-
 Scandic Trust Group strengthens sales network with First Idea Consultant
Scandic Trust Group strengthens sales network with First Idea Consultant
-
Germany recall Sane, hand El Mala debut for World Cup qualifers

-
 India thump Australia to take 2-1 lead in T20 series
India thump Australia to take 2-1 lead in T20 series
-
Cameroon's Biya, world's oldest president, sworn in for 8th term

-
 Flick holding firm on Barca high line despite defensive woes
Flick holding firm on Barca high line despite defensive woes
-
Battered US businesses eye improved China trade at Shanghai expo

-
 France opt for Le Garrec as Dupont replacement for 'best team ever' South Africa
France opt for Le Garrec as Dupont replacement for 'best team ever' South Africa
-
Drugmaker AstraZeneca profit jumps as US business grows

-
 'Vibe coding' named word of the year by Collins dictionary
'Vibe coding' named word of the year by Collins dictionary
-
Vietnam evacuates thousands from coast ahead of Typhoon Kalmaegi

-
 European stocks fall after gains in Asia, US
European stocks fall after gains in Asia, US
-
MotoGP legend Agostini admires Marc Marquez's 'desire to win'

-
 Nepal searches for avalanche victims
Nepal searches for avalanche victims
-
Hezbollah rejects any negotiations between Lebanon and Israel

-
 Chapman blitz leads Black Caps to tight T20 victory over West Indies
Chapman blitz leads Black Caps to tight T20 victory over West Indies
-
France urges EU to sanction Shein platform

-
 France opt for Le Garrec as Dupont replacement for South Africa Test
France opt for Le Garrec as Dupont replacement for South Africa Test
-
Turmoil in tiaras at Miss Universe pageant in Thailand

-
 Probe into Thales defence group looking at Indonesian contract
Probe into Thales defence group looking at Indonesian contract
-
US to cancel flights as longest govt shutdown drags on

-
 Home in Nigeria, ex-refugees find themselves in a war zone
Home in Nigeria, ex-refugees find themselves in a war zone
-
Doncic's Lakers hold off Wembanyama's Spurs, Blazers silence Thunder

-
 For Turkey's LGBTQ community, draft law sparks existential alarm
For Turkey's LGBTQ community, draft law sparks existential alarm
-
Musk's $1 trillion pay package to face Tesla shareholder vote

-
 Tonga rugby league star out of intensive care after seizure
Tonga rugby league star out of intensive care after seizure
-
Argentine ex-president Kirchner goes on trial in new corruption case

-
 Dams, housing, pensions: Franco disinformation flourishes online
Dams, housing, pensions: Franco disinformation flourishes online
-
Endo returns as Japan look to build on Brazil win

-
 Franco captivates young Spaniards 50 years after death
Franco captivates young Spaniards 50 years after death
-
German steel industry girds for uncertain future

-
 IPL champions Bengaluru could be sold for 'as much as $2 billion'
IPL champions Bengaluru could be sold for 'as much as $2 billion'
-
Budget impasse threatens Belgium's ruling coalition

-
 New Zealand ex-top cop admits to having material showing child abuse, bestiality
New Zealand ex-top cop admits to having material showing child abuse, bestiality
-
BoE set for finely balanced pre-budget rate call

-
 Australian kingpin obtains shorter sentence over drug charge
Australian kingpin obtains shorter sentence over drug charge
-
Weatherald's unenviable Ashes task: fill giant hole at top left by Warner

-
 Ovechkin first to score 900 NHL goals as Capitals beat Blues
Ovechkin first to score 900 NHL goals as Capitals beat Blues
-
On Mexico City's streets, vendors fight to make it to World Cup

-
 Asian markets bounce from selloff as US jobs beat forecasts
Asian markets bounce from selloff as US jobs beat forecasts
-
Philippine death toll tops 140 as typhoon heads towards Vietnam

-
 Kyrgios targets 'miracle' Australian Open return after knee improves
Kyrgios targets 'miracle' Australian Open return after knee improves
-
'AI president': Trump deepfakes glorify himself, trash rivals

-
 Belgium probes drone sightings after flights halted overnight
Belgium probes drone sightings after flights halted overnight
-
Five things to know about 'forest COP' host city Belem

-
 World leaders to rally climate fight ahead of Amazon summit
World leaders to rally climate fight ahead of Amazon summit
-
Engine fell off US cargo plane before deadly crash: officials

-
 Mexican leader calls for tougher sexual harassment laws after attack
Mexican leader calls for tougher sexual harassment laws after attack
-
Meghan Markle set for big screen return: reports

-
 Japan deploys troops after wave of deadly bear attacks
Japan deploys troops after wave of deadly bear attacks
-
FIFA announce new peace prize to be awarded at World Cup draw in Washington


