
-
 Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
-
Slot warns Liverpool 'can't afford mistakes' in top-four scrap

-
 Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
-
Artist chains up thrashing robot dog to expose AI fears

-
 Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
-
French PM forces final budget through parliament

-
 French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
-
Dutch watchdog launches Roblox probe over 'risks to children'

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
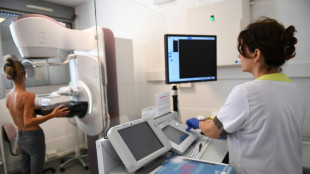
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge


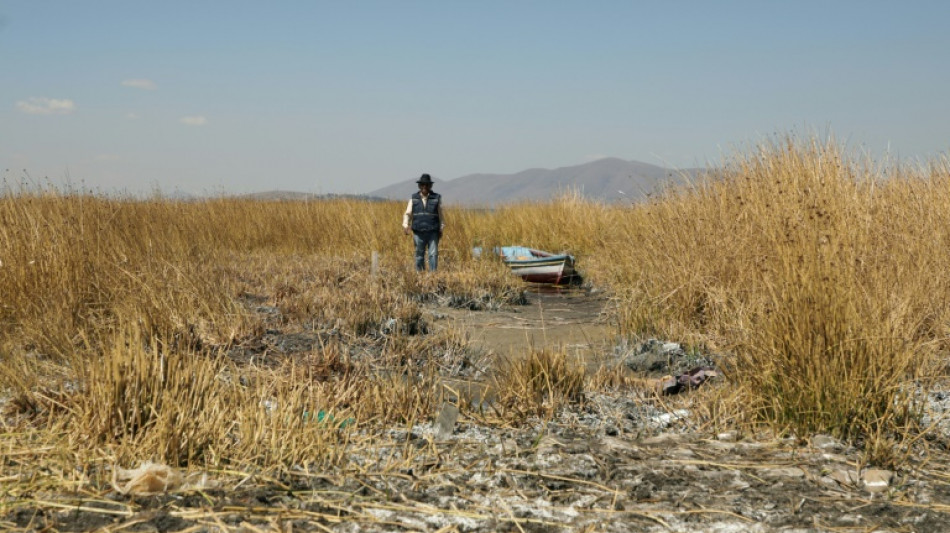
High in the Andes, Lake Titicaca's water levels fall to historic lows
Pedro de la Cruz stands beside his stranded boat and supplicates his God, lifting his arms and praying anxiously for rain to replenish Lake Titicaca, the massive body of water at a breath-sapping altitude in the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Peru.
"Dear God, make more rain come," the 74-year-old says, invoking Pachamama, Mother Earth for Indigenous people of the region. "Help us, please, we are parched here.... Make the rain showers come... Father in heaven, have pity."
De la Cruz, a former state employee, spoke in Aymara, his native language, as he surveyed what was once the shore of Lake Titicaca, some 45 miles (77 kilometers) west of the capital La Paz.
The waters of Lake Titicaca are within 10 inches (25 centimeters) of their all-time low, a record set in 1996, the chief forecaster for Bolivia's weather service (Senhami), Lucia Walper, tells AFP.
Along what was once the 700-mile shoreline of the lake, one now sees boats stranded on dry land and orphan docks stretched over nonexistent water.
Low levels mean that fish that ordinarily spawn near shore are now unable to, and that leads Edwin Katari, a 43-year-old fisherman, to mull a question.
"So where are the fish going to spawn?" Katari asks.
- Dark forecast –
Bolivia's Senhami has measured water levels of the lake since 1974.
At its highest point in 1986, water levels reached 12 feet higher than they are today, topping out at 12,504.2 feet (3,811 meters) above sea level. But in 1996, they had fallen to 12,491.4 feet above sea level.
Walper says falling water levels are "the result of climate change" and the outlook is not good.
"It is very probable that they keep falling until they hit even lower levels," she says.
A satellite survey still has not been made to see how much Lake Titicaca, which once had a surface area of 3,200 square miles (8,300 square kilometers), has shrunk.
It is the highest of the world's large lakes and is one of the largest in South America, after Venezuela's Lake Maracaibo (which is actually connected to the Caribbean Sea) and Brazil's Lagoa dos Patos, a coastal lagoon.
- La Nina and El Nino –
The level of Lake Titicaca "has been progressively decreasing due to many meteorological, hydrological and climatic factors," explains Walper, who emphasizes that "there is less rainfall."
"Over the years, each phenomenon, whether El Nino and/or La Nina, has been presenting a distortion in its parameters and factors," she points out, explaining the characteristics of these events -- associated with rains or droughts -- over time.
The rainfall and the inflow to the lake from Peruvian rivers "were not sufficient to generate the normal rises in times of rain," she says.
El Nino is a natural climatic event, generally associated with increased temperatures, drought in some parts of the world, and heavy rains in others. La Nina, on the other hand, causes the opposite effects, particularly a drop in temperatures.
Other stresses impact the lake. It is heavily polluted by waste from the city of El Alto, a metropolis of one million people in this landlocked country. Additionally, indiscriminate fishing has decimated species.
- Despair sets in –
Because the decline in water levels is linked to climate change, the solution "is a global issue," Walper adds.
The recent summit in Brazil of the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) reaffirmed the call for industrialized countries to fulfill their promises of economic resources to finance actions against climate change.
But in the villages around Lake Titicaca, despair has set in that water levels will never return to normal in the world's highest navigable sea.
"If there is no water, if there is no rain, we will not be able to live," frets De la Cruz.
S.Keller--BTB



