
-
 Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes
-
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six

-
 'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win
-
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs
-
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic

-
 Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three
-
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport

-
 Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
-
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'

-
 Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs

-
 Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
-
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes

-
 Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
-
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration

-
 Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig

-
 Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
-
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says

-
 Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
-
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals

-
 Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
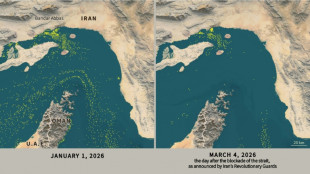 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs


Things to know about a landmark biodiversity agreement
After years of negotiations, the world has agreed a landmark deal to protect vanishing species and ecosystems, dubbed a "peace pact with nature" at the UN meeting in Montreal called COP15.
Here are some of its strengths, as well as where it fell short.
- '30 by 30' -
The cornerstone of the agreement is the so-called 30 by 30 goal -- a pledge to protect 30 percent of the world's land and seas by 2030.
Currently, only about 17 percent of land and seven percent of oceans are protected. The oceans target had reportedly been opposed by some countries but made it into the final text.
And some experts had said 30 percent is a low aim, insisting that protecting 50 percent would be better.
- Indigenous rights -
About 80 percent of the Earth's remaining biodiverse land is currently managed by Indigenous people, and it's broadly recognized that biodiversity is better respected on Indigenous territory.
Activists wanted to make sure their rights are not trampled in the name of conservation -- previous efforts to safeguard land have seen Indigenous communities marginalized or displaced in what has been dubbed "green colonialism."
In the end, Indigenous rights were addressed throughout the text, including in areas covered by the 30 by 30 pledge -- safeguarding Indigenous peoples' right to remain stewards of land they use and ensuring they are not subject to mass evictions.
The International Indigenous Forum on Biodiversity praised the text for its "strong language on respect for the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities."
- Finance -
Finance remained the overriding question.
Developing countries say developed nations grew rich by exploiting their resources and the South should be paid to preserve its ecosystems.
In the end, the text approves the objective for rich countries to provide "at least US$20 billion per year by 2025, and ... at least US$30 billion per year by 2030," approximately double and then triple the current international aid for biodiversity.
It also includes new language that mentions funding from "developed countries, and from countries that voluntarily assume obligations of developed country parties," which a Western source told AFP was meant to involve the United States.
Washington is not formally a part of the Convention on Biological Diversity but supportive of its goals.
Developing countries were also seeking a new funding mechanism, as a signal of the rich world's commitment to this goal, but developed nations said it would take several years to create.
In the end, a halfway solution was adopted: creating a "trust fund" within an existing financial mechanism called the Global Environment Facility, as a stepping stone to a new fund in the future.
- What was missing -
An overriding concern by campaigners was that the final text did not contain enough "milestones" -- key statistical measures countries should achieve before the year 2050.
For example, the text says human-induced extinction of known threatened species is halted, and, by 2050, extinction rate and risk of all species are reduced tenfold -- but there aren't targets that countries must hit before that year.
Also watered down was a mandate for businesses to assess and report on the biodiversity impacts -- instead they are merely "encouraged" to do so.
M.Odermatt--BTB