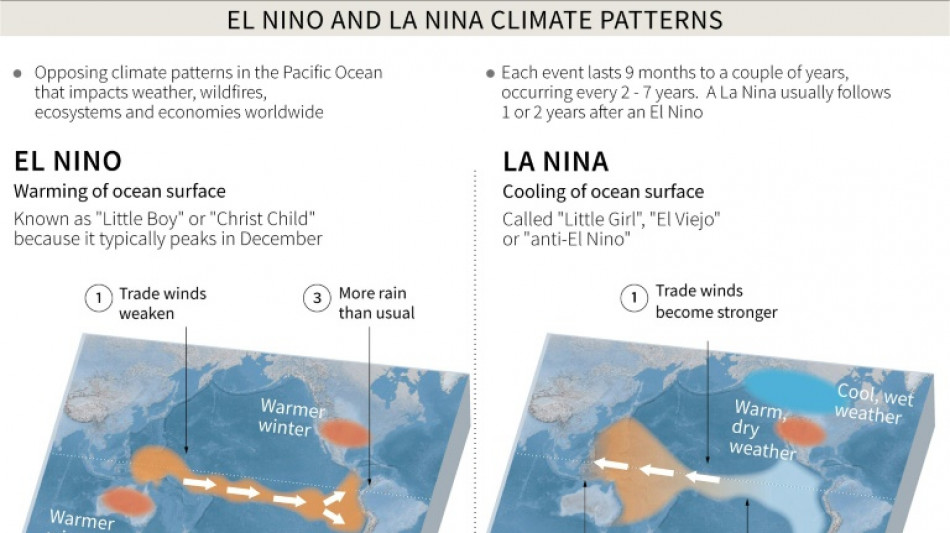
How El Nino could impact health, food and the economy
The El Nino weather phenomenon is just warming up, according to scientists, potentially paving the way for higher temperatures and extreme weather events in a year that has already seen plenty of both.
The first El Nino in years began last month, according to the World Meteorological Organization.
The naturally occurring warming of temperatures in the Pacific Ocean typically lasts between nine to 12 months, and is expected become stronger towards the end of the year.
Scientists have warned the impacts of El Nino -- combined with human-induced global warming -- will likely stretch beyond the weather.
- Disease -
Vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue, have been shown to expand their range as temperatures rise.
Scientists warned that El Nino, coming in addition to already dire global warming, could make the situation worse.
"We can see from previous El Ninos that we get increases and outbreaks of a wide range of vector-borne and other infectious diseases around the tropics, in the area that we know is most affected by El Nino," Madeleine Thomson, head of climate impacts at the Wellcome Trust charity, told journalists on Thursday.
The rise stems from two effects of El Nino: unusual rainfall that increases breeding sites for transmitters such as mosquitoes, and higher temperatures that speed up transmission rates of various infectious diseases.
An El Nino in 1998 was linked to a major malaria epidemic in the Kenyan Highlands.
– Health -
It is difficult to calculate exactly how much El Nino contributes to extreme weather events such as wildfires.
But heatwaves themselves pose a significant danger to health.
"It's sometimes named the silent killer because you don't necessarily see it as a threat," said Gregory Wellenius, head of a climate and health centre at Boston University.
"But heatwaves in fact kill more people than any other type of severe weather events."
More than 61,000 people are estimated to have died due to the heat in Europe alone last summer -- when there was no El Nino.
And July 2023 has now been confirmed as the hottest month in recorded history.
- Food security -
"In an El Nino year, there are countries where the chances of having a bad harvest increase, for example in South and Southeast Asia," said Walter Baethgen of the International Research Institute for Climate and Society.
Last month India, the largest rice exporter in the world, restricted its exports due to crop damage from irregular monsoon rains.
According to the researchers, such actions have the potential for dire consequences for countries dependent on the exports, such as Syria and Indonesia, that could face a "triple challenge" during El Nino.
"The rice harvest in those countries may be lower than normal, the rice trade may be more difficult or less accessible in the international market and because of that, the price of rice will be high," said Baethgen.
"This combination of factors pretty rapidly affects the food insecurity problems," he added.
- Economic growth -
The Panama Canal is central to global trade routes, but last week the passageway announced that low rainfall -- which meteorologists said was exacerbated by El Nino -- forced operators to restrict traffic, resulting in an expected $200 million drop in earnings.
The sidelined ships are just one example of how El Nino can hurt the global economy.
A study published in the journal Science in May estimated that past El Ninos cost the global economy more than $4 trillion in the years that followed them.
Impacts from both El Nino and global warming were "projected to cause $84 trillion in 21st-century economic losses", it said.
However researchers at Oxford Economics have argued against these projections, calling El Nino a "new risk, but not a gamechanger".
The costs may remain unclear, but the scientists hope the predictability of El Nino will improve preparedness for the challenges ahead posed by a warming world.
"Preparation is much more effective than emergency responses," Wellenius said.
M.Odermatt--BTB




