
-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
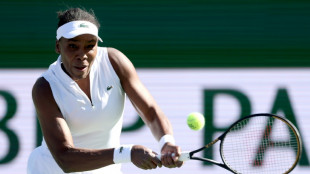
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup

-
 India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
-
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf

-
 Italy bring back Brex to face England
Italy bring back Brex to face England
-
French policeman to be tried over 2023 killing of teen

-
 Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns
Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns
-
More flights take off despite continued fighting in Middle East

-
 Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each
Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each
-
Middle East war halts work at WHO's Dubai emergency hub

-
 Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence
Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence
-
US says attacks on alleged drug boats have spooked traffickers

-
 Dempsey returns as Scotland shuffle pack for Six Nations clash against France
Dempsey returns as Scotland shuffle pack for Six Nations clash against France
-
India pile up 253-7 against England in T20 World Cup semi-final

-
 Wary Europeans pledge 'defensive' military aid in Mideast war
Wary Europeans pledge 'defensive' military aid in Mideast war
-
Seven countries to boycott Paralympics ceremony over Russia: organisers

-
 UK's Crufts dog show opens with growing global appeal
UK's Crufts dog show opens with growing global appeal
-
PSG prepare for Chelsea clash with Monaco rematch

-
 Google opens AI centre as Berlin defends US tech reliance
Google opens AI centre as Berlin defends US tech reliance
-
Second Iranian ship nears Sri Lanka after submarine attack


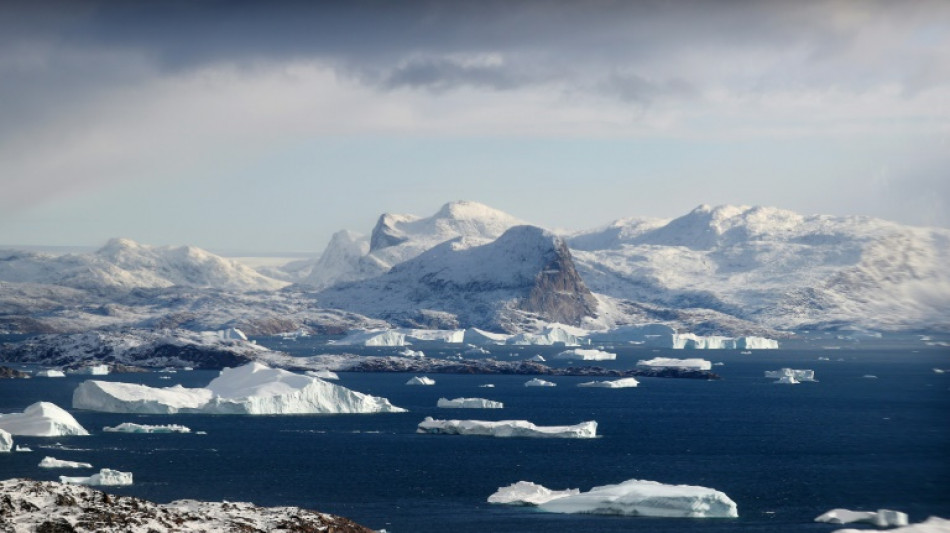
Greenland already locked in to major sea level rise: study
Even without any future global warming, Greenland's melting ice sheet will cause major sea level rise with potentially "ominous" implications over this century as temperatures continue to rise, according to a study published Monday.
Rising sea levels -- pushed up mainly by melting ice sheets on Greenland and Antarctica -- are set to redraw the map over centuries and could eventually swamp land currently home to hundreds of millions of people, depending on humanity's efforts to halt warming.
The Greenland ice sheet is currently the main factor in swelling the Earth's oceans, according to NASA, with the Arctic region heating at a faster rate than the rest of the planet.
In the new study, published in Nature Climate Change, glaciologists found that regardless of any future fossil fuel pollution, warming to date will cause the Greenland ice sheet to shed 3.3 percent of its volume, committing 27.4 centimetres to sea level rise.
While the researchers were not able to give an exact timeframe, they said most of it could happen by 2100 -- meaning that current modelled projections of sea level rise could be understating the risks this century.
The "shocking" results are also a lowest estimate because they do not take future warming into account, said lead author Jason Box, of the National Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland.
"It's a conservative lower bound. The climate has only to continue warming around Greenland for more commitment," he told AFP.
If the high levels of melting seen in 2012 became an annual occurrence, the study estimated sea-level rise could be around 78 cm, enough to swamp vast swathes of low-lying coastlines and supercharge floods and storm surges.
This should serve "as an ominous prognosis for Greenland's trajectory through a 21st century of warming", the authors said.
In a landmark report on climate science last year, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) said the Greenland ice sheet would contribute an estimated maximum of 18cm to sea level rise by 2100 under the highest emissions scenario.
Box, who was an author on that report, said his team's latest research suggests those estimates are "too low".
Instead of using computer models, Box and colleagues used two decades of measurements and observational data to predict how the Greenland ice sheet will adjust to the warming already experienced.
Upper areas of the ice sheet adds mass through snowfall every year, but since the 1980s the territory has been running an ice "budget deficit", which sees it lose more ice than it gains through surface melting and other processes.
- 'Radical' method -
The theory that researchers used was initially developed to explain changes in Alpine glaciers, said Box.
This holds that if more snow piles up on top of a glacier, it causes lower areas to expand. In this case the reduced snow is driving shrinking in lower parts of the glacier as it rebalances, he said.
Box said the methods his team used were "radically different" from computer modelling, but could complement this work to predict the impacts of sea level rise in the coming decades.
He said while climate change was raising more immediate threats like food security, the accelerating pace of sea level rise will become a challenge.
"It's kind of decades in the future when it will just force its way onto the agenda because it will begin displacing people more and more and more," he said.
The world has warmed an average of nearly 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times, unleashing a catalogue of impacts from heatwaves to more intense storms.
Under the Paris climate deal, countries have agreed to limit warming to 2C.
But in their report on climate impacts this year, the IPCC said even if warming is stabilised at 2C to 2.5C, "coastlines will continue to reshape over millennia, affecting at least 25 megacities and drowning low-lying areas", which were home to up to 1.3 billion people in 2010.
B.Shevchenko--BTB



