
-
 Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
-
Slot warns Liverpool 'can't afford mistakes' in top-four scrap

-
 Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
-
Artist chains up thrashing robot dog to expose AI fears

-
 Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
-
French PM forces final budget through parliament

-
 French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
-
Dutch watchdog launches Roblox probe over 'risks to children'

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
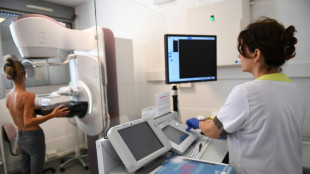
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge


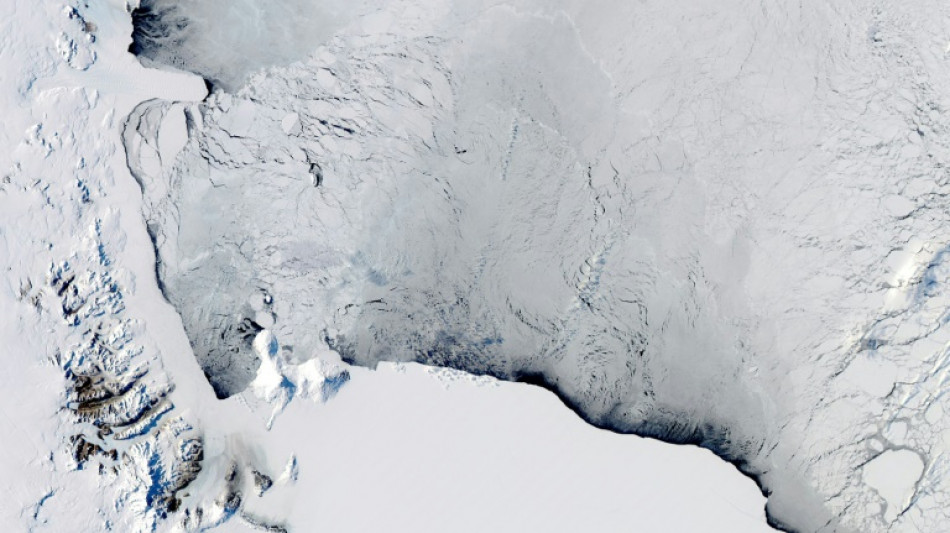
Over 40% of Antarctica's ice shelves lost mass in 25 years: study
More than 40 percent of Antarctica's ice shelves lost volume in 25 years, increasing the risk of sea levels rising and with human-induced warming the likely cause, scientists said on Thursday.
Ice shelves are freshwater extensions of the ice sheets that cover much of Antarctica, floating on the seas that surround the vast and ecologically fragile continent.
They act as giant "plugs" stabilising massive glaciers, slowing down the flow of ice into the ocean.
When ice shelves shrink, these plugs weaken and the rate of ice loss from the glaciers increases.
In a study published in the journal Science Advances on Thursday, scientists analysed more than 100,000 satellite radar images to assess the health of Antarctica's 162 ice shelves.
They found that the volume of 71 fell from 1997 to 2021.
"Acceleration of glaciers due to ice shelf deterioration has added about six millimetres to global sea level since the start of the study period," said Benjamin Davison, a research fellow at the University of Leeds in Britain who led the study.
Although Antarctica only contributes six percent to total sea level rise, "it could increase substantially in the future if ice shelves continue to deteriorate," he told AFP.
The almost 67 trillion tonnes of ice that leaked into the ocean during the quarter-century under review was offset by 59 trillion tonnes being added, giving a net release of 7.5 trillion tonnes of meltwater.
"We expected most ice shelves to go through cycles of rapid but short-lived shrinking, then to regrow slowly," said Davison.
"Instead, we see that almost half of them are shrinking with no sign of recovery."
Without human-caused warming, some ice regrowth would have occurred on West Antarctica's ice shelves through a natural variation in climate patterns, he added.
- 'Steady attrition' -
Different winds and ocean currents affect Antarctica, resulting in changes that are uneven.
Almost all of western Antarctica's ice shelves lost volume as they were exposed to warmer water that eroded them from below.
On the western Getz Ice Shelf alone, melting at the base was responsible for 95 percent of the net loss of 1.9 trillion tonnes of ice.
Calving -- a process whereby chunks of ice break away into the ocean -- accounted for the rest.
Anna Hogg, a University of Leeds professor who co-authored the study, said 48 ice shelves lost more than 30 percent of their initial mass during the period.
In eastern Antarctica, ice shelves mostly stayed the same or grew because a band of cold water along the coast protected them from warmer currents.
"We are seeing a steady attrition due to melting and calving... This is further evidence that Antarctica is changing because the climate is warming," Hogg added.
The melting of ice shelves could have major implications for global ocean circulation, which moves vital nutrients, heat and carbon from the polar ecosystem.
The added freshwater may have diluted the dense and salty waters of the Southern Ocean and made them lighter, delaying their sinking process and potentially weakening the global ocean conveyor belt.
"The ocean absorbs a lot of atmospheric heat and carbon and the Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica is the largest contributor to that, so it's a hugely important regulator of global climate," Davison told AFP.
F.Wagner--VB




