
-
 Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
-
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files

-
 South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
-
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing

-
 Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
-
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery

-
 US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
-
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown

-
 Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
-
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest

-
 Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
-
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains

-
 Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
-
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday

-
 Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
-
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon

-
 Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
-
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation

-
 UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
-
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race

-
 Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
-
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup

-
 Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
-
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns

-
 Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
-
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin

-
 Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs
-
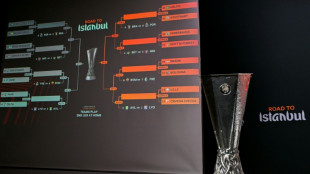
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
 US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
-
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief

-
 New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support
-
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe

-
 Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties
-
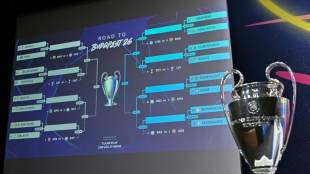
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
-
 Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow
Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow
-
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'

-
 Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble
Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble
-
Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa

-
 Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump
Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump
-
Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'

-
 Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat
Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat
-
Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention

-
 'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal
'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal
-
Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Slot warns Liverpool 'can't afford mistakes' in top-four scrap
Slot warns Liverpool 'can't afford mistakes' in top-four scrap
-
Paris show by late Martin Parr views his photos through political lens

-
 Artist chains up thrashing robot dog to expose AI fears
Artist chains up thrashing robot dog to expose AI fears
-
Alcaraz outlasts Zverev in epic to reach maiden Australian Open final

-
 French PM forces final budget through parliament
French PM forces final budget through parliament
-
French-Nigerian artists team up to craft future hits

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.52% | 51.435 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.69% | 16 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.65% | 83.78 | $ | |
| NGG | -0.43% | 84.69 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.72% | 93.26 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.26% | 23.634 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.17% | 24.02 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.27% | 14.67 | $ | |
| BCE | 0.08% | 25.505 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.42% | 13.01 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.05% | 60.24 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.35% | 79.105 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.42% | 35.66 | $ | |
| BP | -0.09% | 38.005 | $ | |
| RIO | -3.58% | 91.84 | $ |

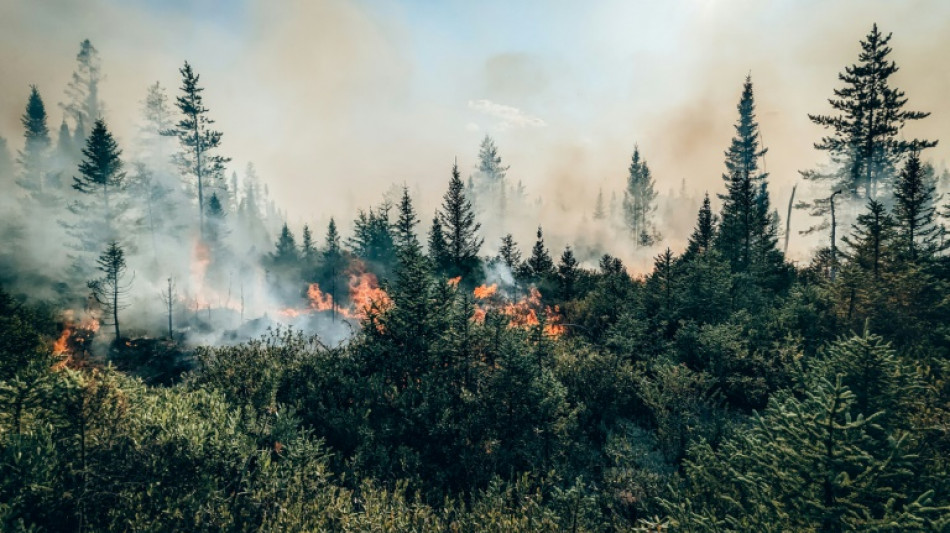
Climate change supercharged 'fire weather' behind Canada blazes
Human-caused climate change made 2023's severe, months-long "fire weather" conditions that powered Canada's record-breaking blazes at least seven times more likely to happen, according to a new scientific analysis published Tuesday.
The study by the World Weather Attribution group also found that over the year, fire-prone conditions were 50 percent more intense as a result of global warming, primarily a result of burning fossil fuels.
"As we continue to warm the planet, these kinds of events are going to get more frequent and they're going to get more intense," first author Clair Barnes, an environmental statistician at Imperial College London, told AFP.
Canada is experiencing its most devastating fire season ever, a result of record high temperatures, low humidity and early thaw of snow melt. Nearly 15.3 million hectares (37.8 million acres) have burned: an area larger than Greece, and more than double the previous 1989 record.
Some 200,000 people have been evacuated, at least four have died, and smoke from the burning forests has led to dangerous air pollution spreading across much of Canada and the United States to the south -- driving spikes in emergency department visits and even school closures.
As of late July, the forest fires had directly emitted more than a billion tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as well as methane and nitrous oxide that had a combined greenhouse effect equivalent of a further 110 million tons of carbon dioxide, according to recent research.
For the current study, scientists examined the eastern province of Quebec, honing in on zones that are similar in climate and vegetation. The region saw an exceptionally high number of fires in May and June, when national temperature records were smashed by 0.8 degrees Celsius (1.4 degrees Fahrenheit).
Because wildfires are highly complex and not driven solely by climate, the researchers focused instead on conditions conducive to blazes, using a metric called the Fire Weather Index (FWI).
This combines temperature, wind speed, humidity and precipitation. The team accumulated this data from January to July to derive a measure of severity of fire weather over the entire season.
While Quebec's fires were unprecedented, analysis of the recent climate record indicated the seasonal conditions causing the blazes are no longer rare, occurring once every 25 years. This means they now have a four percent chance of happening every year.
To understand the contribution of man-made global warming, they used computer model simulations to compare the climate as it is today, after about 1.2C (2.2F) of global warming since the late 1800s, with the climate of the past.
This showed climate change had made seasons of this severity at least seven times more likely to occur compared to pre-industrial times. Barnes stressed, however, that this was a lower-bound estimate, with the researchers choosing to be conservative in the face of statistical uncertainty.
- Indigenous communities hit hardest -
Yan Boulanger, an ecologist with the Canadian Forest Service and the report's second author, told AFP the cumulative impact of circumstances favorable to fire was key. "It's because those fire weather conditions lasted so long that those fires could grow so big."
The team also identified the seven-day-stretch when fire weather conditions were at their highest, and found such peak conditions were more than twice as likely to occur than in the past, as a result of climate change.
If the world continues burning fossil fuels at high rates, the likelihood and intensity of severe fire weather conditions will only increase, the analysis showed.
These fires imperil the future of the forestry sector, Boulanger warned, with a question mark over whether regeneration efforts can keep up with losses.
The most impacted communities meanwhile are remote and have relatively few resources, including Indigenous peoples, who made up 75 percent of those evacuated in July.
"This increasing severity of extreme events and likelihood of extreme events is not going to stop until we reach net zero and stop adding extra greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere," said Barnes, adding it's "not too late" to lobby political leaders to change course.
Y.Bouchard--BTB




