
-
 Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice
Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice
-
Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday

-
 Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
-
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems

-
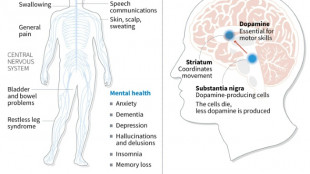 Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'

-
 North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
-
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer

-
 Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
-
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold

-
 Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
-
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
-
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett

-
 Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
-
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche

-
 Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
-
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets

-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup


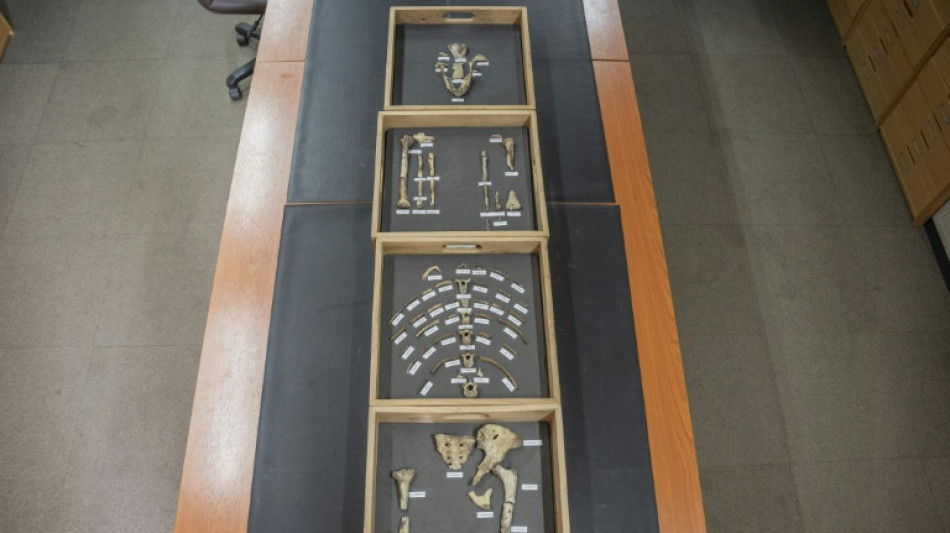
Human ancestor Lucy still has secrets 50 years after discovery
She was, for a while, the oldest known member of the human family. Fifty years after the discovery of Lucy in Ethiopia, the remarkable remains continue to yield theories and questions.
In a non-descript room in the National Museum of Ethiopia, the 3.18-million-year-old bones are delicately removed from a safe and placed on a long table.
They consist of fossilised dental remains, skull fragments, parts of the pelvis and femur that make up the world's most famous Australopithecus afarensis, Lucy.
The hominid was discovered on November 24, 1974, in the Afar region of northeast Ethiopia by a team of scientists led by Maurice Taieb, Yves Coppens, Donald Johanson, Jon Kalb, and Raymonde Bonnefille.
The 52 bone fragments, amounting to some 40 percent of Lucy's skeleton, was, at the time, the most complete ever found, and revolutionised the understanding of our ancestors.
The skeleton was initially called A.L-288-1, in reference to Afar and its geolocation.
But the researchers nicknamed it Lucy after The Beatles' song "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds", which they listened to after celebrating their discovery.
Lucy walked on two legs and is thought to have died aged between 11 and 13 -- considered an adult for this species. She was 1.10 metres tall (3.6 feet) and weighed 29 kg (64 pounds).
For Sahleselasie Melaku, the 31-year-old head of the palaeontology department, Lucy's discovery represented an emergence from a "dark age" in our understanding of human ancestors.
"The impact of the discovery was very big in the discipline and even the whole world," he told AFP.
Lucy showed that members of the human family existed beyond three million years ago, and she also provided a template for fitting together later bone discoveries.
The amount of information that can be gleaned from the bones has allowed some highly detailed theories about Lucy's life.
A slightly deformed vertebra, for instance, "means she probably had back problems", said Melaku.
- 'Exceptional' -
Jean-Renaud Boisserie, a paleonthologist specialised in Ethiopia and the research director at the French National Centre for Scientific Research said it was an "exceptional" breakthrough for the discipline.
"We basically knew very little about the period of three million years ago, and we had nothing as complete," he said.
Lucy was often described as "the grandmother of humanity", but more recent discoveries suggest she may have been more like an aunt or a cousin, experts say.
Skeletal finds in places like Ethiopia, South Africa and Kenya have complicated the picture and led to much debate about when different species of hominid emerged and which should be classified as part of the human or chimpanzee families.
The discovery of "Toumai" in Chad in 2001 -- a skull dated to six or seven million years old -- suggested the human family may go much further back than previously thought.
Meanwhile, Lucy has yet to reveal all her secrets.
A study published in 2016 argued she spent a third of her time in trees, where she nested, and had highly developed upper limbs.
Another study that year in the American journal Plos One theorised that she died after falling from a tree.
A 2022 study in Nature, focused on Lucy's pelvis, concluded that newborn members of Australopithecus had a very immature brain, like human newborns today, and required parental support to survive.
"There are a lot of unanswered questions," said Melaku with a smile. "Especially, we don't know much more about the early livelihoods of these early human ancestors."
The museum receives frequent requests to study it, but the iconic skeleton no longer leaves Ethiopia.
Wider scientific progress and advanced equipment are opening up new avenues for research.
"The studies that can be carried out on her, on her peers, pose the scientific questions of tomorrow," said Boisserie.
"Material as exceptional as this plays a driving role in the evolution of research."
D.Bachmann--VB




