-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'

-
 Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
-
Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?

-
 Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
-
Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
-
EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'

-
 Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
-
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy

-
 Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out
Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out
-
Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final

-
 Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban
Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban
-
Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets
Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets
-
Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat

-
 No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final
No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final
-
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing

-
 EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas
EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas
-
Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash

-
 Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka
Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka
-
Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards

-
 Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone
Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone
-
Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry

-
 Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
-
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China

-
 US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
-
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites

-
 Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
-
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study

-
 Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
-
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits

-
 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China


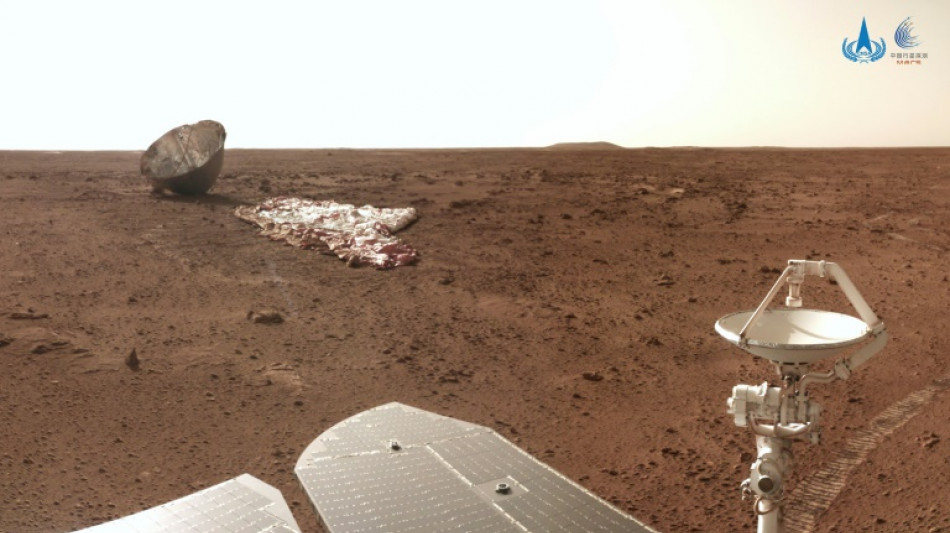
Chinese rover finds signs of ancient ocean on Mars
A Chinese rover has found new evidence to support the theory that Mars was once home to a vast ocean, including tracing some ancient coastline where water may once have lapped, a study said Thursday.
The theory that an ocean covered as much as a third of the Red Planet billions of years ago has been a matter of debate between scientists for decades, and one outside researcher expressed some scepticism about the latest findings.
In 2021, China's Zhurong rover landed on a plain in the Martian northern hemisphere's Utopia region, where previous indications of ancient water had been spotted.
It has been probing the red surface ever since, and some new findings from the mission were revealed in the new study in the journal Nature.
Lead study author Bo Wu of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University told AFP that a variety of features suggesting a past ocean had been spotted around Zhurong's landing area, including "pitted cones, polygonal troughs and etched flows".
Previous research has suggested that the crater-like pitted cones could have come from mud volcanoes, and often formed in areas where there had been water or ice.
Information from the rover, as well as satellite data and analysis back on Earth, also suggested that a shoreline was once near the area, according to the study.
The team of researchers estimated that the ocean was created by flooding nearly 3.7 billion years ago.
Then the ocean froze, etching out a coastline, before disappearing a little 3.4 billion ago, according to their scenario.
Bo emphasised that the team does "not claim that our findings definitively prove that there was an ocean on Mars".
That level of certainty will likely require a mission to bring back some Martian rocks to Earth for a closer look.
- The coast is always changing -
Benjamin Cardenas, a scientist who has analysed other evidence of a Martian ocean, told AFP he was "sceptical" of the new study.
He felt the researchers did not take enough into account how much the strong Martian wind had blown around sediment and worn down rocks over the past few billion years.
"We tend to think of Mars of being not very active, like the Moon, but it is active!" said Cardenas of Pennsylvania State University in the United States.
He pointed to past modelling research which suggested that "even the slow Martian erosion rates" would destroy signs of a shoreline over such a long period.
Bo acknowledged that wind might have worn down some rocks, but said the impact of meteors hitting Mars can also "excavate underground rock and sediment to the surface from time to time".
While the overall theory remains contentious, Cardenas said he tended "to think there was an ocean on Mars".
Finding out the truth could help unravel a greater mystery: whether Earth is alone in the Solar System in being capable of hosting life.
"Most scientists think life on Earth sprung up either under the ocean where hot gases and minerals from the subsurface came to the seafloor, or very close to the interface of water and air, in little tidal pools," Cardenas said.
"So, evidence for an ocean makes the planet appear more hospitable."
M.Vogt--VB



