
-
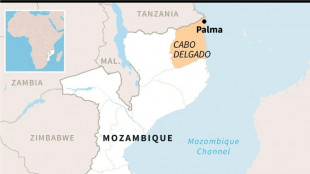 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
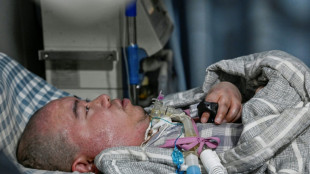
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report


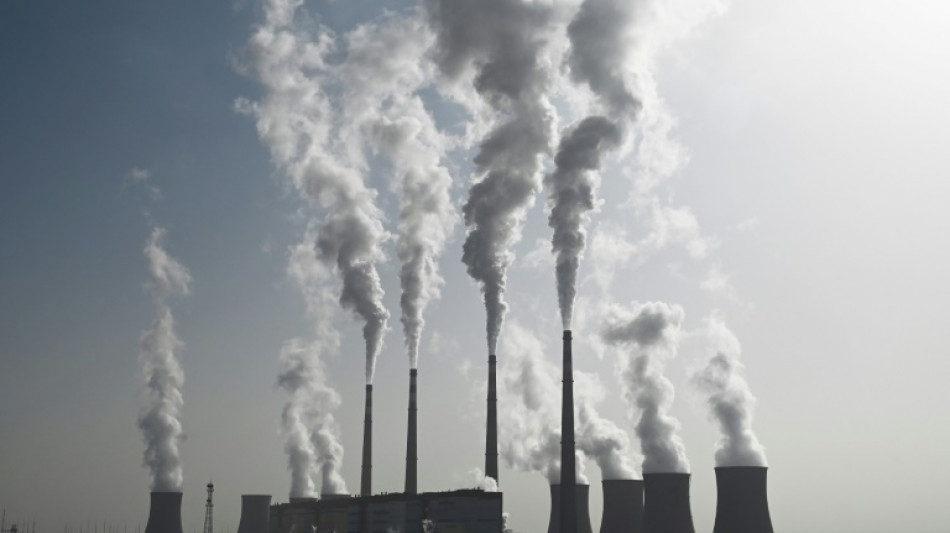
China nears peak emissions as climate envoy meets US counterpart
As climate envoys from the world's top two greenhouse gas producers meet in Beijing this week, experts say China's emissions may finally be nearing their peak.
US climate envoy John Podesta will be looking to solidify Beijing's commitments -- which include topping out its planet-warming emissions by 2030 -- as he meets this week with counterpart Liu Zhenmin.
But with Beijing installing renewable capacity at record speed, and a construction slump dragging down emissions-heavy steel production, there are signs China could hit the peak early, though uncertainties remain.
"So much clean electricity... is being added that China can peak its emissions right now, if those additions are maintained and if overall energy demand growth moderates," said Lauri Myllyvirta of the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA).
China is building almost twice as much wind and solar energy capacity as every other country combined, data showed earlier this year.
That breakneck installation saw it hit a target for wind and solar capacity in August, six years ahead of schedule.
And while coal remains king in China's electricity system, there are signs the world's second-biggest economy may be weaning itself off the fossil fuel.
Coal power permits fell 83 percent in the first half of this year, and no new coal-based steelmaking projects were approved in the same period.
China is the world's top emitter and biggest consumer of coal, making its progress central to global climate goals, said Myllyvirta.
"Whether China's emissions growth continues or turns into a decline is absolutely decisive for our ability to peak global emissions and start reducing them towards net zero," he told AFP.
- 'Establishing before breaking' -
In addition to solar and wind, China's clean energy mix includes a significant amount of hydro and nuclear power.
China is the world's fastest growing nuclear power producer, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency, and last month alone approved plans for 11 new nuclear reactors.
But despite the growth in non-carbon energy sources, China's demand for coal still jumped last year, helping drive a global increase.
And coal-fired power generation is projected to grow again this year in China, albeit at the lowest rate in almost a decade, according to the International Energy Agency.
"However, there is significant uncertainty concerning the availability of hydropower and the growth in power demand," it warned.
Even as coal permits fell, construction began on more than 41 gigawatts of coal projects during the first half of 2024, CREA and Global Energy Monitor said.
That nearly equalled 2022 levels and accounts for over 90 percent of new coal construction worldwide.
The continued build-out reflects China's "cautious approach to its clean electricity transition," said Muyi Yang, senior electricity policy analyst at energy think tank Ember.
That strategy is "characterised by 'establishing before breaking', first building a robust clean electricity system before phasing down fossil fuels", Yang told AFP.
China has already seen drought hit hydropower output, something that is likely to become more frequent with climate change.
But as it builds out other renewable and non-carbon alternatives, its reliance on coal to plug gaps should decline, said Yang.
"China is fast approaching this critical juncture."
- 'Long way to go' -
There are other headwinds, including grid and market reforms, and "opposition from vested interests", warned Myllyvirta.
That could mean even massive renewable growth is insufficient to cover increasing demand.
And it remains an open question whether a peak in China's emissions would be followed by a progressive decline, or merely a plateau.
Still, the direction of travel and signals from top leadership offer cause for some optimism, analysts say.
A survey of 89 experts last year found the majority expected China to peak carbon emissions before 2030.
However, China has declined to sign a global pledge to reduce methane emissions by at least 30 percent from 2020 levels by 2030.
Podesta is expected to press his counterpart on efforts to reduce the potent greenhouse gas.
The talks may also cover ongoing rows over China's domination of green manufacturing, which has sparked tariffs from Washington and elsewhere.
"Those countries that don't want to be reliant on China for that supply still need to sort out their supply chains," Myllyvirta said.
"They have a long way to go in that respect."
S.Leonhard--VB



