-
 US Republicans begin push to hold Clintons in contempt over Epstein
US Republicans begin push to hold Clintons in contempt over Epstein
-
Trump says agreed 'framework' for US deal over Greenland

-
 Algeria's Zidane and Belghali banned over Nigeria AFCON scuffle
Algeria's Zidane and Belghali banned over Nigeria AFCON scuffle
-
Iran says 3,117 killed during protests, activists fear 'far higher' toll
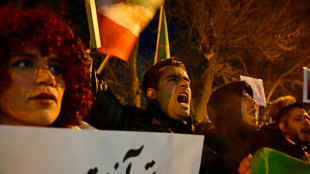
-
 Atletico frustrated in Champions League draw at Galatasaray
Atletico frustrated in Champions League draw at Galatasaray
-
Israel says struck Syria-Lebanon border crossings used by Hezbollah

-
 Snapchat settles to avoid social media addiction trial
Snapchat settles to avoid social media addiction trial
-
'Extreme cold': Winter storm forecast to slam huge expanse of US

-
 Jonathan Anderson reimagines aristocrats in second Dior Homme collection
Jonathan Anderson reimagines aristocrats in second Dior Homme collection
-
Former England rugby captain George to retire in 2027

-
 Israel launches wave of fresh strikes on Lebanon
Israel launches wave of fresh strikes on Lebanon
-
Ubisoft unveils details of big restructuring bet

-
 Abhishek fireworks help India beat New Zealand in T20 opener
Abhishek fireworks help India beat New Zealand in T20 opener
-
Huge lines, laughs and gasps as Trump lectures Davos elite

-
 Trump rules out 'force' against Greenland but demands talks
Trump rules out 'force' against Greenland but demands talks
-
Stocks steadier as Trump rules out force to take Greenland

-
 World's oldest cave art discovered in Indonesia
World's oldest cave art discovered in Indonesia
-
US hip-hop label Def Jam launches China division in Chengdu

-
 Dispersed Winter Olympics sites 'have added complexity': Coventry
Dispersed Winter Olympics sites 'have added complexity': Coventry
-
Man City players to refund fans after Bodo/Glimt debacle

-
 France's Lactalis recalls baby formula over toxin
France's Lactalis recalls baby formula over toxin
-
Pakistan rescuers scour blaze site for dozens missing

-
 Keenan return to Irish squad boosts Farrell ahead of 6 Nations
Keenan return to Irish squad boosts Farrell ahead of 6 Nations
-
US Treasury chief accuses Fed chair of 'politicising' central bank

-
 Trump rules out force against Greenland but demands 'immediate' talks
Trump rules out force against Greenland but demands 'immediate' talks
-
Israeli strike kills three Gaza journalists including AFP freelancer

-
 US Congress targets Clintons in Epstein contempt fight
US Congress targets Clintons in Epstein contempt fight
-
Huge lines, laughs and gasps as Trump addresses Davos elites

-
 Trump at Davos demands 'immediate' Greenland talks but rules out force
Trump at Davos demands 'immediate' Greenland talks but rules out force
-
Australia pauses for victims of Bondi Beach shooting

-
 Prince Harry says tabloid coverage felt like 'full blown stalking'
Prince Harry says tabloid coverage felt like 'full blown stalking'
-
Galthie drops experienced trio for France's Six Nations opener

-
 Over 1,400 Indonesians leave Cambodian scam groups in five days: embassy
Over 1,400 Indonesians leave Cambodian scam groups in five days: embassy
-
ICC rejects Bangladesh's plea to play T20 World Cup matches outside India

-
 Prince Harry says UK tabloid court battle in 'public's interest'
Prince Harry says UK tabloid court battle in 'public's interest'
-
Trump lands in Davos to push Greenland claims

-
 Balkan wild rivers in steady decline: study
Balkan wild rivers in steady decline: study
-
Injured Capuozzo misses out on Italy Six Nations squad

-
 Mourners pay last respects to Italian icon Valentino
Mourners pay last respects to Italian icon Valentino
-
EU parliament refers Mercosur trade deal to bloc's top court

