
-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
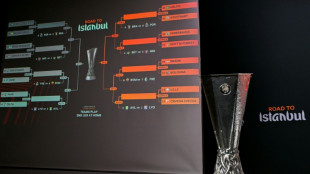 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support

-
 Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
-
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties

-
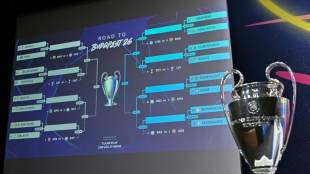 Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
-
Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble

-
 Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
-
Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump

-
 Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
-
Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat

-
 Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention
Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention
-
'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal

-
 Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
-
Slot warns Liverpool 'can't afford mistakes' in top-four scrap

-
 Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
-
Artist chains up thrashing robot dog to expose AI fears

-
 Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
-
French PM forces final budget through parliament

-
 French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
-
Dutch watchdog launches Roblox probe over 'risks to children'

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam


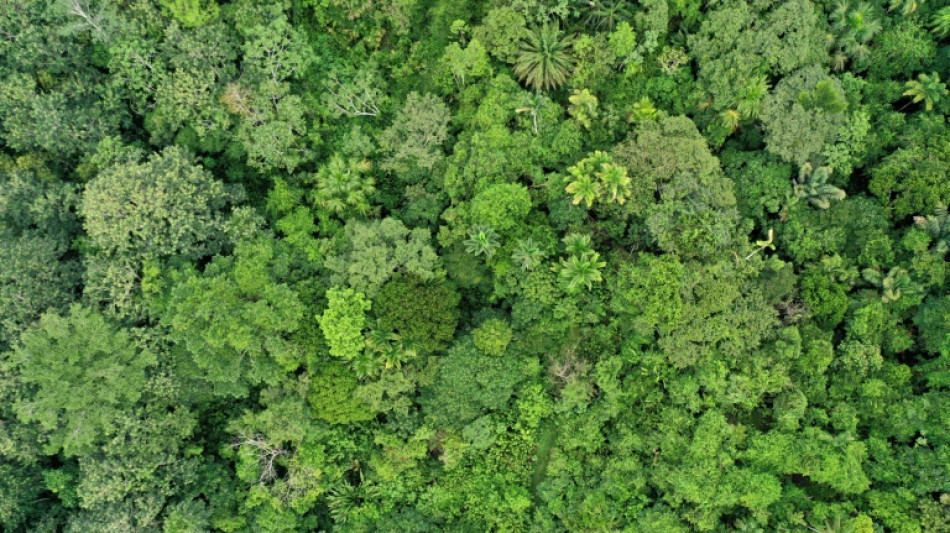
Tropical forests nearing critical temperatures thresholds
Global warming is driving leafy tropical canopies close to temperatures where they can no longer transform sunlight and CO2 into energy, threatening total collapse if the thermometer keeps climbing, according to a study Thursday.
A tiny percentage of upper canopy leaves have already crossed that threshold, reaching temperatures so high -- above 47 degrees Celsius -- as to prevent photosynthesis, the study published in Nature reported.
Currently, some leaves exceed such critical temperatures only 0.01 percent of the time, but impacts could quickly scale up because leaves warm faster than air, the researchers said.
"You heat the air by two to three degrees and the actual upper temperature of these leaves goes up by eight degrees," lead author Christopher Doughty of Northern Arizona University told journalists.
If tropical forest's average surface temperature warms 4C above current levels -- widely considered a worst-case scenario -- "we're predicting possible total leaf death," he said.
The new research suggests that leaf death could become a new factor in the predicted "tipping point" whereby tropical forests transition due to climate change and deforestation into savannah-like landscapes.
If air temperatures increase unabated by 0.03 C per year, the study projected, mass mortality among the canopies could happen in a little more than a century.
Doughty and his team used data from the NASA ECOSTRESS satellite -- designed to measure plant temperatures -- validated with ground observations, based in part on sensors attached to individual leaves.
- Increased tree death -
There remain uncertainties as to how high leaf temperatures might impact the forest as a whole, the scientists cautioned.
"Believe it or not, we don't know terribly much about why trees die," said co-author Gregory Goldsmith of Chapman University.
It doesn't take a scientist to know that when a tree loses its roots it dies, he said.
But the interactions and feedbacks between heat and drought -- and water and temperature -- on overall tree health aren't as clear.
Total leaf death might not necessarily mean total tree death.
The critical temperature at which leaves turn brown and die might also differ by species, depending on the size and thickness of their leaves and the breadth of their canopy.
But there are already concerning signs. In the Amazon, where temperatures are higher than in other tropical forests, the rate at which trees are dying has increased in recent decades.
"The Amazon is currently experiencing higher levels of mortality than Central Africa and that could possibly be due to the high temperatures we've seen there," said Doughty.
Increased fragmentation of the forests from deforestation has also been shown to make the remaining forest areas warmer.
Tropical biomes contain 45 percent of the Earth's forests, and play an outsized role in absorbing human-caused carbon pollution.
They also harbour half or more of the world's plant biodiversity, with at least 40,000 different tree species, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
The fact that a few leaves are overheating at current temperatures is a "canary in the coal mine," said senior author Joshua Fisher of Chapman University.
"You want to be able to detect something happening before it's widespread," he said.
"The fact that we can do that now gives us that ability to actually do something as a collective society."
Scientists not involved in the study said it should serve as a warning that nature's capacity to adapt to climate change has limits.
"It is true that trees and other kinds of vegetation can soak up emissions and provide cooling," commented Leslie Mabon, a lecturer in environmental systems at The Open University.
"However, this study illustrates that without concerted action by humans to reduce emissions and limit global heating at the same time as protecting and enhancing nature, some functions of nature may start to break down at higher temperatures."
K.Brown--BTB



