
-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
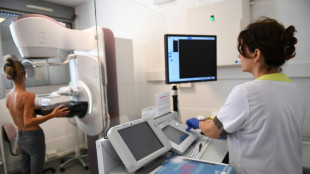 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'

-
 Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
-
Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?

-
 Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
-
Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
-
EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'

-
 Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
-
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy


Planet 'on the brink', with new heat records likely in 2024: UN
Global temperatures "smashed" heat records last year, as heatwaves stalked oceans and glaciers suffered record ice loss, the United Nations said Tuesday -- warning 2024 was likely to be even hotter.
The annual State of the Climate report by the UN weather and climate agency confirmed preliminary data showing 2023 was by far the hottest year ever recorded.
And last year capped off "the warmest 10-year period on record", the World Meteorological Organization said, with even hotter temperatures expected.
"There is a high probability that 2024 will again break the record of 2023", WMO climate monitoring chief Omar Baddour told reporters.
Reacting to the report, UN chief Antonio Guterres said it showed "a planet on the brink".
"Earth's issuing a distress call," he said in a video message, pointing out that "fossil fuel pollution is sending climate chaos off the charts", and warning that "changes are speeding up".
The WMO said that last year the average near-surface temperature was 1.45 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels -- dangerously close to the critical 1.5-degree threshold that countries agreed to avoid passing in the 2015 Paris climate accords.
- 'Red alert' -
"I am now sounding the red alert about the state of the climate," Saulo told reporters, lamenting that "2023 set new records for every single climate indicator".
The organisation said many of the records were "smashed" and that the numbers "gave ominous new significance to the phrase 'off the charts'."
"What we witnessed in 2023, especially with the unprecedented ocean warmth, glacier retreat and Antarctic sea ice loss, is cause for particular concern," Saulo said.
One especially worrying finding was that marine heatwaves gripped nearly a third of the global ocean on an average day last year.
And by the end of 2023, more than 90 percent of the ocean had experienced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, the WMO said.
More frequent and intense marine heatwaves will have "profound negative repercussions for marine ecosystems and coral reefs", it warned.
Meanwhile key glaciers worldwide suffered the largest loss of ice since records began in 1950, "driven by extreme melt in both western North America and Europe".
In Switzerland, where the WMO is based, Alpine glaciers lost 10 percent of their remaining volume in the past two years alone, it said.
The Antarctic sea ice extent was also "by far the lowest on record", WMO said.
- Rising sea levels -
The maximum area at the end of the southern winter was around one million square kilometres below the previous record year -- equivalent to the size of France and Germany combined, according to the report.
Ocean warming and the rapidly melting glaciers and ice sheets drove the sea level last year to its highest point since satellite records began in 1993, WMO said.
The agency highlighted that the global mean sea level rise over the past decade (2014-2023) was more than double the rate in the first decade of satellite records.
The dramatic climate shifts, it said, are taking a heavy toll worldwide, fuelling extreme weather events, flooding and drought, which trigger displacement and drive up biodiversity loss and food insecurity.
"The climate crisis is THE defining challenge that humanity faces and is closely intertwined with the inequality crisis," Saulo said.
- 'Glimmer of hope' -
The WMO did highlight one "glimmer of hope": surging renewable energy generation.
Last year, renewable energy generation capacity -- mainly from solar, wind and hydropower -- increased by nearly 50 percent from 2022, it said.
The report sparked a flood of reactions and calls for urgent action.
"Our only response must be to stop burning fossil fuels so that the damage can be limited," said Martin Siegert, a geosciences professor at the University of Exeter.
Jeffrey Kargel, a senior scientist at the Planetary Science Institute, stressed that the dramatic climae shifts "do not connote the inevitable doom of civilisation".
The outcome, he said, "depends on how people and governments change or don't change behaviours".
Saulo acknowledged that the cost of climate action might seem high.
"But the cost of climate inaction is much higher," she said. "The worst thing would be to do nothing."
Guterres also emphasised that there was still time to "avoid the worst of climate chaos".
"But leaders must step up and act -- now."
F.Mueller--VB



