
-
 Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
-
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China

-
 US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
-
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites

-
 Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
-
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study

-
 Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
-
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits

-
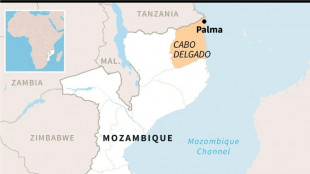 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain


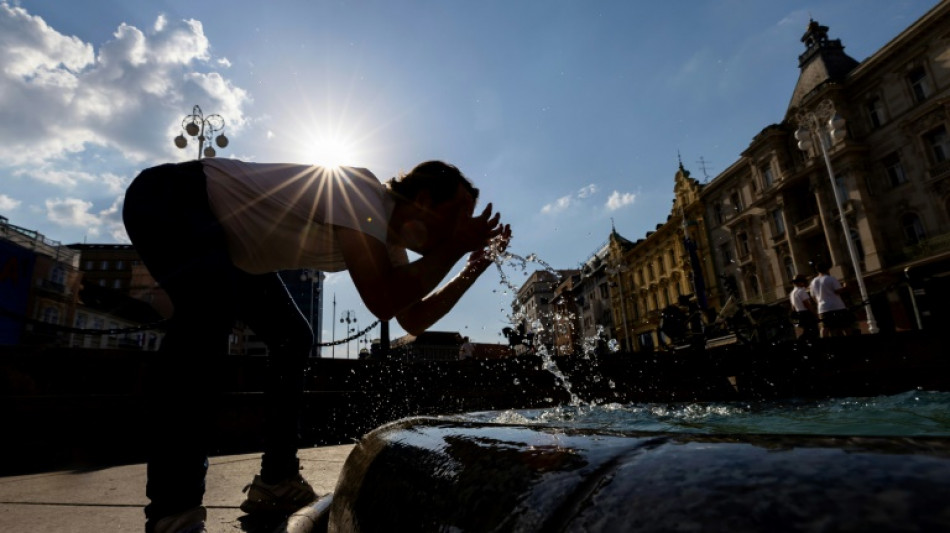
Climate change is fuelling rise in hot nights: analysis
Human-induced climate change is significantly increasing the number of hot nights for nearly one in three people around the world, a global analysis said Thursday.
High nighttime temperatures can become dangerous if they prevent the human body from cooling off and recovering from daytime heat.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends keeping room temperature at or below 24 degrees Celsius during the night -- a threshold above which sleep can be uncomfortable.
This is especially important for vulnerable people, such as babies, the elderly and people with chronic health conditions, according to the WHO.
But burning coal, oil and gas which releases climate-warming emissions into the atmosphere is fuelling a rise in nights above 25C, according to Climate Central, an independent group of scientists and climate communicators.
- 'Cascading impacts' -
Around 2.4 billion people experienced at least two additional weeks on average per year over the past decade when the thermometer didn't fall below 25C at night, it found.
"Warmer nighttime temperatures, particularly during hot times of the year, can harm sleep and can reduce physical recovery from hot daytime temperatures, both of which can have cascading impacts on health outcomes," Nick Obradovich, a chief scientist at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research, told AFP.
This year has seen heat records tumble, with extreme temperatures gripping vast swathes of the world from India to Saudi Arabia and Mexico, often staying high at night.
The analysis compared the annual average of hot nights between 2014 and 2023 with a counterfactual world without human-caused climate change based on a peer-reviewed methodology using models that incorporate historical data.
Long-term historical data being patchy or missing for many countries, researchers decided to compare their findings with an imaginary world where the only thing that has changed is the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
The Caribbean nation of Trinidad and Tobago experienced the largest increase of any country, with an extra 47 nights per year above 25C. The Indian city of Mumbai endured an additional two months of hot nights.
The 25C threshold "isn't some hard-and-fast number below which health is fine and above which health is harmed," Obradovich, who was not involved in the analysis, explained.
"Hotter nighttime temperatures, on average, are worse for health," he added, but the impacts on people vary.
However, when heat is coupled with high humidity levels, the consequences can turn deadly.
Several studies have shown that nocturnal temperatures above 25C deteriorate the quality and length of sleep --- which is vital for humans to function -- and increase the risks of strokes, cardiovascular conditions and mortality.
The elderly and people on lower-income are disproportionally affected, researchers previously found.
D.Bachmann--VB



