauff retires with 'scary' injury to send Eala through at Indian Wells

-
 Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader
Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader
-
Wemby shines as Spurs thrash Rockets, Lakers down Knicks


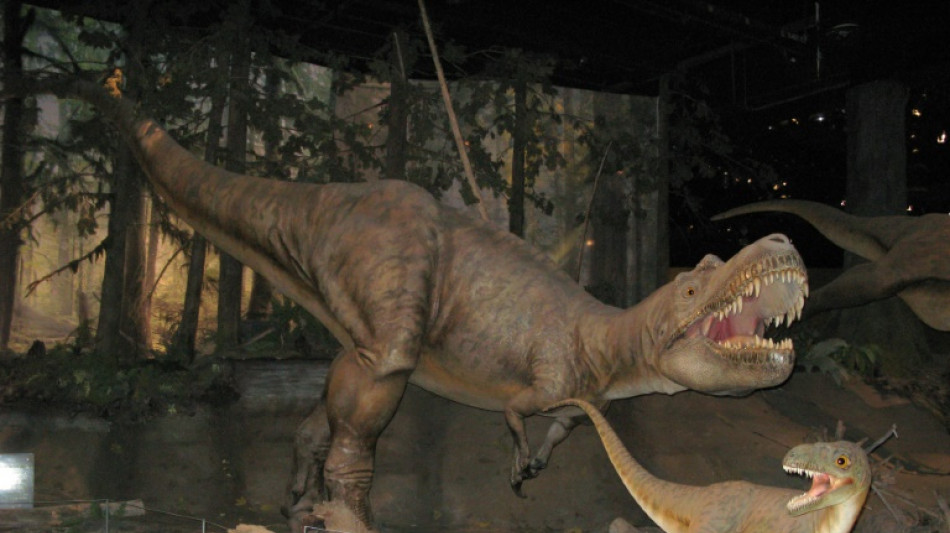
'Appetite for drumsticks': First prey found in a tyrannosaur stomach
Prey has been discovered inside the stomach of a tyrannosaur skeleton for the first time, scientists said Friday, revealing that the mighty dinosaurs had an "appetite for drumsticks" when they were young.
The skeleton of the Gorgosaurus, a member of the tyrannosaurid family that also includes the T-Rex, sheds light on how these dinosaurs grew from fairly slender juveniles into gigantic, bone-crushing, apex-predator adults, they added.
The Gorgosaurus -- which means "dreadful lizard" -- was around six years old when it died more than 75 million years ago, according to a new study in the journal Science Advances.
The fossil was discovered in 2009 at the Dinosaur Provincial Park, east of the Canadian city of Calgary. But when they got the skeleton back to the lab, the scientists noticed something strange.
The study's lead author, Francois Therrien of the Royal Tyrrell Museum, told AFP they were amazed to "discover the remains of the last meal of this young tyrannosaur still preserved in place".
What was most surprising, he added, was that the small leg bones sticking out of the tyrannosaur's ribcage belonged to two young, bird-like dinosaurs called Citipes.
Citipes are thought to have had feathers, wings and a beak and walk on two feet, somewhat resembling modern-day cassowaries, Therrien said.
They are far smaller than the massive plant-eating dinosaurs that adult tyrannosaurs had been known to eat.
Study co-author Darla Zelenitsky, a paleontologist at the University of Calgary, told AFP that this particular "fussy eater" used its sharp teeth to carve itself only the legs of the two baby Citipes.
"This teenage Gorgosaurus seems to have had an appetite for drumsticks," she said.
- Not always an apex predator -
The discovery also offers a rare clue into how tyrannosaurs grew from one-metre-long at birth to some of the biggest predators to have ever walked the Earth.
"This fossil is the first solid evidence that tyrannosaurids drastically changed their diet as they grew from teenagers to adults," Zelenitsky said.
Young tyrannosaurs had slender heads and legs, sharp knife-like teeth for dissecting carcasses, and could probably run quite fast to catch their turkey-like prey.
These youths probably looked more similar to the velociraptors depicted in the movie "Jurassic Park" than the giant T-Rex, Zelenitsky said.
But at roughly 11 years old, as the tyrannosaurs hit their middle-age, their bodies grew almost ten times in size, ending up weighing more than 3,000 kilogrammes (6,600 pounds).
Their heads broadened and their teeth thickened into what Therrien called "killer bananas" capable of crunching through huge bones.
This transformation was driven by a change in diet, as the dinosaurs ditched the drumsticks of their youth and started preying on giant plant-eating dinosaurs.
These kind of drastic dietary changes are not necessarily rare in the animal kingdom -- crocodiles and Komodo dragons start out eating insects before switching to rodents and eventually large mammals, Therrien said.
The researchers said the Gorgosaurus fossil supports the theory that young tyrannosaurs -- including the T-Rex -- filled a role in the food chain known as "mesopredators", before later growing into apex predators.
This change is "probably the reason why tyrannosaurs were so successful and dominated their ecosystems at the end of the Cretaceous in North America and Asia," Therrien said.
H.Weber--VB



