-
 Greenlanders doubtful over Trump resolution
Greenlanders doubtful over Trump resolution
-
Real Madrid top football rich list as Liverpool surge

-
 'One Battle After Another,' 'Sinners' tipped to top Oscar noms
'One Battle After Another,' 'Sinners' tipped to top Oscar noms
-
Higher heating costs add to US affordability crunch

-
 Eight stadiums to host 2027 Rugby World Cup matches in Australia
Eight stadiums to host 2027 Rugby World Cup matches in Australia
-
Plastics everywhere, and the myth that made it possible

-
 Interim Venezuela leader to visit US
Interim Venezuela leader to visit US
-
Australia holds day of mourning for Bondi Beach shooting victims

-
 Liverpool cruise as Bayern reach Champions League last 16
Liverpool cruise as Bayern reach Champions League last 16
-
Fermin Lopez brace leads Barca to win at Slavia Prague

-
 Newcastle pounce on PSV errors to boost Champions League last-16 bid
Newcastle pounce on PSV errors to boost Champions League last-16 bid
-
Fermin Lopez brace hands Barca win at Slavia Prague

-
 Kane double fires Bayern into Champions League last 16
Kane double fires Bayern into Champions League last 16
-
Newcastle pounce on PSV errors to close in on Champions League last 16

-
 In Davos speech, Trump repeatedly refers to Greenland as 'Iceland'
In Davos speech, Trump repeatedly refers to Greenland as 'Iceland'
-
Liverpool see off Marseille to close on Champions League last 16

-
 Caicedo strikes late as Chelsea end Pafos resistance
Caicedo strikes late as Chelsea end Pafos resistance
-
US Republicans begin push to hold Clintons in contempt over Epstein

-
 Trump says agreed 'framework' for US deal over Greenland
Trump says agreed 'framework' for US deal over Greenland
-
Algeria's Zidane and Belghali banned over Nigeria AFCON scuffle

-
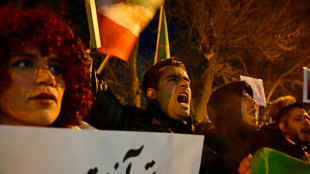 Iran says 3,117 killed during protests, activists fear 'far higher' toll
Iran says 3,117 killed during protests, activists fear 'far higher' toll
-
Atletico frustrated in Champions League draw at Galatasaray

-
 Israel says struck Syria-Lebanon border crossings used by Hezbollah
Israel says struck Syria-Lebanon border crossings used by Hezbollah
-
Snapchat settles to avoid social media addiction trial

-
 'Extreme cold': Winter storm forecast to slam huge expanse of US
'Extreme cold': Winter storm forecast to slam huge expanse of US
-
Jonathan Anderson reimagines aristocrats in second Dior Homme collection

-
 Former England rugby captain George to retire in 2027
Former England rugby captain George to retire in 2027
-
Israel launches wave of fresh strikes on Lebanon

-
 Ubisoft unveils details of big restructuring bet
Ubisoft unveils details of big restructuring bet
-
Abhishek fireworks help India beat New Zealand in T20 opener

-
 Huge lines, laughs and gasps as Trump lectures Davos elite
Huge lines, laughs and gasps as Trump lectures Davos elite
-
Trump rules out 'force' against Greenland but demands talks

-
 Stocks steadier as Trump rules out force to take Greenland
Stocks steadier as Trump rules out force to take Greenland
-
World's oldest cave art discovered in Indonesia

-
 US hip-hop label Def Jam launches China division in Chengdu
US hip-hop label Def Jam launches China division in Chengdu
-
Dispersed Winter Olympics sites 'have added complexity': Coventry

-
 Man City players to refund fans after Bodo/Glimt debacle
Man City players to refund fans after Bodo/Glimt debacle
-
France's Lactalis recalls baby formula over toxin

-
 Pakistan rescuers scour blaze site for dozens missing
Pakistan rescuers scour blaze site for dozens missing
-
Keenan return to Irish squad boosts Farrell ahead of 6 Nations

-
 US Treasury chief accuses Fed chair of 'politicising' central bank
US Treasury chief accuses Fed chair of 'politicising' central bank
-
Trump rules out force against Greenland but demands 'immediate' talks

