
-
 Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'

-
 North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
-
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer

-
 Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
-
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold

-
 Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
-
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
-
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett

-
 Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
-
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche

-
 Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
-
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets

-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup

-
 India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
-
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf

-
 Italy bring back Brex to face England
Italy bring back Brex to face England
-
French policeman to be tried over 2023 killing of teen


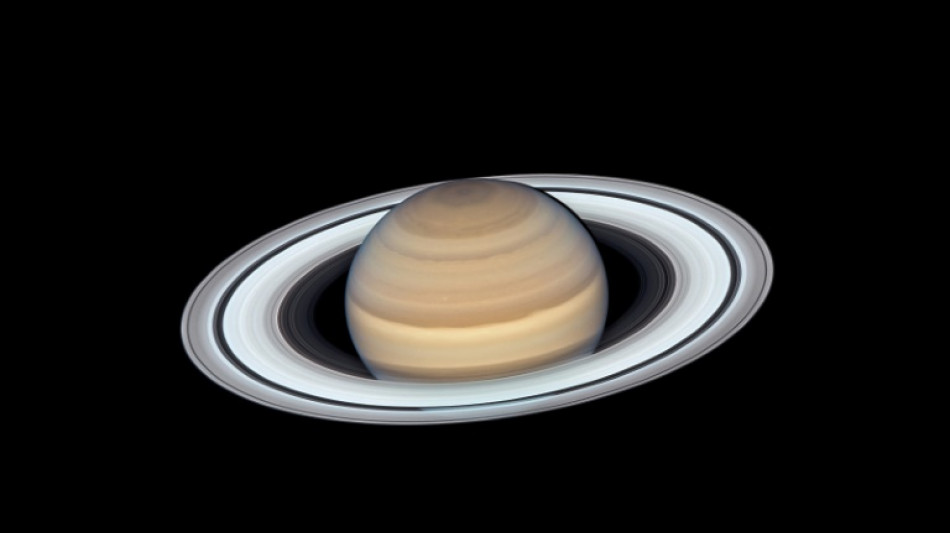
Long lost moon could have been responsible for Saturn's rings
Discovered by Galileo 400 years ago, the rings of Saturn are about the most striking thing astronomers with small telescopes can spot in our solar system.
But even today, experts cannot agree on how or when they formed.
A new study published Thursday in the prestigious journal Science sets out to provide a convincing answer.
Between 100-200 million years ago, an icy moon they named Chrysalis broke up after getting a little too close to the gas giant, they conclude.
While most of it made impact with Saturn, its remaining fragments broke into small icy chunks that form the planet's signature rings.
"It's nice to find a plausible explanation," Jack Wisdom, professor of planetary sciences at MIT and lead author of the new study, told AFP.
Saturn, the sixth planet from the Sun, was formed four and a half billion years ago, at the beginning of the solar system.
But a few decades ago, scientists suggested that Saturn's rings appeared much later: only about 100 million years ago.
The hypothesis was reinforced by observations made by the Cassini probe, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017.
"But because no one could think of a way to make the rings 100 million years ago, some people have been questioning the reasoning that led to that deduction," said Wisdom.
By constructing complex mathematical models, Wisdom and colleagues found an explanation that both justified the timeline, and allowed them to better understand another characteristic of the planet, its tilt.
Saturn has a 26.7 degree tilt. Being a gas giant, it would have been expected that the process of accumulating matter that led to its formation would have prevented tilt.
- Gravitational interactions -
Scientists recently discovered that Titan, the largest of Saturn's 83 moons, is migrating away from the planet, at a rate of 11 centimeters a year.
This changes the rate at which Saturn's axis of tilt loops around the vertical -- the technical term is "precession." Think of a spinning top drawing circles.
Around a billion years ago, this wobble frequency came into sync with Neptune's wobbly orbit, creating a powerful gravitational interaction called "resonance."
In order to maintain this lock, as Titan kept moving out, Saturn had to tilt, scientists argued.
But that explanation hinged on knowing how mass was distributed in the planet's interior, since the tilt would have behaved differently if it were concentrated more at its surface or the core.
In the new study, Wisdom and colleagues modeled the planet's interior using gravitational data gathered by Cassini during its close approach "Grand Finale," its last act before plunging into Saturn's depths.
The model they generated found Saturn is now slightly out of sync with Neptune, which necessitated a new explanation -- an event powerful enough to cause the drastic disruption.
Working through the mathematics, they found a lost moon fit the bill.
"It's pulled apart into a bunch of pieces and those pieces subsequently get pulled apart even more, and gradually rolls into the rings."
The missing Moon was baptized Chrysalis by MIT's Wisdom, likening the emergence of Saturn's rings to a butterfly emerging from a cocoon.
The team thinks Chrysalis was a bit smaller than our own Moon, and about the size of another Saturn satellite, Iapetus, which is made entirely of water ice.
"So it's plausible to hypothesize that Chrysalis is also made of water ice, and that's what it needs to make the rings, because the rings are almost pure water.
Asked whether he felt the mystery of Saturn's rings stood solved, Wisdom replied, soberly, "We've made a good contribution."
The Saturn satellite system still holds "a variety of mysteries," he added.
H.Seidel--BTB




