
-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
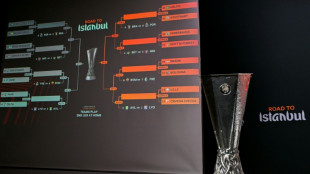 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support

-
 Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
-
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties

-
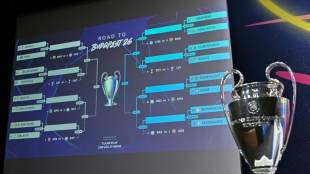 Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
-
Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble

-
 Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
-
Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump

-
 Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
-
Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat

-
 Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention
Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention
-
'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal

-
 Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
-
Slot warns Liverpool 'can't afford mistakes' in top-four scrap

-
 Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens
-
Artist chains up thrashing robot dog to expose AI fears

-
 Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final
-
French PM forces final budget through parliament

-
 French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits
-
Dutch watchdog launches Roblox probe over 'risks to children'

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam


Humanity deep in the danger zone of planetary boundaries: study
Human activity and appetites have weakened Earth's resilience, pushing it far beyond the "safe operating space" that keeps the world liveable for most species, including our own, a landmark study said Wednesday.
Six of nine planetary boundaries -- climate change, deforestation, biodiversity loss, synthetic chemicals including plastics, freshwater depletion, and nitrogen use -- are already deep in the red zone, an international team of 29 scientists reported.
Two of the remaining three -- ocean acidification along with the concentration of particle pollution and dust in the atmosphere -- are borderline, with only ozone depletion comfortably within safe bounds.
The planetary boundaries identify "the important processes that keep the Earth within the kind of the living conditions that prevailed over the last 10,000 years, the period when humanity and modern civilisation developed", said lead author Katherine Richardson, a professor at the University of Copenhagen's Globe Institute.
The study is the second major update of the concept, first unveiled in 2009 when only global warming, extinction rates, and nitrogen had transgressed their limits.
"We are still moving in the wrong direction," said co-author Johan Rockstrom, director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and a co-creator of the schema.
"And there's no indications that any of the boundaries" -- except the ozone layer, slowly on the mend since the chemicals destroying it were banned -- "have started to bend in the right direction", he told journalists in a briefing.
"This means we are losing resilience, that we are putting the stability of the Earth system at risk."
The study quantifies boundaries for all nine interlocking facets of the Earth system.
- Headed for disaster -
For biodiversity, for example, if the rate at which species disappear is less than 10 times the average extinction rate over the last 10 million years, that is deemed acceptable.
In reality, however, extinctions are occurring at least 100 times faster than this so-called background rate, and 10 times faster than the planetary boundary limit.
For climate change, that threshold is keyed to the concentration of atmospheric CO2, which remained very close to 280 parts per million (ppm) for at least 10,000 years prior to the industrial revolution.
That concentration is today 417 ppm, far above the safe boundary of 350 ppm.
"On climate, we're still following a pathway that takes us unequivocally to disaster," said Rockstrom. "We're headed for 2.5C, 2.6C or 2.7C -- a place we haven't seen for the past four million years."
"There's no evidence whatsoever that humans can survive in that environment," he added.
Thousands upon thousands of chemical compounds created by humans -- from micro-plastics and pesticides to nuclear waste and drugs that have leached into the environment -- were quantified for the first time in the new research, and found to exceed safe limits.
Likewise for the depletion of "green" and "blue" water, freshwater coming from soil and plants on the one hand, and from rivers and lakes on the other.
- Setting limits -
An important finding of the new update is that different boundaries feed off and amplify each other.
The study examines in particular the interaction between increasing CO2 concentration and damage to the biosphere, especially forest loss, and projects temperature increases when one or both increase.
It shows that even if humanity rapidly draws down greenhouse gas emissions, unless destruction of carbon-absorbing forests is halted at the same time rising global temperatures could tip the planet onto a trajectory of additional warming that would be hard to stop.
"Next to climate change, integrity of the biosphere is the second pillar for our planet," said co-author Wolfgang Lucht, head of Earth System Analysis at PIK.
"We are currently destabilising this pillar by taking out too much biomass, destroying too much habitat, deforesting too much land."
All the boundaries can be brought back into the safe operating space, the study concluded.
"It's just a question of setting limits for the amount of waste we put into the open environment and the amount of living and non-living raw materials we take out," said Richardson.
Hotly debated at first, the planetary boundaries framework quickly became a pillar of Earth system science, with its influence extending today into the realm of policy and even business.
N.Schaad--VB




