
-
 Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
-
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win

-
 Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs

-
 Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
-
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three

-
 Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
-
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily

-
 Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
-
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
-
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump

-
 Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
-
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level

-
 Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
-
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win

-
 Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
-
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola

-
 Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
-
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
-
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales

-
 Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
-
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January

-
 Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
-
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
-
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march

-
 Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
-
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony

-
 Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round

-
 NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
-
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row

-
 'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
-
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold

-
 Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening
-
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war

-
 Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports
-
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control

-
 Middle East war a new shock for financial markets
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets
-
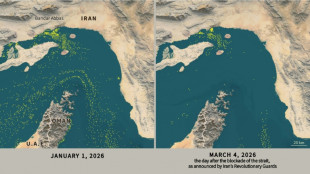
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
 Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup
-
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say

-
 Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up
-
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe

-
 Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs
-
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland


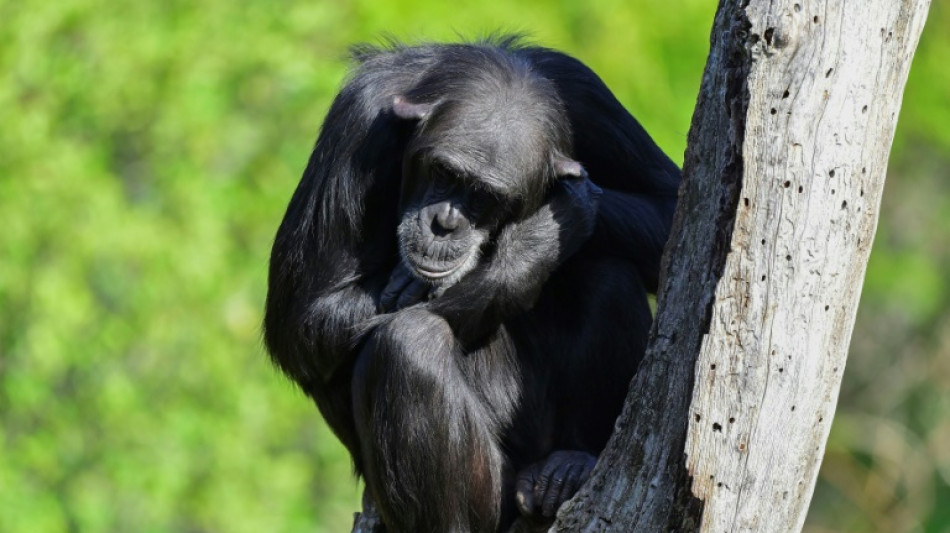
Chimps are upping their tool game, says study
"Planet of the Apes" may have been onto something.
Chimpanzees are steadily honing their tool-using skills -- a process unfolding over millennia, driven by the exchange of ideas through migrations between populations, according to a new study published Thursday in Science.
The finding in chimps -- humans' closest living relatives -- holds relevance for us too, as it supports the idea that, deep in the mists of time, our own ape ancestors leveraged social connections to improve their technologies, lead author Cassandra Gunasekaram told AFP.
Scientists have long marveled at chimps' ability to pass down intricate behaviors, like tool use, from one generation to the next.
Yet while human civilization has leapt from the Stone Age to the Space Age, chimpanzee "culture" -- defined as socially learned behaviors -- seemed to have remained static.
Gunasekaram, a doctoral student at the University of Zurich, set out to challenge this assumption.
- Connections spark innovation -
She and colleagues combined genetic data tracing ancient chimpanzee migrations across Africa with observations of 15 distinct foraging behaviors across dozens of populations and the four subspecies.
These behaviors were categorized into three levels: those requiring no tools, those with simple tools, like using chewed leaves as a sponge to absorb water from tree holes, and the most complex, which involve toolsets.
One striking example of toolset use comes from Congo, where chimps use a stout stick to bore a tunnel into the ground to reach a termite nest, then modify a plant stem by chewing its tip into a brush to "fish" for termites in the tunnel they've made.
The study found that advanced tool use strongly correlated with populations connected by genetic exchanges over the last 5,000–15,000 years, suggesting such behaviors spread when groups interacted.
Areas where three subspecies overlap exhibited the most complex tool use, highlighting how cross-group connections foster cultural knowledge.
By contrast, simpler behaviors, such as foraging without tools, seemed less tied to migration and likely evolved independently in different regions.
- Foraging efficiently -
Gunasekaram said this mirrors how trading ideas and incremental innovation have been critical to human technological progress, taking us from early abacuses to modern smartphones.
"They've become so complex that one person alone could not reinvent them from scratch," she said.
But unlike humans, chimps have far fewer opportunities to encounter new individuals and ideas -- migrations occur gradually, driven by sexually mature females moving to new communities to avoid inbreeding.
Analyzing ancient genetic flows helped the team overcome one of the biggest challenges in studying the evolution of chimpanzee culture: the limited window of observation, as the species has only been researched scientifically for about a century.
What's more, "Chimpanzee tools are made of sticks and stems, which are all perishable," Gunasekaram explained, making it nearly impossible to trace how their artifacts have evolved over time.
So, will chimps one day rival human ingenuity? Hardly. But given enough time, they could become more efficient foragers.
For example, some populations are already more advanced in cracking nuts with hammers and anvils made of stone , and one particularly innovative group has even invented a stabilizer for the anvil, said Gunasekaram.
R.Fischer--VB


