-
 Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
-
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice

-
 Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
-
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election

-
 Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
-
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game

-
 French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
-
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output

-
 Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
-
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut

-
 Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv

-
 US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
-
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates

-
 Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
-
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63

-
 Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
-
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis

-
 El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group
-
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before

-
 Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace
-
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge

-
 Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog
-
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday

-
 'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages
-
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook

-
 France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'
-
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai

-
 Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem
-
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over

-
 Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error
-
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final

-
 Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated
-
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer

-
 Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race
-
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM

-
 EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop
-
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time

-
 India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase
-
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader

-
 Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup
-
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final

-
 Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf
-
Italy bring back Brex to face England

-
 French policeman to be tried over 2023 killing of teen
French policeman to be tried over 2023 killing of teen
-
Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns

-
 More flights take off despite continued fighting in Middle East
More flights take off despite continued fighting in Middle East
-
Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each

-
 Middle East war halts work at WHO's Dubai emergency hub
Middle East war halts work at WHO's Dubai emergency hub
-
Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence


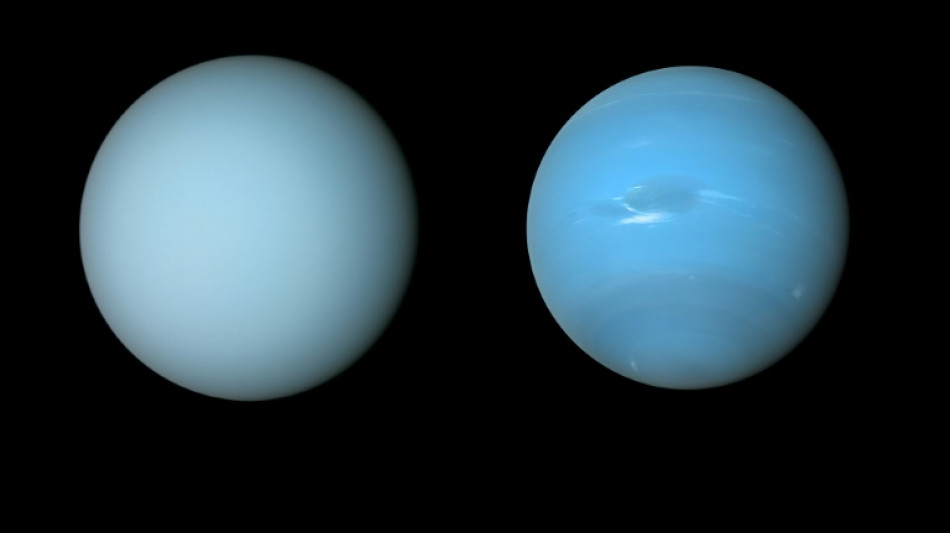
It's raining diamonds across the universe, research suggests
It could be raining diamonds on planets throughout the universe, scientists suggested Friday, after using common plastic to recreate the strange precipitation believed to form deep inside Uranus and Neptune.
Scientists had previously theorised that extremely high pressure and temperatures turn hydrogen and carbon into solid diamonds thousands of kilometres below the surface of the ice giants.
Now new research, published in Science Advances, inserted oxygen into the mix, finding that "diamond rain" could be more common than thought.
Ice giants like Neptune and Uranus are thought to be the most common form of planet outside our Solar System, which means diamond rain could be occurring across the universe.
Dominik Kraus, a physicist at Germany's HZDR research lab and one of the study's authors, said that diamond precipitation was quite different to rain on Earth.
Under the surface of the planets is believed to be a "hot, dense liquid", where the diamonds form and slowly sink down to the rocky, potentially Earth-size cores more than 10,000 kilometres (6,200 miles) below, he said.
There fallen diamonds could form vast layers that span "hundreds of kilometres or even more", Kraus told AFP.
While these diamonds might not be shiny and cut like a "a nice gem on a ring", he said they were formed via similar forces as on Earth.
Aiming to replicate the process, the research team found the necessary mix of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a readily available source -- PET plastic, which is used for everyday food packaging and bottles.
Kraus said that while the researchers used very clean PET plastic, "in principle the experiment should work with Coca-Cola bottles".
The team then turned a high-powered optical laser on the plastic at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California.
"Very, very short X-ray flashes of incredible brightness" allowed them to watch the process of nanodiamonds -- tiny diamonds too small to see with the naked eye -- as they formed, Kraus said.
"The oxygen that is present in large amounts on those planets really helps suck away the hydrogen atoms from the carbon, so it's actually easier for those diamonds to form," he added.
- New way to make nanodiamonds? -
The experiment could point towards a new way to produce nanodiamonds, which have a wide and increasing range of applications including drug delivery, medical censors, non-invasive surgery and quantum electronics.
"The way nanodiamonds are currently made is by taking a bunch of carbon or diamond and blowing it up with explosives," said SLAC scientist and study co-author Benjamin Ofori-Okai.
"Laser production could offer a cleaner and more easily controlled method to produce nanodiamonds," he added.
The diamond rain research remains hypothetical because little is known about Uranus and Neptune, the most distant planets in our Solar System.
Only one spacecraft -- NASA's Voyager 2 in the 1980s -- has flown past the two ice giants, and the data it sent back is still being used in research.
But a NASA group has outlined a potential new mission to the planets, possibly launching next decade.
"That would be fantastic," Kraus said.
He said he is greatly looking forward to more data -- even if it takes a decade or two.
F.Pavlenko--BTB