-
 Odermatt seeks first Kitzbuehel victory with eye on Olympics
Odermatt seeks first Kitzbuehel victory with eye on Olympics
-
Italy's Brignone to be rested for Spindleruv Mlyn giant slalom

-
 Alcaraz spearheads big names into Australian Open third round
Alcaraz spearheads big names into Australian Open third round
-
European stocks dip ahead of Trump's Davos speech

-
 Trump flies into Davos maelstrom over Greenland
Trump flies into Davos maelstrom over Greenland
-
EU won't ask Big Tech to pay for telecoms overhaul

-
 Railway safety questioned as Spain reels from twin train disasters
Railway safety questioned as Spain reels from twin train disasters
-
Marcell Jacobs back with coach who led him to Olympic gold

-
 Syria army enters Al-Hol camp holding relatives of jihadists: AFP
Syria army enters Al-Hol camp holding relatives of jihadists: AFP
-
Brook apologises, admits nightclub fracas 'not the right thing to do'


Webb telescope spots signs of universe's biggest stars
The James Webb Space Telescope has helped astronomers detect the first chemical signs of supermassive stars, "celestial monsters" blazing with the brightness of millions of Suns in the early universe.
So far, the largest stars observed anywhere have a mass of around 300 times that of our Sun.
But the supermassive star described in a new study has an estimated mass of 5,000 to 10,000 Suns.
The team of European researchers behind the study previously theorised the existence of supermassive stars in 2018 in an attempt to explain one of the great mysteries of astronomy.
For decades, astronomers have been baffled by the huge diversity in the composition of different stars packed into what are called globular clusters.
The clusters, which are mostly very old, can contain millions of stars in a relatively small space.
Advances in astronomy have revealed an increasing number of globular clusters, which are thought to be a missing link between the universe's first stars and first galaxies.
Our Milky Way galaxy, which has more than 100 billion stars, has around 180 globular clusters.
But the question remains: Why do the stars in these clusters have such a variety of chemical elements, despite presumably all being born around the same time, from the same cloud of gas?
- Rampaging 'seed star' -
Many of the stars have elements that would require colossal amounts of heat to produce, such as aluminium which would need a temperature of up to 70 million degrees Celsius.
That is far above the temperature that the stars are thought to get up to at their core, around the 15-20 million Celsius mark which is similar to the Sun.
So the researchers came up with a possible solution: a rampaging supermassive star shooting out chemical "pollution".
They theorise that these huge stars are born from successive collisions in the tightly packed globular clusters.
Corinne Charbonnel, an astrophysicist at the University of Geneva and lead author of the study, told AFP that "a kind of seed star would engulf more and more stars".
It would eventually become "like a huge nuclear reactor, continuously feeding on matter, which will eject out a lot of it," she added.
This discarded "pollution" will in turn feed young forming stars, giving them a greater variety of chemicals the closer they are to the supermassive star, she added.
But the team still needed observations to back up their theory.
- 'Like finding a bone' -
They found them in the galaxy GN-z11, which is more than 13 billion light years away -- the light we see from it comes from just 440 million years after the Big Bang.
It was discovered by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2015, and until recently held the record of oldest observed galaxy.
This made it an obvious early target for Hubble's successor as most powerful space telescope, the James Webb, which started releasing its first observations last year.
Webb offered up two new clues: the incredible density of stars in globular clusters and -- most crucially -- the presence of lots of nitrogen.
It takes truly extreme temperatures to make nitrogen, which the researchers believe could only be produced by a supermassive star.
"Thanks to the data collected by the James Webb Space Telescope, we believe we have found a first clue of the presence of these extraordinary stars," Charbonnel said in a statement, which also called the stars "celestial monsters".
If the team's theory was previously "a sort of footprint of our supermassive star, this is a bit like finding a bone," Charbonnel said.
"We are speculating about the head of the beast behind all this," she added.
But there is little hope of ever directly observing this beast.
The scientists estimate that the life expectancy of supermassive stars is only around two million years -- a blink of an eye in the cosmic time scale.
However they suspect that globular clusters were around until roughly two billion years ago, and they could yet reveal more traces of the supermassive stars they may have once hosted.
The study was published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics this month.
M.Ouellet--BTB