
-
 Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
-
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'

-
 Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs

-
 Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
-
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes

-
 Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
-
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration

-
 Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig

-
 Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
-
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says

-
 Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
-
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals

-
 Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
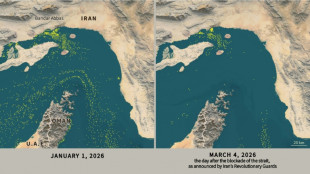 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs

-
 Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
-
Voices from Iran: protests, fear and scarcity

-
 Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
-
This is how Ukraine has countered Russia's Iran-designed drones

-
 Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
-
Sleepless Iranians count cost of war as damage mounts

-
 Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
-
Leading satellite firm to hold back Gulf state images


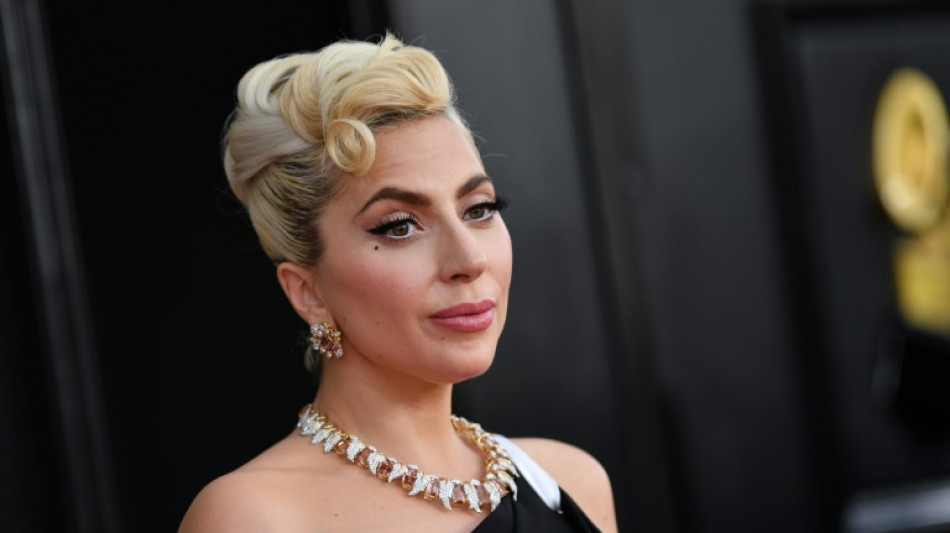
Born this way: rats move to beat of Lady Gaga, study says
Nodding along to catchy music is not just a human habit, according to Japanese scientists who have discovered that rats also move to the beat of songs by stars like Lady Gaga.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo played Mozart, Queen and Lady Gaga's "Born This Way" to rats wearing miniature sensors to detect even the tiniest movements.
They found the rodents had an innate ability to synchronise their moves to the beat, previously believed to be a skill unique to people.
"Rats' brains are designed to respond well to music," even though their bodies move only a little, said associate professor Hirokazu Takahashi, part of the team who conducted the study.
"We all believe that music has magical powers, but we don't know anything about its mechanisms," he told AFP on Tuesday.
So "we wanted to find out what kind of sound connections appeal to the brain, without the influence of emotion or memory."
For rats, the "bopping" effect was most pronounced for music in the range of 120-140 beats per minute -- the same as humans.
This led the scientists to hypothesise that it could be a reaction that is consistent across different species.
"Music moves the body. It goes beyond the auditory system and affects the motor system... the power of sound is that great," Takahashi said.
The research mainly focused on Mozart's Sonata for Two Pianos in D Major, K.448, played at four different tempos.
But the scientists also tried out "Born This Way" and the driving rhythm of Queen's "Another One Bites the Dust", tracks picked by Takahashi's students.
Unlike other pets such as parrots, which are famous for their uncanny imitations of music and other sounds, it was the first time the rats in the study had listened to music.
The effect of music on rats may have been overlooked until now because previous research was mainly carried out using video footage, not movement sensors, making the animals' tiny movements more difficult to detect, Takahashi said.
The study was published last week in the peer-reviewed Science Advances journal.
In the future, Takahashi said he wants to go beyond rhythm and explore the effects of melody and harmony on the brain.
"If music has an emotional effect, it would be really interesting if we could get to the point where we could see it in animals," he said.
M.Furrer--BTB


