-
 Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France
Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France
-
Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash

-
 Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels
Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels
-
Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn

-
 Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes
Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes
-
Scotland stun France 50-40 to take Six Nations to wire

-
 Pogacar begins season with dominant Strade Bianche win
Pogacar begins season with dominant Strade Bianche win
-
Failed Israeli commando operation to find airman remains kills 41 in Lebanon

-
 Bronze and Stanway on target for England in World Cup qualifying
Bronze and Stanway on target for England in World Cup qualifying
-
'No pressure, no fun', says India's Suryakumar ahead of World Cup final

-
 Women rule the roost atop the Gdansk shipyard cranes
Women rule the roost atop the Gdansk shipyard cranes
-
'Fun day' for Olympic champion Braathen in giant slalom win

-
 Bayern's Neuer out of Atalanta tie with calf tear
Bayern's Neuer out of Atalanta tie with calf tear
-
Arsenal survive FA Cup scare to keep quadruple dream alive

-
 Ohtani homers again as Japan edge South Korea at World Baseball Classic
Ohtani homers again as Japan edge South Korea at World Baseball Classic
-
Japan hammer India 11-0 in Women's Asian Cup mismatch

-
 Trump threatens to escalate bombing as Iran vows no surrender
Trump threatens to escalate bombing as Iran vows no surrender
-
Pirovano overtakes Vonn after 'crazy' World Cup downhill double

-
 Russian strikes kill 11 across Ukraine
Russian strikes kill 11 across Ukraine
-
Nepal's rapper politician who took on the old guard and won

-
 Pirovano doubles up with second Val di Fassa downhill win
Pirovano doubles up with second Val di Fassa downhill win
-
Rapper-turned-politician Shah unseats former Nepal PM in own constituency

-
 Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
-
Sri Lanka to treat Iranian sailors according to 'international law'

-
 New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
-
Farrell welcomes bonus-point win over 'tough' Welsh

-
 Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
-
Nepal's Balendra Shah holds unassailable poll lead for seat

-
 Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
-
Pole-sitter Russell says his Mercedes more go-kart than 'bouncing bus'

-
 Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
-
Thousands of Taiwan fans turn Tokyo blue at World Baseball Classic

-
 Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
-
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes

-
 Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
-
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win

-
 Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs

-
 Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
-
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three

-
 Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
-
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily

-
 Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
-
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
-
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump

-
 Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
-
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level


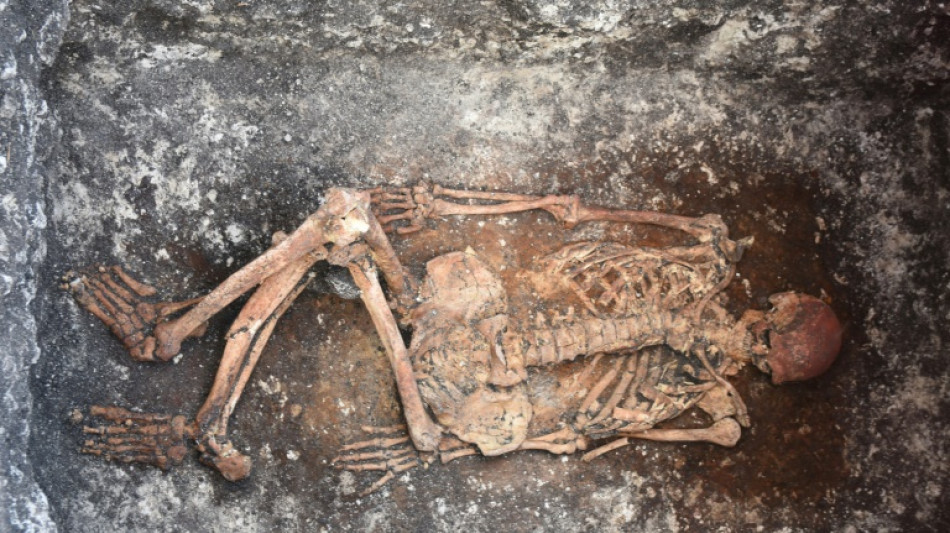
Horseback riding may have begun 5,000 years ago in Europe: study
Who were the first people to ride horses?
Researchers believe they have found the earliest evidence of horseback riding, by the ancient Yamnaya people in Europe some 5,000 years ago.
Their conclusions, based on an analysis of human skeletal remains found in Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania, were published on Friday in the journal Science Advances.
Domestication of horses for milk is widely accepted to have begun around 3500 BC to 3000 BC, the study said, but the "origins of horseback riding remain elusive."
The researchers from the University of Helsinki and other European institutions date the earliest horsemanship to 3000 BC to 2500 BC among members of the Yamnaya culture.
"Our findings provide a strong argument that horseback riding was already a common activity for some Yamnaya individuals as early as 3000 BC," the researchers said.
Horse bones have been discovered in Yamnaya settlements but they are not as well preserved as human skeletons, which were given proper burials in earth-covered mounds known as "kurgans."
The researchers said the human skeletons provided the best source of information about horse riding because any riding tack used by early riders would have been made using perishable materials.
The researchers said some of the human skeletons they analyzed bore skeletal traits indicative of what they called "horsemanship syndrome."
"A skeleton of a living person is reacting," Martin Trautmann, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki and one of the authors of the study, told AFP.
"If you sit on horseback you need to balance with every step of your mount, you need to cling tightly with your legs."
Doing that repeatedly leaves tell-tale changes in bone morphology, Trautmann said, including "stress-induced vertebral degeneration," a common ailment among avid horse riders.
"We know that saddles and stirrups dated much later," Trautmann said, and the early horse riders were probably riding bareback and gripping the mane of the horse.
- 'Cowboys, not warriors' -
Volker Heyd, a professor of archeology at the University of Helsinki, said the findings "fit very nicely into the overall picture" of Yamnaya culture.
"We were already suspecting them of using horses," Heyd said, and it could help explain the "exceptional" geographic expansion of their society in a few generations.
"It is difficult to envision how this expansion could have taken place without improved means of transport," the researchers said.
"Using horses for transport was a decisive step in human cultural development," they said.
"Trade and cultural exchange as well as conflicts and migrations leapt with the increase in speed and range provided by horsemanship."
The researchers said the Yamnaya were probably not initially using horses for warfare.
"They were cowboys, not warriors," said Trautmann.
Heyd said the early horse riders "were probably helping the Yamnaya people in guarding their animals, their cattle and sheep mostly."
According to the researchers, the earliest figurative evidence of horse riding comes from the Mesopotamian Ur III period shortly before 2000 BC through depictions of a horse and rider.
Images and mentions in cuneiform texts of horseback riding are also found in the Old Babylonian period from around 1880 BC to 1595 BC.
L.Dubois--BTB



