
-
 Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
-
Sri Lanka to treat Iranian sailors according to 'international law'

-
 New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
-
Farrell welcomes bonus-point win over 'tough' Welsh

-
 Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
-
Nepal's Balendra Shah holds unassailable poll lead for seat

-
 Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
-
Pole-sitter Russell says his Mercedes more go-kart than 'bouncing bus'

-
 Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
-
Thousands of Taiwan fans turn Tokyo blue at World Baseball Classic

-
 Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
-
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes

-
 Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
-
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win

-
 Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs

-
 Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
-
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three

-
 Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
-
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily

-
 Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
-
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
-
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump

-
 Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
-
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level

-
 Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
-
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win

-
 Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
-
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola

-
 Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
-
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
-
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales

-
 Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
-
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January

-
 Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
-
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
-
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march

-
 Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
-
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony

-
 Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round

-
 NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
-
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row

-
 'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
-
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold


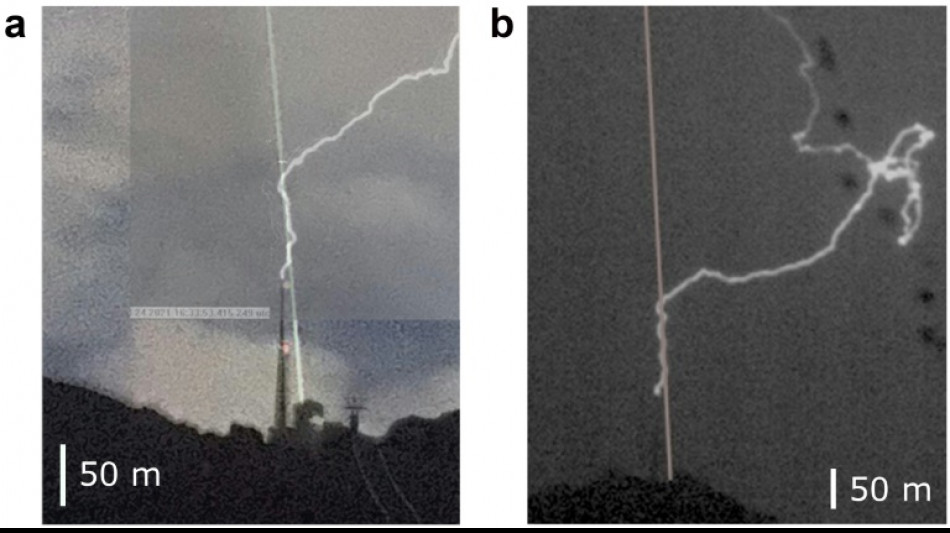
Scientists use laser to guide lightning bolt for first time
Scientists said Monday they have used a laser beam to guide lightning for the first time, hoping the technique will help protect against deadly bolts -- and one day maybe even trigger them.
Lightning strikes between 40-120 times a second worldwide, killing more than 4,000 people and causing billions of dollars worth of damage every year.
Yet the main protection against these bolts from above is still the humble lightning rod, which was first conceived by American polymath Benjamin Franklin in 1749.
A team of scientists from six research institutions have been working for years to use the same idea but replace the simple metal pole with a far more sophisticated and precise laser.
Now, in a study published in the journal Nature Photonics, they describe using a laser beam -- shot from the top of a Swiss mountain -- to guide a lightning bolt for more than 50 metres.
"We wanted to give the first demonstration that the laser can have an influence on lightning -- and it is simplest to guide it," said Aurelien Houard, a physicist at the applied optics laboratory of the ENSTA Paris institute and the study's lead author.
But for future applications "it would be even better if we could trigger lightning," Houard told AFP.
- How to catch lightning -
Lightning is a discharge of static electricity that has built up in storm clouds, or between clouds and the ground.
The laser beam creates plasma, in which charged ions and electrons heat the air.
The air becomes "partially conductive, and therefore a path preferred by the lightning," Houard said.
When scientists previously tested this theory in New Mexico in 2004, their laser did not grab the lightning.
That laser failed because it did not emit enough pulses per second for lightning, which brews in milliseconds, Houard said.
He added that it was also difficult to "predict where the lightning was going to fall".
For the latest experiment, the scientists left little to chance.
They lugged a car-sized laser -- which can fire up to a thousand pulses of light a second -- up the 2,500-metre peak of Santis mountain in northeastern Switzerland.
The peak is home to a communications tower that is struck by lightning around 100 times year.
After two years building the powerful laser, it took several weeks to move it in pieces via a cable car.
Finally, a helicopter had to drop off the large containers that would house the telescope.
The telescope focused the laser beam to maximum intensity at a spot around 150 metres in the air -- just above the top of the 124-metre tower.
The beam has a diameter of 20 centimetres at the beginning, but narrows to just a few centimetres at the top.
- Ride the lightning -
During a storm in the summer of 2021, the scientists were able to photograph their beam driving a lightning bolt for 50 around metres.
Three other strikes were also guided, interferometric measurements showed.
Most lightning builds up from precursors inside clouds, but some can come up from the ground if the electric field is strong enough.
"The current and power of a lightning bolt really becomes clear once the ground is connected with the cloud," Houard said.
The laser guides one of these precursors, making it "much faster than the others -- and straighter," he said.
"It will then be the first to connect with the cloud before it lights up."
This means that, in theory, this technique could be used not just to drive lightning away, but to trigger it in the first place.
That could allow scientists to better protect strategic installations, such as airports or rocket launchpads, by igniting strikes at the time of their choosing.
In practice, that would require a high conductivity in the laser's plasma -- which scientists do not think they have mastered yet.
N.Fournier--BTB

