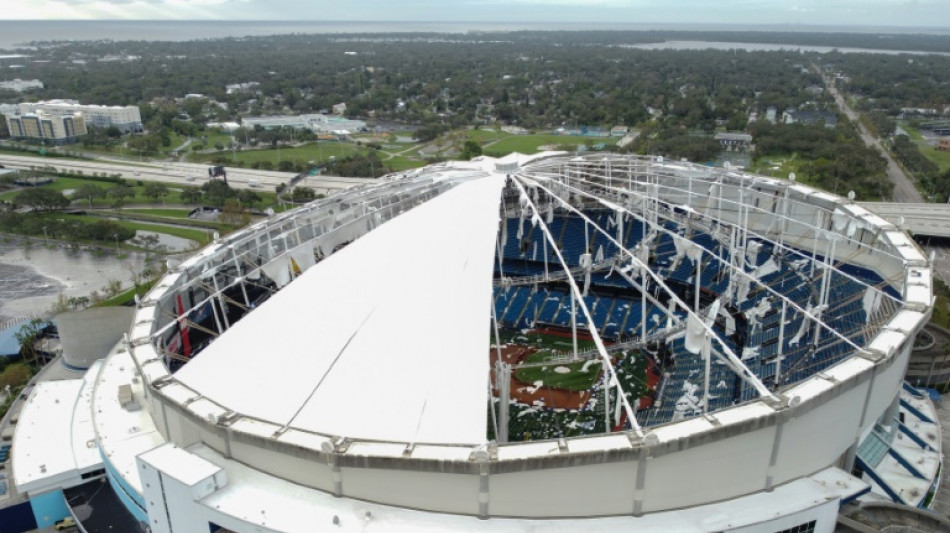

-
 Nepal's Balendra Shah holds unassailable poll lead for seat
Nepal's Balendra Shah holds unassailable poll lead for seat
-
Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP

-
 Pole-sitter Russell says his Mercedes more go-kart than 'bouncing bus'
Pole-sitter Russell says his Mercedes more go-kart than 'bouncing bus'
-
Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million

-
 Thousands of Taiwan fans turn Tokyo blue at World Baseball Classic
Thousands of Taiwan fans turn Tokyo blue at World Baseball Classic
-
Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying

-
 Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes
-
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six

-
 'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win
-
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs
-
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic

-
 Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three
-
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport

-
 Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
-
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'

-
 Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs

-
 Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
-
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes

-
 Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
-
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration

-
 Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig

-
 Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
-
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says

-
 Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
-
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals

-
 Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets


2024's record ocean heat revved up Atlantic hurricane wind speeds: study
Human-driven warming of ocean temperatures increased the maximum wind speeds of every Atlantic hurricane in 2024, according to a new analysis released Wednesday, highlighting how climate change is amplifying the destructive power of storms.
The study, published by the research institute Climate Central, found that all eleven hurricanes in 2024 intensified by nine to 28 miles per hour (14-45 kph) during the record-breaking ocean warmth of the 2024 hurricane season.
"Emissions from carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases have influenced the temperatures of sea surfaces around the world," author Daniel Gilford said in a call with reporters.
In the Gulf of Mexico, these emissions made sea surface temperatures around 2.5 degrees Fahrenheit (1.4C) hotter than they would have been in a world without climate change.
This rise fuels stronger hurricanes.
The increased temperatures intensified storms like Debby and Oscar, which grew from tropical storms into full-fledged hurricanes.
Other hurricanes were pushed up a category on the Saffir-Simpson scale, including Milton and Beryl which escalated from Category 4 to Category 5 due to climate change, while Helene climbed from Category 3 to Category 4.
Each rise in category corresponds to a roughly fourfold increase in destructive potential.
Helene proved particularly devastating, claiming more than 200 lives, making it the second deadliest hurricane to strike the US mainland in over half a century, surpassed only by Hurricane Katrina in 2005.
The new analytical approach allows researchers to hone in on a given storm's track -- showing for example that, at Hurricane Milton's point of peak intensification before landfall, climate change made the warm sea surface temperatures 100 times more likely to occur than otherwise, and increased maximum wind speed by 24 mph.
Gilford and his colleagues also published a peer-reviewed study in the journal Environmental Research Climate examining hurricane intensities from 2019 to 2023. They found that 84 percent of hurricanes during that period were significantly strengthened by human-caused ocean warming.
While their two studies focused on the Atlantic Basin, the researchers said that their methods could be applied to tropical cyclones globally.
Climatologist Friederike Otto of Imperial College London, who leads World Weather Attribution, praised the team's methodology for advancing beyond previous research that primarily linked climate change to hurricane-related rainfall.
Otto warned that these climate supercharged storms are occurring with the world at just 1.3C (2.3F) above pre-industrial temperatures, and that the impacts are likely to worsen as temperatures rise beyond 1.5C (2.7F).
"The hurricane scale is capped at Category Five -- but we might need to think about, should that continue to be the case just so that people are aware that something is going to hit them that is different from everything else they've experienced before," she said.
I.Stoeckli--VB