-
 Israeli strike kills three Gaza journalists including AFP freelancer
Israeli strike kills three Gaza journalists including AFP freelancer
-
US Congress targets Clintons in Epstein contempt fight

-
 Huge lines, laughs and gasps as Trump addresses Davos elites
Huge lines, laughs and gasps as Trump addresses Davos elites
-
Trump at Davos demands 'immediate' Greenland talks but rules out force

-
 Australia pauses for victims of Bondi Beach shooting
Australia pauses for victims of Bondi Beach shooting
-
Prince Harry says tabloid coverage felt like 'full blown stalking'

-
 Galthie drops experienced trio for France's Six Nations opener
Galthie drops experienced trio for France's Six Nations opener
-
Over 1,400 Indonesians leave Cambodian scam groups in five days: embassy


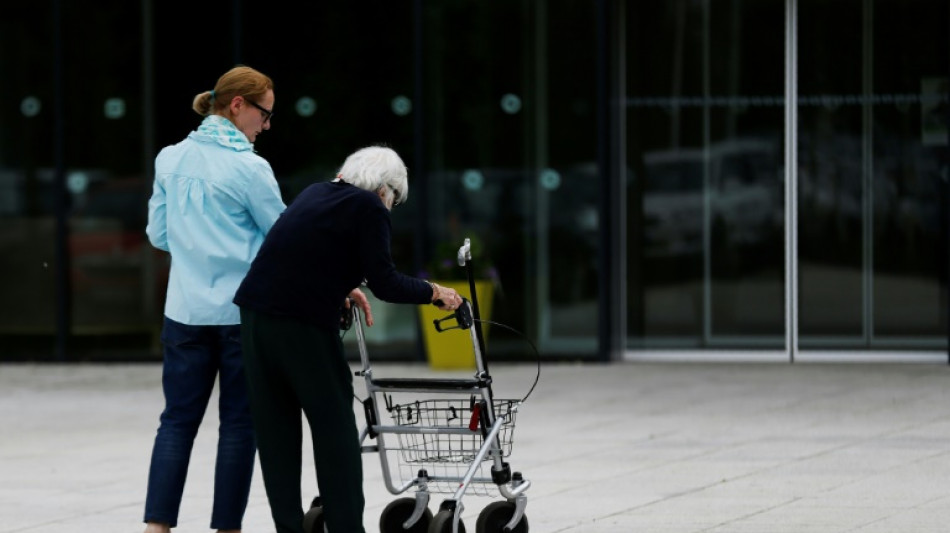
Gene variant linked to multiple sclerosis severity
Scientists have discovered a genetic variant linked with multiple sclerosis becoming more debilitating over time, in research hailed as a first step towards a new drug.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a lifelong condition in which a person's body is attacked by its own immune system, causing a range of symptoms including problems with vision, movement and balance.
For some people, the symptoms can come and go in phases called relapses, while in others they become progressively worse.
There are treatments that can help control the symptoms, but there is no cure or way to slow down the disease from getting worse.
In a study published in the journal Nature Wednesday, researchers from more than 70 institutes around the world said they had found the first-ever genetic variant linked to MS severity.
First, the researchers combined the genetic data of 12,000 people with MS to study what variants they shared and how quickly their disease advanced.
Out of seven million variants, they found a single one associated with the disease progressing faster.
The variant sits between two genes called DYSF and ZNF638, which had never before been linked to MS, according to the study.
The first gene works to repair damaged cells, while the other helps control viral infections.
The genes are much more active in the brain and spinal cord than the immune system, where drug research has previously focused, the study said.
To confirm what they found, the researchers then looked at the genetics of nearly 10,000 more patients, finding similar results.
"Inheriting this genetic variant from both parents accelerates the time to needing a walking aid by almost four years," US researcher and study co-author Sergio Baranzini said in a statement.
Ruth Dobson, a neurologist at the Queen Mary University of London who was not involved in the research, told AFP there was "a lot of excitement about this study" in MS circles.
"It's the first step towards treatments that work in a different way," she said, emphasising that any such drug was a long way from being available.
That the research points to the nervous system, rather than the immune system, "opens up a new potential pathway for treatments, which is really exciting", she added.
More than 2.8 million people worldwide live with multiple sclerosis.
M.Ouellet--BTB