
-
 BMW reports rising profitability, shares jump
BMW reports rising profitability, shares jump
-
Bolivia Supreme Court orders release of jailed ex-president Jeanine Anez

-
 Wall Street stocks rise after positive jobs data
Wall Street stocks rise after positive jobs data
-
'Hostage diplomacy': longstanding Iran tactic presenting dilemma for West

-
 Rybakina stays perfect at WTA Finals with win over alternate Alexandrova
Rybakina stays perfect at WTA Finals with win over alternate Alexandrova
-
Le Garrec welcomes Dupont help in training for Springboks showdown

-
 Brussels wants high-speed rail linking EU capitals by 2040
Brussels wants high-speed rail linking EU capitals by 2040
-
Swiss business chiefs met Trump on tariffs: Bern

-
 Spain's exiled king recounts history, scandals in wistful memoir
Spain's exiled king recounts history, scandals in wistful memoir
-
Wall Street stocks steady after positive jobs data

-
 Trump blasts Democrats as government shutdown becomes longest ever
Trump blasts Democrats as government shutdown becomes longest ever
-
Indian pilgrims find 'warm welcome' in Pakistan despite tensions

-
 Inter and AC Milan complete purchase of San Siro
Inter and AC Milan complete purchase of San Siro
-
Swedish authorities inspect worksite conditions at steel startup Stegra

-
 Keys withdraws from WTA Finals with illness
Keys withdraws from WTA Finals with illness
-
Prince Harry says proud to be British despite new life in US

-
 EU strikes last-ditch deal on climate targets as COP30 looms
EU strikes last-ditch deal on climate targets as COP30 looms
-
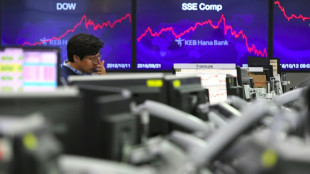
Stocks retreat as tech bubble fears grow
-
 Shein opens first permanent store amid heavy police presence
Shein opens first permanent store amid heavy police presence
-
West Indies edge New Zealand despite Santner brilliance

-
 French pair released by Iran await return home
French pair released by Iran await return home
-
German factory orders up but outlook still muted

-
 Death toll tops 100 as Philippines digs out after typhoon
Death toll tops 100 as Philippines digs out after typhoon
-
Attack on key city in Sudan's Kordofan region kills 40: UN

-
 'No one could stop it': Sudanese describe mass rapes while fleeing El-Fasher
'No one could stop it': Sudanese describe mass rapes while fleeing El-Fasher
-
Champagne and cheers across New York as Mamdani soars to victory

-
 Medieval tower collapse adds to Italy's workplace toll
Medieval tower collapse adds to Italy's workplace toll
-
BMW boosts profitability despite China, tariff woes

-
 South Africa's Wiese wary of 'hurt' France before re-match
South Africa's Wiese wary of 'hurt' France before re-match
-
Beyond limits: Croatian freediver's breathtaking record

-
 Tottenham supporting Udogie after alleged gun threat in London
Tottenham supporting Udogie after alleged gun threat in London
-
Thunder roll Clippers to stay unbeaten as SGA keeps streak alive

-
 In appeal, Australian mushroom murderer alleges 'miscarriage of justice'
In appeal, Australian mushroom murderer alleges 'miscarriage of justice'
-
Toyota hikes profit forecasts 'despite US tariffs'

-
 Ex-France lock Willemse challenges Meafou to become 'the bully'
Ex-France lock Willemse challenges Meafou to become 'the bully'
-
Ukrainians to honour sporting dead by building country they 'died for': minister

-
 At least 7 dead after UPS cargo plane crashes near Louisville airport
At least 7 dead after UPS cargo plane crashes near Louisville airport
-
US Supreme Court hears challenge to Trump tariff powers

-
 US government shutdown becomes longest in history
US government shutdown becomes longest in history
-
India's Modi readies bellwether poll in poorest state

-
 Green goals versus growth needs: India's climate scorecard
Green goals versus growth needs: India's climate scorecard
-
Where things stand on China-US trade after Trump and Xi talk

