
-
 Who rules the seas? Torpedoed Iran ship brings focus underwater
Who rules the seas? Torpedoed Iran ship brings focus underwater
-
Mideast war escalates as fresh strikes batter Iran

-
 Pirovano takes downhill at Val di Fassa for first World Cup win
Pirovano takes downhill at Val di Fassa for first World Cup win
-
Iran drone strike on Azerbaijan raises fears of Mideast war spreading to Caucasus

-
 Decades of planning and US backing helps fuel Israel's air power
Decades of planning and US backing helps fuel Israel's air power
-
Hungary to expel seven Ukrainians as Zelensky, Orban quarrel over Russian oil

-
 Mideast war is heightening uncertainty, Lufthansa warns
Mideast war is heightening uncertainty, Lufthansa warns
-
Fresh Israeli strikes on Lebanon as PM warns of 'looming humanitarian disaster'

-
 Italian general challenges Meloni from the right
Italian general challenges Meloni from the right
-
China says 'clearly aware' of economic risks, vows to boost spending

-
 Hungary detains seven Ukrainians as Kyiv, Budapest quarrel over Russian oil
Hungary detains seven Ukrainians as Kyiv, Budapest quarrel over Russian oil
-
North Korea, China power into Women's Asian Cup quarter-finals

-
 Extensive destruction in Beirut's southern suburbs following Israeli strikes
Extensive destruction in Beirut's southern suburbs following Israeli strikes
-
Most Asian equities drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 'Super special' Allen can light up big occasion for New Zealand
'Super special' Allen can light up big occasion for New Zealand
-
'Genie' Bumrah: India's yorker king who carries a billion hopes

-
 'There will be nerves': India face New Zealand for T20 World Cup glory
'There will be nerves': India face New Zealand for T20 World Cup glory
-
Lufthansa warns of heightened 'uncertainty' from Mideast war

-
 Mideast war enters 'next phase' as strikes hit Iran, Lebanon
Mideast war enters 'next phase' as strikes hit Iran, Lebanon
-
Equities mixed as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Sri Lanka denounces war deaths, houses Iran sailors
Sri Lanka denounces war deaths, houses Iran sailors
-
Inoue primed for 'historic' Nakatani clash in Tokyo

-
 Italy challenges EU over key climate tool
Italy challenges EU over key climate tool
-
Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice

-
 Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday
Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday
-
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn

-
 Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems
-
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
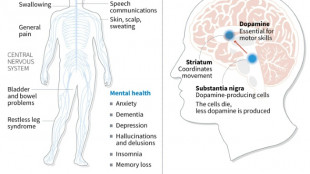
-
 Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'
-
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning

-
 Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer
-
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse

-
 Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
-
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice

-
 Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
-
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election

-
 Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
-
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game

-
 French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
-
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output

-
 Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
-
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut

-
 Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv

-
 US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
-
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates

-
 Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
-
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63

-
 Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
-
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis


Record measurement of universe suggests 'something is fishy'
The most precise measurements ever made of the universe's composition and how fast it is expanding suggest "something is fishy" in our understanding of the cosmos, the astrophysicist who led the research said Wednesday.
The comprehensive new study published in The Astrophysical Journal further confirmed that there is a significant discrepancy between two different ways to estimate the speed at which the universe is expanding.
The study said that around five percent of the universe is made up of what we might think of as normal matter, while the rest is dark matter and dark energy -- both of which remain shrouded in mystery.
Dark energy, a hypothetical force causing the universe to expand at an ever-increasing rate, makes up 66.2 percent of the cosmos, according to the study published in The Astrophysical Journal.
The remaining 33.8 percent is a combination of matter and dark matter, which is also unknown but may consist of some as-yet-undiscovered subatomic particle.
To arrive at the most precise limits yet put on what our universe is made up of, an international team of researchers observed exploding stars called supernovae.
They analysed the light from 1,550 different supernovae, ranging from close to home to more than 10 billion lights year away, back when the universe was a quarter of its current age.
"We can compare them and see how the universe is behaving and evolving over time," said Dillon Brout of the Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and lead author of the study, called Pantheon+.
- Two decades of analysis -
The study updated the data from the Pantheon project a couple of years ago, stamping out possible problems and nailing down more precise calculations.
"This latest Pantheon+ analysis is a culmination of more than two decades' worth of diligent efforts by observers and theorists worldwide in deciphering the essence of the cosmos," US astrophysicist Adam Reiss, 2011's physics Nobel winner, said in a statement.
It was by observing supernovae back in the late 1990s that Reiss and other scientists discovered the universe was not only expanding but also doing so at an increasing rate, meaning galaxies are racing away from each other.
"It was like if you threw a ball up, and instead of the ball coming down, it shot up and kept accelerating," Brout said of the surprise of that discovery.
Pantheon+ also pooled data with the SH0ES supernova collaboration to find what is believed to be the most accurate measurement for how rapidly the universe is expanding.
They estimated the universe is currently expanding 73.4 kilometres a second every megaparsec, or 3.26 million light years. That works out to be around 255,000 kilometres (160,000 miles) per hour, according to a Harvard-Smithsonian statement.
But there's a problem.
- The Hubble tension -
Measuring cosmic microwave background radiation, which can look much farther back in time to around 300,000 years after the Big Bang, suggests the universe is expanding at a significantly slower rate -- around 67 kilometres per megaparsec.
This discrepancy has been called the Hubble tension, after US astronomer Edwin Hubble.
The Pantheon+ results have raised the certainty of the Hubble tension above what is known as the five sigma threshold, which means the discrepancy "can no longer be attributed to luck", Brout said.
"It certainly indicates that potentially something is fishy with our understanding of the universe," Brout told AFP.
Some possible, unverified theories for the discrepancy could include another kind of dark energy in the very early universe, primordial magnetic fields, or even that the Milky Way sits in a cosmic void, potentially slowing it down.
But for now, Brout said that "we, as scientists thrive on not understanding everything.
"There's still potentially a major revolution in our understanding, coming potentially in our lifetimes," he added.
J.Horn--BTB