-
 Sri Lanka targets big fish in anti-corruption push
Sri Lanka targets big fish in anti-corruption push
-
NY elects leftist mayor on big election night for Democrats

-
 Injured Jordie Barrett to miss rest of All Blacks tour
Injured Jordie Barrett to miss rest of All Blacks tour
-
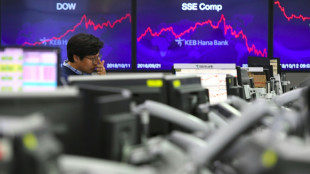
Asian markets tumble as tech bubble fears grow
-
 Pay to protect: Brazil pitches new forest fund at COP30
Pay to protect: Brazil pitches new forest fund at COP30
-
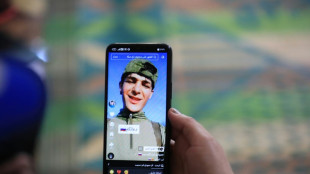
Iraq's social media mercenaries dying for Russia
-
 Young leftist Trump foe elected New York mayor
Young leftist Trump foe elected New York mayor
-
Concerns at ILO over expected appointment of close Trump advisor


Alzheimer's drug data shows results but also risks
Experts hailed full data Wednesday showing a new drug can slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer's patients, but warned improvements were comparatively small and the treatment can have serious side effects.
Preliminary data from a trial of lecanemab was released in September and found it slowed cognitive decline by 27 percent across an 18-month period.
The complete trial data, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, fleshes out those findings but also raises concern about the incidence of "adverse effects" including brain bleeds and swelling.
The results showed 17.3 percent of patients administered the drug experienced brain bleeds, compared with nine percent of those receiving a placebo.
And 12.6 percent of those taking the drug experienced brain swelling, compared with just 1.7 percent of those in the placebo group.
Deaths were reported at approximately the same rate in both arms of the trial of the drug, which was developed by firms Biogen and Eisai.
The results were broadly welcomed by researchers and campaigners for patients with the disease, including Bart De Strooper, director of the UK Dementia Research Institute.
"This is the first drug that provides a real treatment option for people with Alzheimer's," he said.
"While the clinical benefits appear somewhat limited, it can be expected that they will become more apparent if the drug is administered over a longer time period."
- Longer trials needed -
In Alzheimer's disease, two key proteins, tau and amyloid beta, build up into tangles and plaques, known together as aggregates, which cause brain cells to die and lead to brain shrinkage.
Lecanemab works by targeting amyloid, and De Strooper said the drug proved effective at clearing it but also had "beneficial effects on other hallmarks of Alzheimer's, including tau".
The phase 3 trial involved nearly 1,800 people, divided between those given the drug and given a placebo, and ran over 18 months.
They were assessed on a clinical scale for Alzheimer's patients that measures cognition and function, as well as for changes in amyloid levels and other indicators.
But Tara Spires-Jones, programme lead at the UK Dementia Research Institute, noted that "there is not an accepted definition of clinically meaningful effects in the cognitive test they used".
"It is not clear yet whether the modest reduction in decline will make a big difference to people living with dementia. Longer trials will be needed to be sure that the benefits of this treatment outweigh the risks," she added.
The drug also only targets those in the early stages of the disease with a certain level of amyloid build-up, limiting the number of people who could potentially use the treatment.
And as Alzheimer's is not always caught quickly, some experts said an overhaul in early diagnosis would be needed to ensure more people could benefit.
"This isn't the end of the journey for lecanemab –- it's being explored in further trials to see how well it works over a longer period of time," said Richard Oakley, associate director of research at the Alzheimer's Society.
"The safety of drugs is crucial and lecanemab did have side effects, but they will be closely looked at when decisions are made about whether or not to approve lecanemab, to see if the benefits outweigh the risks," he said.
Biogen and Eisai previously brought the Alzheimer's drug Aduhelm to market, but there was significant controversy over the evidence that it worked, and its approval led to three high-level resignations in the US Food and Drug Administration.
O.Krause--BTB




